Abstract
Background
Preoperative valgus deformity is present in an estimated 10–20% of patients undergoing total knee replacement (TKR).
Questions/Purposes
The objective of this study was to compare the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores after TKR in a matched cohort of patients with preoperative valgus and varus deformities.
Methods
This is a matched cohort study of 162 patients with varus native knees and 162 patients with valgus native knees who underwent TKR and were prospectively followed in our institutional registry. Patients matched were based on age, BMI, sex, and severity of preoperative knee deformity, which was classified as mild, moderate, severe varus or valgus, or no deformity. Outcomes were evaluated using the WOMAC preoperatively and at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year postoperatively.
Results
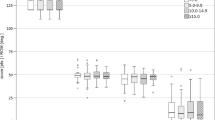
No significant difference was found between the matched varus and valgus cohorts in all WOMAC subdomain scores except for a marginally worse stiffness at 1 year in patients with valgus deformity (WOMAC stiffness, 75.1 varus vs. 70.1 valgus; P = 0.049). This is below the minimal clinically important difference for WOMAC scores. There was no significant difference in postoperative varus/valgus alignment between the two groups (P = 0.092)
Conclusion
We found no clinically significant difference in any of the WOMAC domains in patients with preoperative varus deformity versus valgus deformity within the first year after TKR. These findings may allow surgeons to more appropriately counsel patients with osteoarthritis with valgus deformity that they can expect similar outcomes compared to patients with varus deformity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Buzzi R. Correction of combined deformity. In: Scuderi GR, Tria A, ed. Surgical Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2002.
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:1833–1840.
Clarke HD, Fuchs R, Scuderi GR, Scott WN, Insall JN. Clinical results in valgus total knee arthroplasty with the “pie crust” technique of lateral soft tissue releases. J Arthroplast. 2005;20:1010–1014.
Colebatch AN, Hart DJ, Zhai G, Williams FM, Spector TD, Arden NK. Effective measurement of knee alignment using AP knee radiographs. Knee. 2009;16:42–45.
Elkus M, Ranawat CS, Rasquinha VJ, Babhulkar S, Rossi R, Ranawat AS. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. Five to fourteen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A:2671–2676.
Favorito PJ, Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Total knee arthroplasty in the valgus knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002;10:16–24.
Fiddian NJ, Blakeway C, Kumar A. Replacement arthroplasty of the valgus knee. A modified lateral capsular approach with repositioning of vastus lateralis. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 1998;80:859–861.
Gonzalez Della VA, Leali A, Haas S. Etiology and surgical interventions for stiff total knee replacements. HSS J. 2007;3:182–189.
Hinman RS, May RL, Crossley KM. Is there an alternative to the full-leg radiograph for determining knee joint alignment in osteoarthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2006;55:306–313.
Karachalios T, Sarangi PP, Newman JH. Severe varus and valgus deformities treated by total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 1994;76:938–942.
Keblish PA. The lateral approach to the valgus knee. Surgical technique and analysis of 53 cases with over two-year follow-up evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991:52–62.
Peters CL, Jimenez C, Erickson J, Anderson MB, Pelt CE. Lessons learned from selective soft-tissue release for gap balancing in primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 1216 consecutive total knee arthroplasties: AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:e152.
Quintana JM, Escobar A, Bilbao A, Arostegui I, Lafuente I, Vidaurreta I. Responsiveness and clinically important differences for the WOMAC and SF-36 after hip joint replacement. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2005;13:1076–1083.
Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87 1:271–284.
Stern SH, Moeckel BH, Insall JN. Total knee arthroplasty in valgus knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991:5–8.
Su EP, Su SL, Della Valle AG. Stiffness after TKR: how to avoid repeat surgery. Orthopedics. 2010;33:658.
Funding
No extramural funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Cynthia A. Kahlenberg, MD; Myra Trivellas, BS; and Yuo-yu Lee, MS have declared that they have no conflict of interest. Douglas E. Padgett, MD, reports other from American Joint Replacement Registry, Journal of Arthroplasty, and The Hip Society and personal fees from PixarBio and DJ Orthopaedics outside the work.
Human/Animal Rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5).
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Required Author Forms
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the online version of this article.
Additional information
Level of Evidence: III: Retrospective Cohort Study.
Investigation was performed at Hospital for Special Surgery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kahlenberg, C.A., Trivellas, M., Lee, Yy. et al. Preoperative Valgus Alignment Does Not Predict Inferior Outcome of Total Knee Arthroplasty. HSS Jrnl 14, 50–54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-017-9576-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-017-9576-2