Abstract
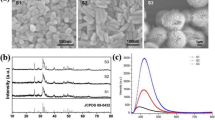
When orthopedic joints coated by hydroxyapatite (HA) were implanted in the human body, they release wear debris into the surrounding tissues. The generation and accumulation of wear particles will induce aseptic loosening. However, the potential bioeffect and mechanism of HA-coated orthopedic implants on bone cells are poorly understood. In this study, defect-related luminescent bur-like hydroxyapatite (BHA) microspheres with the average diameter of 7–9 μm which are comparable to that of the wear-debris particles from aseptically loosened HA implants or HA debris have been synthesized by hydrothermal synthesis and the MC3T3-E1 cells were set as a cells model to study the potential bioeffect and mechanism of BHA microspheres. The studies demonstrated that BHA microspheres could be taken into MC3T3-E1 cells via endocytosis involved in micropinocytosis- and clathrin-mediated endocytosis process, and exert cytotoxicity effect. BHA microspheres could induce the cell apoptosis by intracellular production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which led to not only an increase in the permeability of lysosome and release of cathepsins B, but also mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage. Our results provide novel evidence to elucidate their toxicity mechanisms and might be helpful for more reasonable applications of HA-based orthopaedic implants in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auclair-Daigle, C., Bureau, M.N., Legoux, J.G., and Yahia, L.H. (2005). Bioactive hydroxyapatite coatings on polymer composites for orthopedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res 73A, 398–408.
Bajgai, M.P., Parajuli, D.C., Park, S.J., Chu, K.H., Kang, H.S., and Kim, H. Y. (2010). In vitro bioactivity of sol-gel-derived hydroxyapatite particulate nanofiber modified titanium. J Mater Sci-Mater Med 21, 685–694.
Banaszkiewicz, P.A. (2014). Reactions of the articular capsule to wear products of artificial joint prostheses. In: Class Pap Orthop. (London: Springer), pp. 157–164.
Bloebaum, R.D., Zou, L., Bachus, K.N., Shea, K.G., Hofmann, A.A., and Dunn, H.K. (1997). Analysis of particles in acetabular components from patients with osteolysis. Clin Orthopaedics Related Res 338, 109–118.
Chambers, B., St. Clair, S.F., and Froimson, M.I. (2007). Hydroxyapatitecoated tapered cementless femoral components in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 22, 71–74.
Chandra, J., Samali, A., and Orrenius, S. (2000). Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radical Biol Med 29, 323–333.
Chang, J.C., Kou, S.J., Lin, W.T., and Liu, C.S. (2010). Regulatory role of mitochondria in oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. World J Cardiol 2, 150–159.
Chen, Q.Y., Shi, J.G., Yao, Q.H., Jiao, D.M., Wang, Y.Y., Hu, H.Z., Wu, Y. Q., Song, J., Yan, J., and Wu, L.J. (2012). Lysosomal membrane permeabilization is involved in curcumin-induced apoptosis of A549 lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 359, 389–398.
Doostmohammadi, A., Monshi, A., Salehi, R., Hossein Fathi, M., Seyedjafari, E., Shafiee, A., and Soleimani, M. (2011). Cytotoxicity evaluation of 63s bioactive glass and bone-derived hydroxyapatite particles using human bone-marrow stem cells. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 155, 323–326.
Duan, J., Yu, Y., Li, Y., Yu, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, X., Huang, P., and Sun, Z. (2013). Toxic effect of silica nanoparticles on endothelial cells through DNA damage response via Chk1-dependent G2/M checkpoint. PLoS ONE 8, e62087.
Eruslanov, E., and Kusmartsev, S. (2010). Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry. Methods Mol Biol 594, 57–72.
Fang, L., Neutzner, A., Turtschi, S., Flammer, J., and Mozaffarieh, M. (2015). Comet assay as an indirect measure of systemic oxidative stress. J Vis Exp 22, e52763.
Fearnhead, H.O., Rodriguez, J., Govek, E.E., Guo, W., Kobayashi, R., Hannon, G., and Lazebnik, Y.A. (1998). Oncogene-dependent apoptosis is mediated by caspase-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 13664–13669.
Gao, W., Jiang, L., Ge, L., Chen, M., Geng, C., Yang, G., Li, Q., Ji, F., Yan, Q., and Zou, Y., et al. (2015). Sterigmatocystin-induced oxidative DNA damage in human liver-derived cell line through lysosomal damage. Toxicol In Vitro 29, 1–7.
Ge, K., Zhang, C., Jia, G., Ren, H., Wang, J., Tan, A., Liang, X.J., Zang, A., and Zhang, J. (2015). Defect-related luminescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles employed for novel detectable nanocarrier. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7, 10905–10914.
Geetha, R., Sathiya, P.C., and Anuradha, C.V. (2017). Troxerutin abrogates mitochondrial oxidative stress and myocardial apoptosis in mice fed calorie-rich diet. Chem Biol Interact 278, 74–83.
Glant, T.T., Jacobs, J.J., Molnár, G., Shanbhag, A.S., Valyon, M., and Galante, J.O. (1993). Bone resorption activity of particulate-stimulated macrophages. J Bone Miner Res 8, 1071–1079.
Glant, T.T., and Jacobs, J.J. (1994). Response of three murine macrophage populations to particulate debris: bone resorption in organ cultures. J Orthop Res 12, 720–731.
Goldring, S.R., Clark, C.R., and Wright, T.M. (1993). The problem in total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surgery 75, 799–801.
Gratton, S.E.A., Ropp, P.A., Pohlhaus, P.D., Luft, J.C., Madden, V.J., Napier, M.E., and DeSimone, J.M. (2008). The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 11613–11618.
Greulich, C., Diendorf, J., Simon, T., Eggeler, G., Epple, M., and Köller, M. (2011). Uptake and intracellular distribution of silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater 7, 347–354.
Guicciardi, M.E., Deussing, J., Miyoshi, H., Bronk, S.F., Svingen, P.A., Peters, C., Kaufmann, S.H., and Gores, G.J. (2000). Cathepsin B contributes to TNF-a-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis by promoting mitochondrial release of cytochrome c. J Clin Invest 106, 1127–1137.
Hardwick, J.M., Chen, Y., and Jonas, E.A. (2012). Multipolar functions of BCL-2 proteins link energetics to apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 22, 318–328.
Hellmich, C., and Ulm, F.J. (2003). Average hydroxyapatite concentration is uniform in the extracollagenous ultrastructure of mineralized tissues: evidence at the 1-10-microm scale. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2, 21–36.
Horowitz, S.M., Rapuano, B.P., Lane, J.M., and Burstein, A.H. (1994). The interaction of the macrophage and the osteoblast in the pathophysiology of aseptic loosening of joint replacements. Calcif Tissue Int 54, 320–324.
Hsin, Y.H., Chen, C.F., Huang, S., Shih, T.S., Lai, P.S., and Chueh, P.J. (2008). The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS-and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 179, 130–139.
Huerta-García, E., Pérez-Arizti, J.A., Márquez-Ramírez, S.G., Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L., Chirino, Y.I., Iglesias, G.G., and López-Marure, R. (2014). Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce strong oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in glial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 73, 84–94.
Hutmacher, D.W., Schantz, J.T., Lam, C.X.F., Tan, K.C., and Lim, T.C. (2007). State of the art and future directions of scaffold-based bone engineering from a biomaterials perspective. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 1, 245–260.
Jin, Y., Chen, S., Duan, J., Jia, G., and Zhang, J. (2015). Europium-doped Gd2O3 nanotubes cause the necrosis of primary mouse bone marrow stromal cells through lysosome and mitochondrion damage. J Inorg Biochem 146, 28–36.
Jin, Y., Liu, X., Liu, H., Chen, S., Gao, C., Ge, K., Zhang, C., and Zhang, J. (2017). Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles through lysosomal and mitochondrial pathways. RSC Adv 7, 13010–13018.
Kido, H.W., Ribeiro, D.A., de Oliveira, P., Parizotto, N.A., Camilo, C.C., Fortulan, C.A., Marcantonio Jr., E., da Silva, V.H.P., and Muniz Renno, A.C. (2014). Biocompatibility of a porous alumina ceramic scaffold coated with hydroxyapatite and bioglass. J Biomed Mater Res 102, 2072–2078.
Lahiri, D., Benaduce, A.P., Rouzaud, F., Solomon, J., Keshri, A.K., Kos, L., and Agarwal, A. (2011). Wear behavior and in vitro cytotoxicity of wear debris generated from hydroxyapatite-carbon nanotube composite coating. J Biomed Mater Res 96A, 1–12.
Löbrich, M., and Jeggo, P.A. (2007). The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nat Rev Cancer 7, 861–869.
Ma, Y.H., Huang, C.P., Tsai, J.S., Shen, M.Y., Li, Y.K., and Lin, L.Y. (2011). Water-soluble germanium nanoparticles cause necrotic cell death and the damage can be attenuated by blocking the transduction of necrotic signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett 207, 258–269.
Maloney, W.J., Smith, R.L., Schmalzried, T.P., Chiba, J., Huene, D., and Rubash, H. (1995). Isolation and characterization of wear particles generated in patients who have had failure of a hip arthroplasty without cement.. J Bone Joint Surgery 77, 1301–1310.
Nativo, P., Prior, I.A., and Brust, M. (2008). Uptake and intracellular fate of surface-modified gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2, 1639–1644.
Oberle, C., Huai, J., Reinheckel, T., Tacke, M., Rassner, M., Ekert, P.G., Buellesbach, J., and Borner, C. (2010). Lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cathepsin release is a Bax/Bak-dependent, amplifying event of apoptosis in fibroblasts and monocytes. Cell Death Differ 17, 1167–1178.
Ormsby, R.T., Cantley, M., Kogawa, M., Solomon, L.B., Haynes, D.R., Findlay, D.M., and Atkins, G.J. (2016). Evidence that osteocyte perilacunar remodelling contributes to polyethylene wear particle induced osteolysis. Acta Biomater 33, 242–251.
Pioletti, D.P., Leoni, L., Genini, D., Takei, H., Du, P., and Corbeil, J. (2002). Gene expression analysis of osteoblastic cells contacted by orthopedic implant particles. J Biomed Mater Res 61, 408–420.
Ross, R.D., Virdi, A.S., Liu, S., Sena, K., and Sumner, D.R. (2014). Particle-induced osteolysis is not accompanied by systemic remodeling but is reflected by systemic bone biomarkers. J Orthop Res 32, 967–973.
Roussi, S., Gossé, F., Aoudé-Werner, D., Zhang, X., Marchioni, E., Geoffroy, P., Miesch, M., and Raul, F. (2007). Mitochondrial perturbation, oxidative stress and lysosomal destabilization are involved in 7β-hydroxysitosterol and 7β-hydroxycholesterol triggered apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Apoptosis 12, 87–96.
Shi, Z., Huang, X., Cai, Y., Tang, R., and Yang, D. (2009). Size effect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of osteoblast-like cells. Acta Biomater 5, 338–345.
Singh, S., Meena, V.K., Sharma, M., and Singh, H. (2015). Preparation and coating of nano-ceramic on orthopaedic implant material using electrostatic spray deposition. Mater Des 88, 278–286.
Sinha, S., Jothiramajayam, M., Ghosh, M., and Mukherjee, A. (2014). Evaluation of toxicity of essential oils palmarosa, citronella, lemongrass and vetiver in human lymphocytes. Food Chem Toxicol 68, 71–77.
Smith, J., Tho, L.M., Xu, N., and Gillespie, D.A. (2010). The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 108, 73–112.
Stratton-Powell, A.A., Pasko, K.M., Brockett, C.L., and Tipper, J.L. (2016). The biologic response to polyetheretherketone (PEEK) wear particles in total joint replacement: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 474, 2394–2404.
Sun, J., Bai, S., Bai, W., Zou, F., Zhang, L., Su, Z., Zhang, Q., Ou, S., and Huang, Y. (2013). Toxic mechanisms of 3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol on progesterone production in R2C rat leydig cells. J Agric Food Chem 61, 9955–9960.
Suzuki, H., Toyooka, T., and Ibuki, Y. (2007). Simple and easy method to evaluate uptake potential of nanoparticles in mammalian cells using a flow cytometric light scatter analysis. Environ Sci Technol 41, 3018–3024.
Tang, P.S., Mura, M., Seth, R., and Liu, M. (2008). Acute lung injury and cell death: how many ways can cells die? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294, L632–L641.
Turkez, H., Yousef, M.I., Sönmez, E., Togar, B., Bakan, F., Sozio, P., and Stefano, A.D. (2014). Evaluation of cytotoxic, oxidative stress and genotoxic responses of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on human blood cells. J Appl Toxicol 34, 373–379.
Wang, X., Takahashi, N., Uramoto, H., and Okada, Y. (2005). Chloride channel inhibition prevents ROS dependent apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion in mouse cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 16, 147–154.
Wang, L., Yeung, J.H.K., Hu, T., Lee, W.Y., Lu, L., Zhang, L., Shen, J., Chan, R.L.Y., Wu, W.K.K., and Cho, C.H. (2013). Dihydrotanshinone induces p53-independent but ROS-dependent apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Life Sci 93, 344–351.
White, A.A., Best, S.M., and Kinloch, I.A. (2007). Hydroxyapatite-carbon nanotube composites for biomedical applications: a review. Int J Appl Ceramic Tech 4, 1–13.
Xiao, Z.S., Hjelmeland, A.B., and Quarles, L.D. (2004). Selective deficiency of the “bone-related” Runx 2-II unexpectedly preserves osteoblastmediated skeletogenesis. J Biol Chem 279, 20307–20313.
Xu, Z., Liu, C., Wei, J., and Sun, J. (2012). Effects of four types of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with different nanocrystal morphologies and sizes on apoptosis in rat osteoblasts. J Appl Toxicol 32, 429–435.
Yadavilli, S., Martinez-Ceballos, E., Snowden-Aikens, J., Hurst, A., Joseph, T., Albrecht, T., and Muganda, P.M. (2007). Diepoxybutane activates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and mediates apoptosis in human lymphoblasts through oxidative stress. Toxicol In Vitro 21, 1429–1441.
Yang, H., Liu, C., Yang, D., Zhang, H., and Xi, Z. (2009). Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: the role of particle size, shape and composition. J Appl Toxicol 29, 69–78.
Yao, J., Cs-Szabo, G., Jacobs, J.J., and Kuettner, K.E. (1997). Suppression of osteoblast function by titanium particles. J Bone Joint Surgery-Am Volume 79, 107–112.
Zeng, X., Zhang, Y., and Nyström, A.M. (2012). Endocytic uptake and intracellular trafficking of bis-MPA-based hyperbranched copolymer micelles in breast cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 13, 3814–3822.
Zeng, T., Zhu, L., Liao, M., Zhuo, W., Yang, S., Wu, W., and Wang, D. (2017). Knockdown of PYCR1 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer. Med Oncol 34, 27.
Zhang, C., Yang, J., Quan, Z., Yang, P., Li, C., Hou, Z., and Lin, J. (2009). Hydroxyapatite nano-and microcrystals with multiform morphologies: controllable synthesis and luminescence properties. Cryst Growth Des 9, 2725–2733.
Zhang, C., Li, C., Huang, S., Hou, Z., Cheng, Z., Yang, P., Peng, C., and Lin, J. (2010). Self-activated luminescent and mesoporous strontium hydroxyapatite nanorods for drug delivery. Biomaterials 31, 3374–3383.
Zhang, S., Chen, S., Gao, C., Jin, Y., Jia, G., J., Li, Z., Liu, D. Liang, X., Yang, X., and Zhang, J. (2017). Apoptosis induced by NaYF4:Eu3+ nanoparticles in liver cells via mitochondria damage dependent pathway. Sci China Chem 60, 1–8.
Zhao, C.Q., Liu, D., Li, H., Jiang, L.S., and Dai, L.Y. (2007). Interleukin-1β enhances the effect of serum deprivation on rat annular cell apoptosis. Apoptosis 12, 2155–2161.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21301046, 51302062), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2017201125, B2017201100), the Second Batch of Top Youth Talent Support Program of Hebei Province and Distinguished Young Scholars Fund of Hebei University (2015JQ04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Chen, S., Li, N. et al. Defect-related luminescent bur-like hydroxyapatite microspheres induced apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells by lysosomal and mitochondrial pathways. Sci. China Life Sci. 61, 464–475 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9258-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9258-3