Abstract
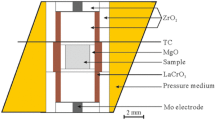
Tuite has been suggested as a potential reservoir for trace elements in the deep mantle, but no evidence confirms this supposition. By using a natural apatite as starting material, the trace-element-bearing tuite large crystals were obtained under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions (15 GPa and 1800 K). X-ray diffraction pattern and Micro-Raman spectrum of the run product confirm that tuite was synthesized. The concentrations of trace elements in tuite crystals were analyzed by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). The rare earth element patterns of tuite show enrichment of light rare earth elements relative to heavy rare earth elements. Tuite shows high concentrations of Th and Sr, and negative anomalies of Rb, Nb, and Hf. The results show that tuite can accommodate a large amount of trace elements. Tuite might be an important host to accommodate trace elements if there is much apatite subducted into the deep mantle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bau M, Dulski P. 1995. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 119: 213–223
Baziotis I P, Liu Y, DeCarli P S, et al. 2013. The Tissint Martian meteorite as evidence for the largest impact excavation. Nat Commun, 4: 1404
Beswick A E, Carmichael I S E. 1978. Constrains on mantle source compositions imposed by phosphorous and the rare earth elements. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 67: 317–330
Dégi J, Abart R, Török K. 2010. Symplectite formation during decompression induced garnet breakdown in lower crustal mafic granulite xenoliths: Mechanisms and rates. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 159: 293–314
Dowty E. 1977. Phosphate in Angra dos Reis: Structure and composition of the Ca3(PO4)2 minerals. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 35: 347–351
Gaspar M, Knaack C, Meinert L D, et al. 2008. REE in sharn systems: A LA-ICP-MS study of garnets from the Crown Jewel gold deposit. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 72: 185–205
Gopal R, Calvo C. 1972. Structure relationship of whitlockite and β-Ca3-(PO4)2. Nat Phys Sci, 237: 30–32
Grammaccioli C M, Diella V, Demartin F. 1999. The role of fluoride complexes in REE geochemistry and the importance of 4f electrons: Some examples in minerals. Eur J Mineral, 11: 983–992
Greshake A, Fritz J. 2009. Discovery of ringwoodite, wadsleyite, and γ-Ca3(PO4)2 in Chassigny: Constraints on shock conditions. Lunar Planet Inst Sci Conf Abs, 40: 1586
Griffin W L, Åmli R, Heier K S. 1972. Whitlockite and apatite from lunar rock 14310 and from ÖdegÅrden, Norway. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 15: 53–68
Jackson S E, Longerich H P, Dunning G R, et al. 1992. The application of laser-ablation microprobe; inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LAM-ICP-MS) to in situ trace-element determinations in minerals. Can Mineral, 30: 1049–1064
Jolliff B L, Haskin L A, Colson R O, et al. 1993. Partitioning in REE-saturating minerals: Theory, experiment, and modeling of whitlockite, apatite, and evolution of lunar residual magmas. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 57: 4069–4094
Konzett J, Frost D J. 2009. The high P-T stability of hydroxyl-apatite in natural and simplified MORB—An experimental study to 15 GPa with implications for transport and storage of phosphorus and halogens in subduction zones. J Petrol, 50: 2043–2062
Konzett J, Rhede D, Frost D J. 2012. The high PT stability of apatite and Cl partitioning between apatite and hydrous potassic phases in peridotite: An experimental study to 19 GPa with implications for the transport of P, Cl and K in the upper mantle. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 163: 277–296
Manthilake M A G M, Sawada Y, Sakai S. 2008. Genesis and evolution of Eppawala carbonatites, Sri Lanka. J Asian Earth Sci, 32: 66–75
McDonough W F, Sun S. 1995. The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol, 120: 223–253
Miyahara M, Ohtani E, Ozawa S, et al. 2011. Natural dissociation of olivine to (Mg, Fe)SiO3 perovskite and magnesiowüstite in a shocked Martian meteorite. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108: 5999–6003
Murayama J K, Nakai S, Kato M, et al. 1986. A dense polymorph of Ca3(PO4)2: A high pressure phase of apatite decomposition and its geochemical significance. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 44: 293–303
Nash W P. 1984. Phosphate minerals in terrestrial igneous and metamorphic rocks. In: Nriagu J O, Moore P B, eds. Phosphate Minerals. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. 215–241
Pearce N J G, Perkins W T, Westgate J A, et al. 1997. A compilation of new and published major and trace element data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 glass reference materials. Geostand Newsl, 21: 115–144
Prewitt C T, Rothbard D R. 1975. Crystal structures of meteoritic and lunar whitlockites. Lunar Planet Sci, 6: 646–648
Puchelt H, Emmermann R. 1976. Bearing of rare earth patterns of apatites from igneous and metamorphic rocks. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 31: 279–286
Python M, Ishisa Y, Ceuleneer G, et al. 2007. Trace element heterogeneity in hydrothermal diopside: Evidence for Ti depletion and Sr-Eu-LREE enrichment during hydrothermal metamorphism of mantle harzburgite. J Mineral Petrol Sci, 102: 143–149
Ozawa S, Ohtani E, Suzuki A, et al. 2007. Shock metamorphism of L6 chondrites Sahara 98222 and Yamato 74445: The P-T conditions and the shock age. AGU Fall Meet Abs, 1: 1234
Santosh M, Rajesh V J, Tsunogae T, et al. 2010. Diopsidites from a Neoproterozoic-Cambrian suture in southern India. Geol Mag, 147: 777–788
Schwinn G, Markl G. 2005. REE systematics in hydrothermal fluorite. Chem Geol, 216: 225–248
Sugiyama K, Tokonami M. 1987. Structure and crystal chemistry of a dense polymorph of tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2: A host to accommodate large lithophile elements in the Earth’s mantle. Phys Chem Miner, 15: 125–130
Van Achterberg E, Ryan C G, Jackson S, et al. 2001. Data reduction software for LA-ICP-MS. In: Sylvester P, ed. Laser-Ablation-ICPMS in the Earth Sciences: Principles and Applications. Mineralogical Society of Canada. 239–243
Xie X, Chen M. 2008. Formation conditions of tuite (in Chinese). Geochimica, 37: 297–303
Xie X, Minitti M E, Chen M, et al. 2002. Natural high-pressure polymorph of merrillite in the shock veins of the Suizhou meteorite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 66: 2439–2444
Xie X, Minitti M E, Chen M, et al. 2003. Tuite, γ-Ca3(PO4)2: A new mineral from the Suizhou L6 chondrite. Eur J Mineral, 15: 1001–1005
Zhai S, Liu X, Shieh S R, et al. 2009. Equation of state of γ-tricalcium phosphate, to lower mantle pressures. Am Mineral, 94: 1388–1391
Zhai S, Wu X, Ito E. 2010. High-pressure Raman spectra of tuite, γ-Ca3-(PO4)2. J Raman Spectrosc, 41: 1011–1013
Zhai S, Xue W, Lin C, et al. 2011. Raman spectra and X-ray diffraction of tuite at various temperatures. Phys Chem Miner, 38: 639–646
Zhang R Y, Liou J G, Zheng J P, et al. 2009. Petrogenesis of eclogites enclosed in mantle-derived peridotites from the Sulu UHP terrane: Constraints from trace elements in minerals and Hf isotopes in zircon. Lithos, 109: 176–192
Zheng J P, Zhang R Y, Griffin W L, et al. 2005. Heterogeneous and metasomatized mantle recorded by trace elements in minerals of the Donghai garnet peridotites, Sulu UHP terrane, China. Chem Geol, 221: 243–259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, S., Xue, W., Yamazaki, D. et al. Trace element composition in tuite decomposed from natural apatite in high-pressure and high-temperature experiments. Sci. China Earth Sci. 57, 2922–2927 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-014-4980-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-014-4980-7