Abstract
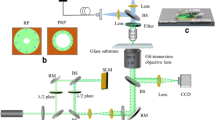
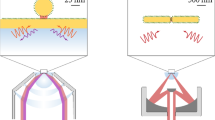
Propagating surface plasmon (PSP) excitation, based on the total internal reflection configuration, was introduced into the nanoparticle (NP)-plane junction Raman spectroscopy. Experimental results demonstrated that silver nanospheres within the propagation region of PSP are effectively activated and detected by CCD camera due to their impressive Raman enhancement, which presents around 20 times improvement compared with the conventional NP-induced PSP/LSP co-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. This impressive Raman enhancement along with its high reproducibility of NP-plane junctions makes our configuration an attractive candidature for the PSP-assisted gap-mode surface-enhancement Raman spectroscopy and tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willets KA, Van Duyne RP (2007) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu Rev Phys Chem 58:267–297
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 110:7238–7248
Mock JJ, Barbic M, Smith DR, Schultz DA, Schultz S (2002) Shape effects in plasmon resonance of individual colloidal silver nanoparticles. J Chem Phys 116:6755–6759
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Sherry LJ, Chang SH, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP, Wiley BJ, Xia YN (2005) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver nanocubes. Nano Lett 5:2034–2038
Sherry LJ, Jin RC, Mirkin CA, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2006) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver triangular nanoprisms. Nano Lett 6:2060–2065
Orendorff CJ, Gearheart L, Jana NR, Murphy CJ (2006) Aspect ratio dependence on surface enhanced Raman scattering using silver and gold nanorod substrates. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:165–170
Wiley BJ, Chen YC, McLellan JM, Xiong YJ, Li ZY, Ginger D et al (2007) Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanobars and nanorice. Nano Lett 7:1032–1036
Felidj N, Aubard J, Levi G, Krenn JR, Hohenau A, Schider G et al (2003) Optimized surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold nanoparticle arrays. Appl Phys Lett 82:3095–3097
Brandl DW, Mirin NA, Nordlander P (2006) Plasmon modes of nanosphere trimers and quadrumers. J Phys Chem B 110:12302–12310
Du LP, Zhang XJ, Mei T, Yuan XC (2010) Localized surface plasmons, surface plasmon polaritons, and their coupling in 2D metallic array for SERS. Opt Express 18:1959–1965
Hao E, Schatz GC (2004) Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J Chem Phys 120:357–366
Talley CE, Jackson JB, Oubre C, Grady NK, Hollars CW, Lane SM et al (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from individual Au nanoparticles and nanoparticle dimer substrates. Nano Lett 5:1569–1574
McMahon JM, Henry AI, Wustholz KL, Natan MJ, Freeman RG, Van Duyne RP et al (2009) Gold nanoparticle dimer plasmonics: finite element method calculations of the electromagnetic enhancement to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:1819–1825
Dadosh T, Sperling J, Bryant GW, Breslow R, Shegai T, Dyshel M et al (2009) Plasmonic control of the shape of the Raman spectrum of a single molecule in a silver nanoparticle dimer. ACS Nano 3:1988–1994
Vlckova B, Moskovits M, Pavel I, Siskova K, Sladkova M, Slouf M (2008) Single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy from a molecularly bridged silver nanoparticle dimer. Chem Phys Lett 455:131–134
Nie SM, Emery SR (1997) Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Science 275:1102–1106
Kneipp K, Wang Y, Kneipp H, Perelman LT, Itzkan I, Dasari R et al (1997) Single molecule detection using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Phys Rev Lett 78:1667–1670
Zheng JW, Zhou YG, Li XW, Ji L, Lu TH, Gu RA (2003) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of 4-aminothiophenol in assemblies of nanosized particles and the macroscopic surface of silver. Langmuir 19:632–636
Braun G, Lee SJ, Dante M, Nguyen TQ, Moskovits M, Reich N (2007) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for DNA detection by nanoparticle assembly onto smooth metal films. J Am Chem Soc 129:6378–6379
Kinnan MK, Chumanov G (2007) Surface enhanced Raman scattering from silver nanoparticle arrays on silver mirror films: plasmon-induced electronic coupling as the enhancement mechanism. J Phys Chem C 111:18010–18017
Kim K, Yoon JK (2005) Raman scattering of 4-aminobenzenethiol sandwiched between Ag/Au nanoparticle and macroscopically smooth Au substrate. J Phys Chem B 109:20731–20736
Daniels JK, Chumanov G (2005) Nanoparticle-mirror sandwich substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Phys Chem B 109:17936–17942
Park WH, Ahn SH, Kim ZH (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from a single nanoparticle-plane junction. Chemphyschem 9:2491–2494
Ikeda K, Fujimoto N, Uehara H, Uosaki K (2008) Raman scattering of aryl isocyanide monolayers on atomically at Au(111) single crystal surfaces enhanced by gap-mode plasmon excitation. Chem Phys Lett 460:205–208
Nordlander P, Le F (2006) Plasmonic structure and electromagnetic field enhancements in the metallic nanoparticle-film system. Appl Phys B Laser Optic 84:35–41
Orendorff CJ, Gole A, Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of self-assembled monolayers: sandwich architecture and nanoparticle shape dependence. Anal Chem 77:3261–3266
Liu Y, Xu SP, Li HB, Jian XG, Xu WQ (2011) Localized and propagating surface plasmon co-enhanced Raman spectroscopy based on evanescent field excitation. Chem Comm 47:3784–3786
Zhan QW (2009) Cylindrical vector beams: from mathematical concepts to applications. Adv Opt Photon 1:1–57
Chen WB, Zhan QW (2009) Realization of an evanescent Bessel beam via surface plasmon interference excited by a radially polarized beam. Opt Lett 34:722–724
Moh KJ, Yuan XC, Bu J, Burge RE, Gao BZ (2007) Generating radial or azimuthal polarization by axial sampling of circularly polarized vortex beams. Appl Opt 46:7544–7551
Palik ED (1997) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic, New York
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant no. (10974101 and 61036013), Ministry of Science and Technology of China under grant no. 2009DFA52300 for China–Singapore collaborations, and National Research Foundation of Singapore under grant no. NRF-G-CRP 2007–01. XCY acknowledges the support given by Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission under grant no. 11JCZDJC15200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors Luping Du and Guanghui Yuan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, L., Yuan, G., Tang, D. et al. Tightly Focused Radially Polarized Beam for Propagating Surface Plasmon-Assisted Gap-Mode Raman Spectroscopy. Plasmonics 6, 651–657 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9247-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9247-y