Abstract
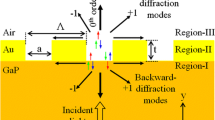
We fabricate a double-layer wire grid polarizer (WGP) and perform optical characterization to clarify the relationship between the structural and polarization characteristics. For normal incidence, the fabricated double-layer WGP exhibits an extinction ratio of 30.4 dB for a period of 400 nm. The transverse magnetic transmittance peak angle is found to vary with the period of the WGP. The peak shift can be explained on the basis of the extraordinary optical transmittance phenomena exhibited by the surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) of metal slit structures according to the dispersion curve of the SPP. From the simulation of rigorous coupled-wave analysis, it is considered that the incident light passes through the resist layer, followed by the excitation of SPPs at the interface between the resist and Au. Subsequently, the SPPs combine with the transmitted light in the glass substrate, leading to strong transmitted light with transverse magnetic polarization. Therefore, we demonstrate the extraordinary optical transmittance phenomena exhibited by the SPPs by both experiment and simulation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird GR, Parrish M Jr (1960) The wire grid as a near-infrared polarizer. J Opt Soc Am 50:886–891. doi:10.1364/JOSA.50.000886
Hass M, O’Hara M (1965) Sheet infrared transmission polarizers. Appl Opt 4:1027–1031. doi:10.1364/AO.4.001027
Auton JP (1967) Infrared transmission polarizers by photolithography. Appl Opt 6:1023–1027. doi:10.1364/AO.6.001023
Stenkamp B, Abraham M, Ehrfeld W, Knapek E, Hintermaier E, Gale MT, Morf R (1994) Grid polarizer for the visible spectral region. Proc SPIE 2213:288–296. doi:10.1117/12.180973
Lochbihler H, Depine R (1993) Highly conducting wire gratings in the resonance region. Appl Opt 32:3459–3465. doi:10.1364/AO.32.003459
Tamada H, Doumuki T, Yamaguchi T, Matsumoto S (1997) Al wire-grid polarizer using the s-polarization resonance effect at the 0.8-mm-wavelength band. Opt Lett 22:419–421. doi:10.1364/OL.22.000419
Yu XJ, Kwok HS (2003) Optical wire-grid polarizers at oblique angles of incidence. J Appl Phys 93:4407–4412. doi:10.1063/1.1559937
Xu M, Urbach HP, de Boer DKG, Cornelissen HJ (2005) Wire-grid diffraction gratings used as polarizing beam splitter for visible light and applied in liquid crystal on silicon. Opt Express 13:2303–2320. doi:10.1364/OPEX.13.002303
Wang JJ, Walters F, Liu X, Sciortino P, Deng X (2007) High-performance, large area, deep ultraviolet to infrared polarizers based on 40 nm line/78 nm space nanowire grids. Appl Phys Lett 90:061104. doi:10.1063/1.2437731
Hsu SY, Lee KL, Lin EH, Lee MC, Wei PK (2009) Giant birefringence induced by plasmonic nanoslit arrays. Appl Phys Lett 95:013105. doi:10.1063/1.3167772
Beresna M, Gecevičius M, Kazansky PG, Gertus T (2011) Radially polarized optical vortex converter created by femtosecond laser nanostructuring of glass. Appl Phys Lett 98:201101. doi:10.1063/1.3590716
Iwami K, Ishii M, Kuramochi Y, Ida K, Umeda N (2012) Ultrasmall radial polarizer array based on patterned plasmonic nanoslits. Appl Phys Lett 101:161119. doi:10.1063/1.4761943
Ishii M, Iwami K, Umeda N (2015) An Au nanofin array for high efficiency plasmonic optical retarders at visible wavelengths. Appl Phys Lett 106:021115. doi:10.1063/1.4905369
Djalalian-Assl A, Cadusch AA, Teo ZQ, Davis TJ, Roberts A (2015) Surface plasmon wave plates. Appl Phys Lett 106:041104. doi:10.1063/1.4906596
Yu Z, Deshpande P, Wu W, Wang J, Chou SY (2000) Reflective polarizer based on a stacked double-layer subwavelength metal grating structure fabricated using nanoimprint lithography. Appl Phys Lett 77:927–929. doi:10.1063/1.1288674
Ekinci Y, Solak HH, David C, Sigg H (2006) Bilayer Al wire-grids as broadband and high performance polarizers. Opt Express 14:2323–2334. doi:10.1364/OE.14.002323
Ye Z, Peng Y, Zhai T, Zhou Y, Liu D (2011) Surface plasmon-mediated transmission in double-layer metallic grating polarizers. J Opt Soc Am B 28:502–507. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.28.000502
Ye Z, Zheng J, Sun S, Chen S, Liu D (2013) Compact color filter and polarizer of bilayer metallic nanowire grating based on surface plasmon resonances. Plasmonics 8:555–559. doi:10.1007/s11468-012-9433-6
Ma Y, Sun N, Zhang R, Guo L, She Y, Zheng J, Ye Z (2014) Integrated color filter and polarizer based on two-dimensional superimposed nanowire arrays. J Appl Phys 116:044314. doi:10.1063/1.4891804
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Wolff PA (1998) Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391:667–669. doi:10.1038/35570
Klein Koerkamp KJ, Enoch S, Segerink FB, van Hulst NF, Kuipers L (2004) Strong influence of hole shape on extraordinary transmission through periodic arrays of subwavelength holes. Phys Rev Lett 92:183901. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.183901
Schouten HF, Kuzmin N, Dubois G, Visser TG, Gbur G, Alkemade PFA, Blok H, ‘t Hooft GW, Lenstra D, Eliel G (2005) Plasmon-assisted two-slit transmission: Young’s experiment revisited. Phys Rev Lett 94:053901. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.053901
Motogaito A, Hiramatsu K (2013) Fabrication of binary diffractive lenses and the application to LED lighting for controlling luminosity distribution. Opt Photon J 3:67–73. doi:10.4236/opj.2013.31011
Okamoto K, Kawakami Y (1999) High-efficiency InGaN/GaN light emitters based on nanophotonics and plasmonics. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 15:1199–1209. doi:10.1109/JSTQE.2009.2021530
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Nippon Sheet Glass Foundation for Materials Science and Engineering and JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Numbers 25600090, 26390082, 15H03556). The authors would like to thank Edanz for English language support.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motogaito, A., Morishita, Y., Miyake, H. et al. Extraordinary Optical Transmission Exhibited by Surface Plasmon Polaritons in a Double-Layer Wire Grid Polarizer. Plasmonics 10, 1657–1662 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9980-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9980-8