Abstract
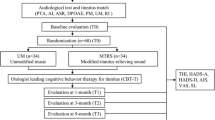
The present study examined the therapeutic efficacy of neurofeedback treatment (NFT) on the severity of symptoms and quality of life (QOL) in patients with chronic subjective tinnitus. 12 patients diagnosed with chronic tinnitus by an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist were selected by convenience sampling among the patients attending an ENT clinic in Ahvaz, Iran. The Patients were randomly assigned to the intervention and control groups. The intervention group received 15 sessions of neurofeedback treatment. All participants in this study completed severity of symptoms and quality of life symptoms questionnaires at three points in time: pre-test, post-test and 3-month follow-up. Using the Mann–Whitney U test, neurofeedback was found to significantly reduce the severity of tinnitus (z = −2.61, U = 0, and p < 0.009), and increase the quality of life (z = −2.62, U = 0, and p < 0.009) of participants. In addition, our findings show that NFT acts selectively on tinnitus with no side effects, and thus, can be used as an alternative or adjunctive treatment with medications and psychological therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abshirini, H., Saki, N., Nikakhlagh, S., Eslamijoo, F., Samadi, S., & Karimi, M. (2013a). Audiologic findings of tinnitus patients. Apadana Journal of Clinical Research, 2(1), 13–6.
Abshirini, H., Saki, N., Nikakhlagh, S., Rahim, F., Eslamijoo, F., & Samadi, S. (2013b). Hearing evaluation and audiology of tinnitus patients. Apadana Journal of Clinical Research, 2(1), 13–16.
Ali, Y., & Mahmud, N. A. (2014). Neurofeedback treatments for depression disorders: review of current advances. Oriental Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 7(3), 443–452.
Ali, Y., Mahmud, N. A., & Samaneh, R. (2015). Current advances in neurofeedback techniques for the treatment of ADHD. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal, 8, 165–77.
Baehr, E. (2009). Neurofeedback for the treatment of depression: current status of theoretical issues and clinical research. Introduction to quantitative EEG and neurofeedback: advanced theory and applications, 295.
Baldo, P., Doree, C., Lazzarini, R., Molin, P., McFerran, D. (2006). Antidepressants for patients with tinnitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 4(4).
Bigdeli, I., Rahimian Bogar, E., & Najafi, M. (2009). Health clinical psychology formulation and treatment. Semnan University.
Coles, R. (1984). Epidemiology of tinnitus: demographic and clinical features. The Journal of Laryngology and Otology, 98(S9), 195–202.
Crocetti, A., Forti, S., & Del Bo, L. (2011). Neurofeedback for subjective tinnitus patients. Auris Nasus Larynx, 38(6), 735–738.
Daneshi, A., Mahmoudian, S., Farhadi, M., Hasanzadeh, S., & Ghalebaghi, B. (2005). Auditory electrical tinnitus suppression in patients with and without implants. International Tinnitus Journal, 11(1), 85.
Dobie, R. A. (1999). A review of randomized clinical trials in tinnitus. The Laryngoscope, 109(8), 1202–1211.
Dohrmann, K., Weisz, N., Schlee, W., Hartmann, T., & Elbert, T. (2007). Neurofeedback for treating tinnitus. Progress in Brain Research, 166, 473–554.
Eggermont, J. J., & Roberts, L. E. (2004). The neuroscience of tinnitus. Trends in Neurosciences, 27(11), 676–82.
Gerami, H., Saberi, N. S., Taghavi, A., Kazem Nezhad, S. E., Sadeghi, E., Gerami, A. K., & Sardasht, M. (2013). The study of impact of oxcarbazepine and carbamazepine medications on tinnitus. Medical Faculty Journal of Mashhad Medical Sciences University, 1, 6–51.
Goebel, G., & Büttner, U. (2004). Grundlagen zu Tinnitus: Diagnostik und Therapie. Psychoneuro, 30(06), 322–329.
Gosepath, K., Nafe, B., Ziegler, E., & Mann, W. (2001). Neurofeedback in der Therapie des Tinnitus. HNO, 49(1), 29–35.
Greimel, K., Leibetseder, M., Unterrainer, J., & Albegger, K. (1999). Can tinnitus be measured? Methods for assessment of tinnitus-specific disability and presentation of the tinnitus disability questionnaire. HNO, 47(3), 196.
Henry, J. A., Zaugg, T. L., Myers, P. J., & Schechter, M. A. (2008). Using therapeutic sound with progressive audiologic tinnitus management. Trends in Amplification, 12(3), 188–209.
Kessler, R. C., McGonagle, K. A., Zhao, S., Nelson, C. B., Hughes, M., Eshleman, S., & Kendler, K. S. (1994). Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States: results from the national comorbidity survey. Archives of General Psychiatry, 51(1), 8–19.
Koller, M., Schecklmann, M., Langguth, B., & Landgrebe, M. (2012). Tinnitus assessment by means of standardized self-report questionnaires: psychometric properties of the tinnitus questionnaire (TQ), the tinnitus handicap inventory (THI), and their short versions in an international and multi-lingual sample. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 10, 128.
Kröner-Herwig, B., Frenzel, A., Fritsche, G., Schilkowsky, G., & Esser, G. (2003). The management of chronic tinnitus: comparison of an outpatient cognitive–behavioral group training to minimal-contact interventions. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 54(4), 381–389.
Lorenz, I. (2007). From signal space to source space: does source space projection improve the neurofeedback therapy in chronic tinnitus patients?
Madani Saam, K. (2002). The study of characteristics of tinnitus in patients reffered to ear, nose and throat clinic of Boo-Ali Sina Hospital of Sari in 1999. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, 32, 23.
Miller, N. E. (1975). Clinical applications of biofeedback: Voluntary control of heart rate, rhythm, and blood pressure. New horizons in cardiovascular practice. Baltimore: University Park Press.
Moffat, G., Adjout, K., Gallego, S., Thai-Van, H., Collet, L., & Norena, A. (2009). Effects of hearing aid fitting on the perceptual characteristics of tinnitus. Hearing Research, 254(1), 82–91.
Moradi, A., Pouladi, F., Pishva, N., Rezaei, B., Torshabi, M., & Mehrjerdi, Z. A. (2011). Treatment of anxiety disorder with neurofeedback: case study. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 30, 103–107.
Newman, C. W., Jacobson, G. P., & Spitzer, J. B. (1996). Development of the tinnitus handicap inventory. Archives of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 122(2), 143–148.
Niv, S. (2013). Clinical efficacy and potential mechanisms of neurofeedback. Personality and Individual Differences, 54(6), 676–686.
Searchfield, G., Jerram, C., Wise, K., & Raymond, S. (2007). The impact of hearing loss on tinnitus severity. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Audiology, 29(2), 67.
Tyler, R. S., & Baker, L. J. (1983). Difficulties experienced by tinnitus sufferers. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders, 48(2), 150–4.
Verment, R. (2011). Tinnitus treatment with neurofeedback: a case study. Neuroscience Letters, 500, e5.
Weise, C., Heinecke, K., & Rief, W. (2008). Biofeedback-based behavioral treatment for chronic tinnitus: results of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 76(6), 1046.
Weisz, N., Moratti, S., Meinzer, M., Dohrmann, K., & Elbert, T. (2005). Tinnitus perception and distress is related to abnormal spontaneous brain activity as measured by magnetoencephalography. PLoS Medicine, 2(6), e153.
Zeman, F., Koller, M., Figueiredo, R., Aazevedo, A., Rates, M., Coelho, C., Landgrebe, M. (2011). Tinnitus handicap inventory for evaluating treatment Effects which changes are clinically eelevant? Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 145(2), 282–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Authors have equally contributed in the designing, conducting, and preparation of this manuscript and have no conflict of interests on publishing this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
khoramzadeh, S., Saki, N., Davoodi, I. et al. Investigating the Therapeutic Efficacy of Neurofeedback Treatment on the Severity of Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Tinnitus. Int J Ment Health Addiction 14, 982–992 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-016-9670-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-016-9670-6