Abstract
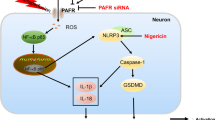
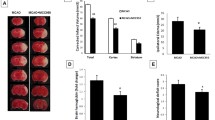
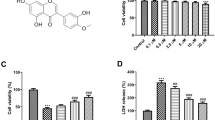
Increasing studies showed that several anti-platelet drugs turned out to be a promising strategy for inflammatory response. In this study, we investigated the protective efficiency of pretreatment of indobufen or aspirin combined with clopidogrel or ticagrelor (IACT) on cerebral ischemic injury via NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury was simulated in vivo by middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) model, and rats were pretreated with indobufen and aspirin and their combinations with clopidogrel or ticagrelor respectively. The platelet aggregation, cerebral infarct size, water content, neurological impairment and LDH release were measured. The relative expression of inflammasome mediated pyroptosis was determined by ELISA, RT-PCR, Tunel, Immunofluorescence and Western blotting as appropriate. In vitro, I/R injury was simulated in PC12 cells using oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce pyroptosis. The effect of combinations were significantly greater than MCAO/R group on decreasing the platelet aggregation, infarct size, brain edema, LDH release and neurologic impairment. LPS aggravated I/R-induced PC12 cell injury, which was significantly suppressed by pretreatment of IACT and Bay11–7082. Mechanistically, IACT alleviated transcriptionally encoded IL-1β, IL-18 and NLRP3 via inhibiting nuclear transportation of NF-κB. Importantly, at protein level, NLRP3, Caspase-1, IL-18, IL-1β and GSDMD were significantly decreased in combination groups both in vivo and vitro. IACT reduce inflammasome mediated pyroptosis in MCAO/R rats and OGD/R PC12 cells through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway, which suggests that drug combination is a protective strategy with clinical potential against I/R-induced injury.

Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulafia DP, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Lozano JD, Lotocki G, Keane RW, Dietrich WD (2009) Inhibition of the inflammasome complex reduces the inflammatory response after thromboembolic stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:534–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2008.143
Barrington J, Lemarchand E, Allan SM (2017) A brain in flame; do inflammasomes and pyroptosis influence stroke pathology? Brain Pathol (Zurich, Switzerland) 27:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12476
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17:472–476. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.17.3.472
Belcaro G, Errichi BM, Laurora G, Marinucci R, Cesarone MR, De Cenzo A (1989) Chronic treatment of vascular diseases with indobufen. Minerva Cardioangiol 37:241–250
Belton O, Byrne D, Kearney D, Leahy A, Fitzgerald DJ (2000) Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2-dependent prostacyclin formation in patients with atherosclerosis. Circulation 102:840–845. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.102.8.840
Bergamasco B, Benna P, Carolei A, Rasura M, Rudelli G, Fieschi C (1997) A randomized trial comparing ticlopidine hydrochloride with indobufen for the prevention of stroke in high-risk patients (TISS study). Ticlopidine Indobufen Stroke Study. Funct Neurol 12:33–43
China MoSaTotpsRo (2020) The relationship between indobufen and aspirin in acute ischemic stroke. https://ichgcp.net/zh/clinical-trials-registry/NCT03871517. Accessed 18 Nov 2020
Facci L, Barbierato M, Zusso M, Skaper SD, Giusti P (2018) Serum amyloid a primes microglia for ATP-dependent interleukin-1β release. J Neuroinflammation 15:164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1205-6
Fang YC et al (2006) Induction of prostacyclin/PGI2 synthase expression after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:491–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600205
Fann DY-W et al (2013) Intravenous immunoglobulin suppresses NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal death in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 4:e790–e790. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.326
Fantuzzi G, Dinarello CA (1999) Interleukin-18 and interleukin-1 beta: two cytokine substrates for ICE (caspase-1). J Clin Immunol 19:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020506300324
Fornaro G, Rossi P, Mantica PG, Caccia ME, Aralda D, Lavezzari M, Pamparana F, Milanesi G (1993) Indobufen in the prevention of thromboembolic complications in patients with heart disease. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Circulation 87:162–164. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.87.1.162
Guo H, Callaway JB, Ting JPY (2015) Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med 21:677–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3893
Han D, Fang W, Zhang R, Wei J, Kodithuwakku ND, sha L, Ma W, liu L, Li F, Li Y (2016) Clematichinenoside protects blood brain barrier against ischemic stroke superimposed on systemic inflammatory challenges through up-regulating A20. Brain Behav Immun 51:56–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.07.025
He Y, Hara H, Núñez G (2016) Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem Sci 41:1012–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002
Hua KF, Chou JC, Ka SM, Tasi YL, Chen A, Wu SH, Chiu HW, Wong WT, Wang YF, Tsai CL, Ho CL, Lin CH (2015) Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome-derived IL-1β production. J Cell Physiol 230:863–874. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24815
Huang B, Qian Y, Xie S, Ye X, Chen H, Chen Z, Zhang L, Xu J, Hu H, Ma S, Héroux P, Wang D, Shen HM, Wu Y, Xia D (2020) Ticagrelor inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome to protect against inflammatory disease independent of the P2Y(12) signaling pathway. Cell Mol Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0444-5
Ibáñez L, Vidal X, Vendrell L, Moretti U, Laporte JR (2006) Upper gastrointestinal bleeding associated with antiplatelet drugs. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02759.x
James S, Åkerblom A, Cannon CP, Emanuelsson H, Husted S, Katus H, Skene A, Steg PG, Storey RF, Harrington R, Becker R, Wallentin L (2009) Comparison of ticagrelor, the first reversible oral P2Y(12) receptor antagonist, with clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes: rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the PLATelet inhibition and patient. Outcomes (PLATO) trial. Am Heart J 157:599–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2009.01.003
Johnston SC, Amarenco P, Denison H, Evans SR, Himmelmann A, James S, Knutsson M, Ladenvall P, Molina CA, Wang Y (2020) Ticagrelor and aspirin or aspirin alone in acute ischemic stroke or TIA. N Engl J Med 383:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1916870
Kim C-B, Park S-J, Jeong J-C, Choi S-M, Krause H-J, Song D-Y, Hong H (2019) Construction of 3D-rendering imaging of an ischemic rat brain model using the planar FMMD technique. Sci Rep 9:19050–19050. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55585-x
Kolati SR, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN, Mahareddy JR, Uppulapu SK, Gogoi R, Barua CC, Lahkar M (2015) BAY 11-7082 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by attenuating hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammation via NF-κB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39:690–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.01.019
Kral M, Herzig R, Sanak D, Skoloudik D, Vlachova I, Bartkova A, Hlustik P, Kovacik M, Kanovsky P (2010) Oral antiplatelet therapy in stroke prevention. Minireview. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech 154:203–210. https://doi.org/10.5507/bp.2010.031
Lammerding L, Slowik A, Johann S, Beyer C, Zendedel A (2016) Poststroke inflammasome expression and regulation in the peri-infarct area by gonadal steroids after transient focal ischemia in the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 103:460–475. https://doi.org/10.1159/000439435
Lee J-Y, Sung K-C, Choi H-I (2016) Comparison of aspirin and indobufen in healthy volunteers. Platelets 27:105–109. https://doi.org/10.3109/09537104.2015.1042853
Li F, Xu D, Hou K, Gou X, Li Y (2020) The role of P2Y12 receptor inhibition in ischemic stroke on microglia, platelets and vascular smooth muscle cells. J Thromb Thrombolysis 50:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-020-02098-4
Luo B, Li B, Wang W, Liu X, Liu X, Xia Y, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhang M, An F (2014) Rosuvastatin alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and MAPK pathways in a type 2 diabetes rat model. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 28:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6498-1
Ma Q, Chen S, Hu Q, Feng H, Zhang JH, Tang J (2014) NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Ann Neurol 75:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24070
Machado-Carvalho L et al (2016) Low E-prostanoid 2 receptor levels and deficient induction of the IL-1β/IL-1 type I receptor/COX-2 pathway: vicious circle in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137:99–107.e107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.028
Mdzinarishvili A, Kiewert C, Kumar V, Hillert M, Klein J (2007) Bilobalide prevents ischemia-induced edema formation in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience 144:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.037
Medling BD, Bueno R, Chambers C, Neumeister MW (2010) The effect of vitamin e succinate on ischemia reperfusion injury. Hand (N Y) 5:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-009-9196-5
Mehran R, Baber U, Sharma SK, Cohen DJ, Angiolillo DJ, Briguori C, Cha JY, Collier T, Dangas G, Dudek D, Džavík V, Escaned J, Gil R, Gurbel P, Hamm CW, Henry T, Huber K, Kastrati A, Kaul U, Kornowski R, Krucoff M, Kunadian V, Marx SO, Mehta SR, Moliterno D, Ohman EM, Oldroyd K, Sardella G, Sartori S, Shlofmitz R, Steg PG, Weisz G, Witzenbichler B, Han YL, Pocock S, Gibson CM (2019) Ticagrelor with or without aspirin in high-risk patients after PCI. N Engl J Med 381:2032–2042. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1908419
Nakanishi K, Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Okamura H (2001) Interleukin-18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses. Annu Rev Immunol 19:423–474. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.423
Omoyinmi E, Standing A, Keylock A, Price-Kuehne F, Melo Gomes S, Rowczenio D, Nanthapisal S, Cullup T, Nyanhete R, Ashton E, Murphy C, Clarke M, Ahlfors H, Jenkins L, Gilmour K, Eleftheriou D, Lachmann HJ, Hawkins PN, Klein N, Brogan PA (2017) Clinical impact of a targeted next-generation sequencing gene panel for autoinflammation and vasculitis. PLoS One 12:e0181874. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181874
Pan Z, Cui M, Dai G, Yuan T, Li Y, Ji T, Pan Y (2018) Protective effect of anthocyanin on neurovascular unit in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Front Neurosci 12:947–947. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00947
Poyet JL, Srinivasula SM, Tnani M, Razmara M, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2001) Identification of Ipaf, a human caspase-1-activating protein related to Apaf-1. J Biol Chem 276:28309–28313. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C100250200
Qiu Z, He Y, Ming H, Lei S, Leng Y, Xia Z-Y (2019) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) aggravates high glucose- and hypoxia/Reoxygenation-induced injury through activating ROS-dependent NLRP3 Inflammasome-mediated Pyroptosis in H9C2 Cardiomyocytes. J Diabetes Res 2019:8151836. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8151836
Rahman H, Khan SU, Nasir F, Hammad T, Meyer MA, Kaluski E (2019) Optimal duration of aspirin plus clopidogrel after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. Stroke 50:947–953. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023978
Rivera A, Siracusa MC, Yap GS, Gause WC (2016) Innate cell communication kick-starts pathogen-specific immunity. Nat Immunol 17:356–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3375
Rogan J (1990) Indobufen in secondary prevention of transient ischaemic attack. Multicentre Ischaemic Attack Study Group. J Int Med Res 18:240–244. https://doi.org/10.1177/030006059001800310
Rollini F, Tello-Montoliu A, Patel R, Darlington A, Wilson RE, Franchi F, Muñiz-Lozano A, Desai B, Bender N, Sakariassen KS, Angiolillo DJ (2014) Pharmacodynamic effects of EV-077 in patients with diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease on aspirin or clopidogrel monotherapy: results of an in vitro pilot investigation. J Thromb Thrombolysis 37:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-013-0979-8
She Y et al (2019) Neuroprotective effect of glycosides in Buyang Huanwu Decoction on pyroptosis following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 242:112051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112051
Shi J et al (2015) Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526:660–665. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15514
Shi H-Q, Zhang Y, Cheng M-H, Fan B-S, Tian J-S, Yu J-G, Chen B (2016) Sodium sulfide, a hydrogen sulfide-releasing molecule, attenuates acute cerebral ischemia in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther 22:625–632. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12558
Siddesha JM, Valente AJ, Sakamuri SSVP, Gardner JD, Delafontaine P, Noda M, Chandrasekar B (2014) Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits IL-18-induced cardiac fibroblast migration through the induction of RECK. J Cell Physiol 229:845–855. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24511
Signorini GP, Salmistraro G, Maraglino G (1988) Efficacy of indobufen in the treatment of intermittent claudication. Angiology 39:742–746. https://doi.org/10.1177/000331978803900806
Song W, Wei L, Du Y, Wang Y, Jiang S (2018) Protective effect of ginsenoside metabolite compound K against diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NF-κB/p38 signaling pathway in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int Immunopharmacol 63:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.07.027
Suzuki T, Kohyama K, Moriyama K, Ozaki M, Hasegawa S, Ueno T, Saitoe M, Morio T, Hayashi M, Sakuma H (2020) Extracellular ADP augments microglial inflammasome and NF-κB activation via the P2Y12 receptor. Eur J Immunol 50:205–219. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201848013
Thomas MR et al (2015) Platelet P2Y12 inhibitors reduce systemic inflammation and its prothrombotic effects in an experimental human model. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35:2562–2570. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.115.306528
Wang J, Chen T, Shan G (2017) miR-148b regulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rat ischemic stroke model. Front Cell Neurosci 11:329. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00329
Wang C et al (2018) Artificially cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis alleviates diabetic nephropathy and its Podocyte injury via inhibiting P2X7R expression and NLRP3 Inflammasome activation. J Diabetes Res 2018:1390418. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1390418
Wang Y et al (2019) Ticagrelor plus aspirin versus clopidogrel plus aspirin for platelet reactivity in patients with minor stroke or transient ischaemic attack: open label, blinded endpoint, randomised controlled phase II trial. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed) 365:l2211. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l2211
Wiseman LR, Fitton A, Buckley MM (1992) Indobufen. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in cerebral, peripheral and coronary vascular disease. Drugs 44:445–464. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199244030-00009
Wu L et al (2017) P2y12 receptor promotes pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling via platelet-driven inflammation in mice. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex : 1979) 70:759–769. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.09262
Xu D, Hou K, Li F, Chen S, Fang W, Li Y (2019) XQ-1H alleviates cerebral ischemia in mice through inhibition of apoptosis and promotion of neurogenesis in a Wnt/β-catenin signaling dependent way. Life Sci 235:116844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116844
Yan YY et al (2018) Therapeutic effects of JLX001 on cerebral ischemia through inhibiting platelet activation and thrombus formation in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 106:805–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.023
Yang F et al (2014) NLRP3 deficiency ameliorates neurovascular damage in experimental ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:660–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.242
Yilmaz Ö, Lee KL (2015) The inflammasome and danger molecule signaling: at the crossroads of inflammation and pathogen persistence in the oral cavity. Periodontol 2000 69:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12084
Zhang T, Xiu H-H, Liu J-X, Ma Y, Xu K-Q, Huang W-Q (2017) Protective effect of aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 on hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats: the role of miR-146b. Int Immunopharmacol 51:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.008
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C, Han J (2018) Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res 28:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.133
Zhang D, Qian J, Zhang P, Li H, Shen H, Li X, Chen G (2019a) Gasdermin D serves as a key executioner of pyroptosis in experimental cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model both in vivo and in vitro. J Neurosci Res 97:645–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24385
Zhang LY, Zhan DL, Chen YY, Wang WH, He CY, Lin Y, Lin YC, Lin ZN (2019b) Aflatoxin B1 enhances pyroptosis of hepatocytes and activation of Kupffer cells to promote liver inflammatory injury via dephosphorylation of cyclooxygenase-2: an in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo study. Arch Toxicol 93:3305–3320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02572-w
Zheng Y, Hu Q, Manaenko A, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Xu L, Tang J, Tang J, Zhang JH (2015) 17β-estradiol attenuates hematoma expansion through estrogen receptor α/silent information regulator 1/nuclear factor-kappa b pathway in hyperglycemic intracerebral hemorrhage mice. Stroke 46:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006372
Zhou X, Wu Y, Ye L, Wang Y, Zhang K, Wang L, Huang Y, Wang L, Xian S, Zhang Y, Chen Y (2019) Aspirin alleviates endothelial gap junction dysfunction through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in LPS-induced vascular injury. Acta Pharm Sin B 9:711–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2019.02.008
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China [2016ZX09101031] and [2018ZX09301043] and China Pharmaceutical University “Double First-Class” Construction Technology Innovation Team Project [CPU2018GY23] and [CPU2018GY24].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.L. and D.X. performed most of the experiments and were involved in writing a draft manuscript; K.H., X.G. and N.L. performed information consolidation and were involved in modifying article; Y.L and W.F. were involved in selecting theme. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of China Pharmaceutical University.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 253 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Xu, D., Hou, K. et al. Pretreatment of Indobufen and Aspirin and their Combinations with Clopidogrel or Ticagrelor Alleviates Inflammasome Mediated Pyroptosis Via Inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 16, 835–853 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-020-09978-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-020-09978-9