Abstract
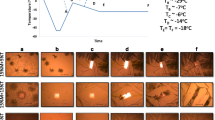
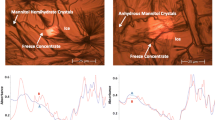
Sugars are the most common excipients added to pharmaceutical and biotechnological formulations as protein protectants due to their adequate physicochemical properties, low toxicity, high purity and low cost. However, a second excipient is generally required to extend their protection in supercooled media. The effect of electrolytes is of special interest because of their universal presence in biological systems, their major influence on water structure, and their capability to interact with biomolecules. The purpose of the present work was to analyze the effect of different salts on the stability of catalase in amorphous (glassy and supercooled) trehalose matrices. Trehalose-Mg2+ system was better than trehalose alone to protect the enzyme both during freeze-drying and later storage at low RH (22%). The stabilizing effect observed for certain salts in these systems was not related with an increase of the Tg value. Under conditions at which trehalose crystallizes (43 %RH), salts (especially Mg2+) were detrimental since the enzyme became confined in a salt-concentrated region. Protein denaturation and aggregation were analyzed through differential scanning calorimetry in order to correlate activity changes with physical changes. Trehalose systems without salt and Mg2+-containing systems showed almost no aggregation after denaturation, in agreement with the thermal stability of the enzyme. Thus, the two major parameters related to enzyme stability in freeze-dried non-crystallized systems are: enzyme characteristics (type, quaternary structure) and salt-protein specific interactions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.L. Lee, A.E. Hafeman, P.G. Debenedetti, B.A. Pethica, D.J. Moore, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45(14), 5134–5147 (2006)
T. Lipiäinen, H. Räikkönen, A.-M. Kolu, M. Peltoniemi, A. Juppo, Int. J. Pharm. 543(1-2), 21–28 (2018)
M.V. Traffano-Schiffo, M. Castro-Giraldez, P.J. Fito, P.R. Santagapita, Food Res. Int. 100, 296–303 (2017)
C. Olsson, H. Jansson, J. Swenson, J. Phys. Chem. B 120(20), 4723–4731 (2016)
A. Patist, H. Zoerb, Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 40(2), 107–113 (2005)
P.R. Santagapita, L. Gómez Brizuela, M.F. Mazzobre, H.L. Ramírez, H.R. Corti, R. Villalonga Santana, M.P. Buera, Carbohydr. Polym. 83(1), 203–209 (2011)
P.R. Santagapita, M.F. Mazzobre, A.G. Cruz, H.R. Corti, R. Villalonga Santana, M.P. Buera, Biotechnol. Prog. 29(3), 786–795 (2013)
C. Schebor, M.F. Mazzobre, M.P. Buera, Carbohydr. Res. 345(2), 303–308 (2010)
P.R. Santagapita, M.P. Buera, Food Biophys. 3(1), 87–93 (2008)
M. F. Mazzobre, P. R. Santagapita, N. Gutierrez, M. P. Buera, In Food Engineering Integrated Approach Ed. by G. F. Gutierrez-López, G. B. Barbosa-Cánovas, J. Welti-Channes, E. Parada-Arias (Springer, Germany, 2008), pp. 70
A.S. Parmar, M. Muschol, Biophys. J. 97(2), 590–598 (2009)
A. Singhal, V.B. Morris, V. Labhasetwar, A. Ghorpade, Cell Death Dis. 4(11), e903 (2013)
P.R. Santagapita, M.P. Buera, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354(15-16), 1760–1767 (2008)
B. Chance, A. Maehley, Methods Enzymol. 2, 764 (1955)
F. Sussich, A. Cesàro, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 62(3), 757–768 (2000)
M.F. Mazzobre, M.P. Buera, Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1473(2-3), 337–344 (1999)
M.P. Longinotti, M.F. Mazzobre, M.P. Buera, H.R. Corti, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4(3), 533–540 (2002)
D.P. Miller, J. de Pablo, H. Corti, Pharm. Res. 14(5), 578–590 (1997)
M.F. Mazzobre, M.P. Longinotti, H.R. Corti, M.P. Buera, Cryobiology 43(3), 199–210 (2001)
R.L. Remmele, W.R. Gambotz, BioPharm 13, 36 (2000)
M.A. Singer, S. Lindquist, Mol. Cell 1(5), 639–648 (1998)
A.K. Soper, M.A. Ricci, F. Bruni, N.H. Rhys, S.E. McLain, J. Phys. Chem. B 122(29), 7365–7374 (2018)
K. Shiraga, A. Adachi, Y. Ogawa, Chem. Phys. Lett. 678, 59–64 (2017)
C. Branca, S. Magazù, F. Migliardo, P. Migliardo, Physica A 304(1-2), 314–318 (2002)
K. Kajiwara, A. Motegi, N. Murase, CryoLetters 22, 311 (2001)
E. Leontidis, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 7(1-2), 81–91 (2002)
Y. Marcus, J. Solut. Chem. 23(7), 831–848 (1994)
T. Rabilloud, Methods Mol. Biol. 528, 259 (2009)
T. Samejima, M. Kamata, K. Shibata, J. Biochem. Japan 51(3), 181–187 (1962)
S. Calligaris, M.C. Nicoli, Food Chem. 94(1), 130–134 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of ANPCYT (PICT 2012-3070; PICT 2013-1331), CIN-CONICET (PDTS 2015 n° 196) and UBA (Project UBACyT 20020170100459BA). All authors are members of CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
none.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santagapita, P.R., Mazzobre, M.F. & Buera, M.P. Catalase Stability in Amorphous and Supercooled Media Related to Trehalose- Water- Salt Interactions. Food Biophysics 14, 90–96 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9560-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9560-5