Abstract
Current computerized image systems are able to recognize normal blood cells in peripheral blood, but fail with abnormal cells like the classes of lymphocytes associated to lymphomas. The main challenge lies in the subtle differences in morphologic characteristics among these classes, which requires a refined segmentation. A new efficient segmentation framework has been developed, which uses the image color information through fuzzy clustering of different color components and the application of the watershed transformation with markers. The final result is the separation of three regions of interest: nucleus, entire cell, and peripheral zone around the cell. Segmentation of this zone is crucial to extract a new feature to identify cells with hair-like projections. The segmentation is validated, using a database of 4758 cell images with normal, reactive lymphocytes and five types of malignant lymphoid cells from blood smears of 105 patients, in two ways: (1) the efficiency in the accurate separation of the regions of interest, which is 92.24%, and (2) the accuracy of a classification system implemented over the segmented cells, which is 91.54%. In conclusion, the proposed segmentation framework is suitable to distinguish among abnormal blood cells with subtile color and spatial similarities.

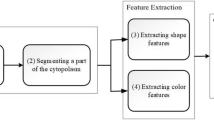
The segmentation framework uses the image color information through fuzzy clustering of different color components and the application of the watershed transformation with markers (Top). The final result is the separation of three regions of interest: nucleus, entire cell, and peripheral zone around the cell. The procedure is also validated by the implementation of a system to automatically classify different types of abnormal blood cells (Bottom)











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alférez S (2015) Methodology for automatic classification of atypical lymphoid cells from peripheral blood cell images. PhD thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya
Alférez S, Merino A, Mujica LE, Ruiz M, Bigorra L, Rodellar J (2014) Automatic classification of atypical lymphoid B cells using digital blood image processing. Int J Lab Hematol 36(4):472–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12175
Alférez S, Merino A, Bigorra L, Mujica L, Ruiz M, Rodellar J (2015) Automatic recognition of atypical lymphoid cells from peripheral blood by digital image analysis. Am J Clin Pathol 143:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCP78IFSTOGZZJN
Alférez S, Merino A, Bigorra L, Rodellar J (2016) Characterization and automatic screening of reactive and abnormal neoplastic b lymphoid cells from peripheral blood. Int J Lab Hematol 38(2):209–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12473
Angulo J (2003) Morphologie mathématique et indexation d’images couleur: application à la microscopie en biomédecine. PhD thesis, Mines ParisTech
Angulo J, Klossa J, Flandrin G (2006) Ontology-based lymphocyte population description using mathematical morphology on colour blood images. Cell Mol Biol 52(6):2–15. https://doi.org/10.1170/T732
Arslan S, Ozyurek E, Gunduz-Demir C (2014) A color and shape based algorithm for segmentation of white blood cells in peripheral blood and bone marrow images. Cytom Part A 85(6):480–490. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.22457
Balafar MA, Ramli AR, Saripan MI, Mashohor S (2010) Review of brain MRI image segmentation methods. Artif Intell Rev 33(3):261–74
Beucher S (1992) The watershed transformation applied to image segmentation. Scanning Microsc Suppl 6:299–314. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nlmcatalog?term=0892-953X%5BISSN%5D
Bezdek JC (1981) Objective function clustering. In: Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms. Advanced applications in pattern recognition. Springer, Boston, DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-0450-1_3, (to appear in print)
Brown G, Pocock A, Zhao MJ, Luján M (2012) Conditional likelihood maximisation: a unifying framework for information theoretic feature selection. J Mach Learn Res 13(1):27–66
Cellavision (2016) Digital cell morphology. Retrieved from: http://www.cellavision.com, (Accessed 2017)
Centre of mathematical morphology MINES ParisTech (2014) Image segmentation and mathematical morphology. Retrieved from: http://cmm.ensmp.fr/beucher/wtshed.html, (Accesed 2017)
Chen S, Zhang D (2004) Robust image segmentation using fcm with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B 34(4):1907–1916. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2004.831165
Chuang KS, Tzeng HL, Chen S, Wu J, Chen TJ (2006) Fuzzy c-means clustering with spatial information for image segmentation. Comput Med Imaging Graph 30(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2005.10.001
Comaniciu D, Meer P, Foran DJ (1999) Image-guided decision support system for pathology. Mach Vis Appl 11(4):213–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001380050104
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Dembele D, Kastner P (2003) Fuzzy C-means method for clustering microarray data. Bioinformatics 19 (8):973–80
Dorini LB, Minetto R, Leite N (2012) Semi-automatic white blood cell segmentation based on multiscale analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 17(1):250–256. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2012.2207398
Ghosh M, Das D, Chakraborty C, Ray AK (2010) Automated leukocyte recognition using fuzzy divergence. Micron 41(7):840–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2010.04.017
Gönen M, Alpaydin E (2011) Multiple kernel learning algorithms. J Mach Learn Res 12(Jul):2211–2268
Gonzalez J, Olmos I, Altamirano L, Morales BA, Reta C, Galindo MC, Alonso JE, Lobato R (2011) Leukemia identification from bone marrow cells images using a machine vision and data mining strategy. Intell Data Anal 15:443–462. https://doi.org/10.3233/IDA-2010-0476
Gutiérrez G, Merino A, Domingo A, Jou JM, Reverter JC (2008) Eqas for peripheral blood morphology in spain: a 6-year experience. Int J Lab Hematol 30(6):460–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-553X.2007.00975.x
Houwen B (2001) The differential cell count. Lab Hematol 7(2):89–100
Madhloom HT, Kareem SA, Ariffin H (2012) A robust feature extraction and selection method for the recognition of lymphocytes versus acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 2012 Int Conf Adv Comput Sci Appl Technol :330–335. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSAT.2012.62
Madhloom HT, Kareem SA, Ariffin H, HA Zaidan AA, Zaidan B (2010) An automated white blood cell nucleus localization and segmentation using image arithmetic and automatic threshold. J Appl Sci 10 (11):959–966. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2010.959.966
Markiewicz T, Osowski S, Mariańska B (2007) White blood cell automatic counting system based on support vector machine. In: Beliczynski B, Dzielinski A, Iwanowski M, Ribeiro B (eds) Adaptive and natural computing algorithms. ICANNGA 2007. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4432. Springer, Berlin, DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71629-7_36
Medica (2016) Easycell assistant. Retrieved from: http://www.medicacorp.com/, products/hematology-imaging-analyzers (Accessed 2016)
Merino A, Puigví L, Boldú L, Alférez S, Rodellar J (2018) Optimizing morphology through blood cell image analysis. Int J Lab Hematol 40(Suppl. 1):54–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12832
Meyer F (1994) Topographic distance and watershed lines. Signal Process 38(1):113–125
Mohapatra S, Patra D (2010) Automated leukemia detection using hausdorff dimension in blood microscopic images. In: 2010 Int Conf, IEEE, Ieee, Emerg Trends Robot Commun Technol (INTERACT), pp 64–68. https://doi.org/10.1109/INTERACT.2010.5706196
Mohapatra S, Samanta SS, Patra D, Satpathi S (2011) Fuzzy based blood image segmentation for automated leukemia detection. 2011 Int Conf Devices Commun :1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDECOM.2011.5738491
Muller K, Mika S, Ratsch G, Tsuda K, Scholkopf B (2001) An introduction to kernel-based learning algorithms. Neural Networks IEEE Trans 12(2):181–201
Münzenmayer C, Schlarb T, Steckhan D, Haßlmeyer E, Bergen T, Aschenbrenner S, Wittenberg T, Weigand C, Zerfaß T (2011) Hemacam - a computer assisted microscopy system for hematology. Springer, pp 233–242
Nikolaou N, Papamarkos N (2009) Color reduction for complex document images. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 19(1):14–2
Pal NR, Bezdek JC (1995) On cluster validity for the fuzzy c-means model. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 3 (3):370–9
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–38. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2005.159
Plissiti ME, Nikou C, Charchanti A (2011) Automated detection of cell nuclei in pap smear images using morphological reconstruction and clustering. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 15(2):233–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2014.09.002
Putzu L, Caocci Gi, Di Ruberto C (2014) Leucocyte classification for leukaemia detection using image processing techniques. Artif Intell Med 62(3):179–191
Ramoser H, Laurain V, Bischof H, Ecker R (2006) Leukocyte segmentation and classification in blood-smear images. In: Eng Med Biol Soc 2005 IEEE-EMBS 2005 27th Annu Int Conf, IEEE, vol 4, pp 3371–3374. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2005.1617200
Rezatofighi SH, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2011) Automatic recognition of five types of white blood cells in peripheral blood. Comput Med Imaging Graph 35(4):333–343
Roerdink J, Meijster A (2000) The watershed transform: definitions, algorithms and parallelization strategies. Fundamenta Informaticae 41:1–40
Ross TJ (2009) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications. Wiley, New Jersey
Sabino DMU, Dafontouracosta L, Gilrizzatti E, Antoniozago M, da Fontoura Costa L, Gil Rizzatti E, Antonio Zago M (2004) A texture approach to leukocyte recognition. Real-Time Imaging 10(4):205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rti.2004.02.007
Sadeghian F, Seman Z, Ramli AR, Abdul Kahar BH, Saripan MI (2009) A framework for white blood cell segmentation in microscopic blood images using digital image processing. Biol Proced Online 11(1):196–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12575-009-9011-2
Scotti F (2005) Automatic morphological analysis for acute leukemia identification in peripheral blood microscope images. In: CIMSA. 2005 IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Intell. Meas. Syst. Appl. 2005., IEEE, July. https://doi.org/10.1109/CIMSA.2005.1522835 https://doi.org/10.1109/CIMSA.2005.1522835, pp 96–101
Scotti F (2006) Robust segmentation and measurements techniques of white cells in blood microscope images. 2006 IEEE Instrum Meas Technol Conf Proc (April):43–48, https://doi.org/10.1109/IMTC.2006.235499
Sinha N, Ramakrishnan A (2003) Automation of differential blood count. TENCON 2003 Conf (i)
Snoek J, Larochelle H, Adams RP (2012) Practical bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. arXiv:1206.2944
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris NL, Stein H, Siebert R, Advani R, Ghielmini M, Salles GA, Zelenetz AD, Jaffe ES (2016) The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 127(20):2375–2390. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569
Tuzel O, Yang L, Meer P, Foran DJ (2007) Classification of hematologic malignancies using texton signatures. Pattern Anal Appl PAA 10(4):277–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-007-0066-x
Yang L, Meer P, Foran DJ (2005) Unsupervised segmentation based on robust estimation and color active contour models. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 9(3):475–86. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2005.847515
Yang L, Tuzel O, Chen W, Meer P, Salaru G, Goodell LA, Foran DJ (2009) Pathminer: a web-based tool for computer-assisted diagnostics in pathology. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 13(3):291–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2008.2008801
Zhang D, Chen S (2002) Fuzzy clustering using kernel method. In: 2002 Int. Conf. Control Autom. 2002. ICCA
Zhang DQ, Chen SC (2004) A novel kernelized fuzzy c-means algorithm with application in medical image segmentation. Artif Intell Med 32(1):37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2004.01.012
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness under Grant DPI2015-64493-R (MINECO/FEDER) and by the Generalitat de Catalunya under Grant SGR-859-2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alférez, S., Merino, A., Acevedo, A. et al. Color clustering segmentation framework for image analysis of malignant lymphoid cells in peripheral blood. Med Biol Eng Comput 57, 1265–1283 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-01954-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-01954-7