Abstract
Objective
The aim of the current study was to investigate the efficacy of ultrasonography-guided aspiration treatment with concomitant steroid injection on relieving reflux blood flow in veins located next to symptomatic Baker’s cyst.
Methods
All patients were examined by ultrasonography at administration and 1 month follow-up after intervention. Puncture and aspiration of the cyst, as well as injection of 1 ml dexamethasone were performed by the same radiologist. Compression on popliteal vein and vena saphena parva and the degrees of reflux before and after treatment were recorded.
Results
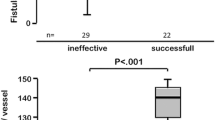
Twenty-six patients were included in the study. An overall reduction of the cyst’s size was observed in all patients of the study group. Reduction of the cyst size is more evident during the 1st week, which was observed by a slight enlargement during the 1st and the 3rd months controls.
Conclusion
Ultrasonography-guided puncture, aspiration and steroid injection seems to yield promising outcomes in terms of relieving venous reflux flow around simple Baker’s cysts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Handy JR (2001) Popliteal cysts in adults: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 31:108–118
Chatzopoulos D, Moralidis E, Markou P, Makris V, Arsos G (2008) Baker’s cysts in knees with chronic osteoarthritic pain: a clinical, ultrasonographic, radiographic and scintigraphic evaluation. Rheumatol Int 29:141–146
Newsham KR (2009) Recurrent popliteal cyst in an adult: a case report and review. Orthop Nurs 28:11–14
Köroğlu M, Callıoğlu M, Eriş HN, Kayan M, Cetin M, Yener M, Gürses C, Erol B, Türkbey B, Parlak AE, Akhan O (2012) Ultrasound guided percutaneous treatment and follow-up of Baker’s cyst in knee osteoarthritis. Eur J Radiol 81:3466–3471
Di Sante L, Paoloni M, Ioppolo F, Dimaggio M, Di Renzo S, Santilli V (2010) Ultrasound-guided aspiration and corticosteroid injection of Baker’s cysts in knee osteoarthritis: a prospective observational study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 89:970–975
Fritschy D, Fasel J, Imbert JC, Bianchi S, Verdonk R, Wirth CJ (2006) The popliteal cyst. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14:623–628
Mendoza E, Berger HA (2001) Provokationsmanöver für die duplex-sonographische Diagnostik der Varikosis. Gefäßchirurgie 6:43–46
Sanchez JE, Conkling N, Labropoulos N (2011) Compression syndromes of the neurovascular bundle due to Baker cyst. J Vasc Surg 54:1821–1829
Centeno CJ, Schultz J, Freeman M (2008) Sclerotherapy of Baker’s cyst with imaging confirmation of resolution. Pain Physician 11:257–261
Helbich TH, Breitenseher M, Trattnig S, Nehrer S, Erlacher L, Kainberger F (1998) Sonomorphologic variants of popliteal cysts. J Clin Ultrasound 26:171–176
Newsham KR (2009) Recurrent popliteal cyst in an adult: a case report and review. Orthop Nurs 28:11–14
Krüger T, Niedermanner I, Hube R, Hein W (2002) Recurrence of Baker’s cysts with regard to operation procedure and intraarticular pathology. Zentralbl Chir 127:905–908
Centeno CJ, Schultz J, Freeman M (2008) Sclerotherapy of Baker’s cyst with imaging confirmation of resolution. Pain Physician 11:257–261
Bui-Mansfield LT, Youngberg RA (1997) Intraarticular ganglia of the knee: prevalence, presentation, etiology, and management. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:123–127
Acknowledgements
No financial support was received for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Emin Cakmakci, Irfan Celebi, Safiye Tokgoz Ozal, Ayse Secil Eksioglu, Ozlem Kolcak and Mucahit Dogru declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patients of all participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cakmakci, E., Celebi, I., Ozal, S.T. et al. Can ultrasonography-guided aspiration and steroid injection treat reflux venous blood flow around symptomatic Baker’s cysts? Our short-term experience. Radiol med 122, 690–695 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-017-0771-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-017-0771-5