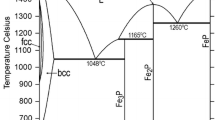
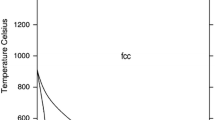
Abstract
Thermodynamic descriptions of the Fe-Al-P system and its binary sub-systems, Fe-Al and Al-P, are developed in the frame of a new Fe-X-P (X = Al, Cr, Cu, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Si, Ti) database. The thermodynamic parameters of the binary Fe-P system are taken from an earlier assessment and those of the Fe-Al, Al-P and Fe-Al-P systems are modified (Fe-Al, Al-P) or optimized (Fe-Al-P) in this study, using experimental thermodynamic and phase equilibrium data from the literature. The solution phases of the system (liquid, bcc_A2 and fcc_A1) are described with the substitutional solution model. The compounds are treated either as stoichiometric (Al5Fe4, Al2Fe, Al5Fe2, Al13Fe4, FeP, AlP) or as semi-stoichiometric phases (Fe3P and Fe2P). Good or reasonable correlation has been obtained between the calculated and the experimental thermodynamic and phase equilibrium data.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 1: Fe-Cr-P, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, 35, p 458-468. doi:10.1007/s11669-014-0314-x
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 2: Fe-Cu-P, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, 35, p 469-475. doi:10.1007/s11669-014-0315-9
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 3: Fe-Mn-P, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, 35, p 587-594. doi:10.1007/s11669-014-0328-4
J. Miettinen, A. Pashkova, and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 4: Fe-Mo-P, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, doi:10.1007/s11669-014-0357-z
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 5: Fe-Nb-P, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, doi:10.1007/s11669-014-0351-5
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 6: Fe-Ni-P, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, doi:10.1007/s11669-014-0358-y
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 7: Fe-Ti-P. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., submitted to
J. Miettinen and G. Vassilev, Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 8: Fe-Ti-P. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., submitted to
J. Miettinen, S. Louhenkilpi, H. Kytönen, and J. Laine, IDS: Thermodynamic-Kinetic-Empirical Tool for Modeling of Solidification, Microstructure and Material Properties, Math. Comput. Simul., 2010, 80, p 1536-1550
U.R. Kattner and B.P. Burton, Al-Fe (Aluminum-Iron), H. Okamoto, ed., Phase Diagrams of Binary Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, 1993, p 12-28
M. Seierstein, COST 507: Thermochemical Database for Light Metal Alloys, Volume 2, European Communities, Belgium, I. Ansara, A.T. Dinsdale, and M.H. Rand, Eds., 1998, p 123-25.
B. Sundman, I. Ohnuma, N. Dupin, U. Kattner, and S. Fries, An Assessment of the Entire Al-Fe System Including D03 Ordering, Acta Mater., 2009, 57, p 2896-2908
M. Jacobs and R. Schmid-Fetzer, Phase Behavior and Thermodynamic Properties in the System Fe-Al, CALPHAD, 2009, 33, p 170-178
I. Ansara, C. Chatillon, H. Lukas, T. Nishizawa, H. Ohtani, K. Ishida, M. Hillert, B. Sundman, B. Argent, A. Watson, T. Chart, and T. Anderson, A Binary Database for III-V Compound Semiconductor Systems, CALPHAD, 1994, 18, p 177-222
H. Tu, F. Yin, X. Su, Y. Liu, and X. Wang, Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Modelling of the Al-P-Zn System, CALPHAD, 2009, 33, p 755-760
S.-M. Liang and R. Schmid-Fetzer, Thermodynamic Assessment of the Al-P system Based on Original Experimental Data, CALPHAD, 2013, 42, p 76-85
J.-H. Shim, C.-S. Oh, and D.N. Lee, Thermodynamic Properties and Calculation of Phase Diagram of the Fe-P System, J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater., 1996, 34, p 1385-1393
C. Wu, W. Huang, X. Su, H. Peng, J. Wang, and Y. Liu, Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of the Fe-Al-P System at Low Phosphorus Contents, CALPHAD, 2012, 38, p 1-6
H. Lukas, S. Fries, and B. Sundman, Computational Thermodynamics: The Calphad Method, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2007
V. Raghavan, Phase Diagrams for Ternary Iron Alloys, Part 3, Indian Institute of Metals, Calcutta, 1988, p 9-16
V. Raghavan, The Al-Fe-P (Aluminum-Iron-Phosphorus) System, J. Alloy Phase Diagr., 1989, 5, p 32-39
V. Raghavan, Phase Diagrams Updates and Evaluations of the Al-Fe-P, B-Fe-U, Bi-Fe-Zn, Cu-Fe-Zn, Fe-Si-Zn and Fe-Ti-V Systems, J. Alloy Phase Diagr., 2013, 34, p 230-243
R. Schmid Fetzer, Aluminum-Iron-Phosphorus, Ternary Alloys, Vol 5, VCH, Weinheim, 1992, 354-363.
A. Gwyer, Über die Legierungen des Aluminums mit Kupfer, Eisen, Nickel, Kobalt, Blei und Cadmium (Alloys of Aluminum with Copper, Iron, Nickel, Cobalt, Lead and Cadmium), Z. Anorg. Chem., 1908, 57, p 113-153, in German
A. Gwyer and J. Phillips, The Constitution of Alloys of Aluminum with Silicon and Iron, J. Inst. Met., 1927, 38, p 29-83
J.R. Lee, Liquidus-Solidus Relations in the System Iron-Aluminum, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1960, 194, p 222-224
E. Schürmann and H.-P. Kaiser, Beitrag zu den Schmelzgleichgewichten der Eisen-Aluminum- und Eisen-Phosphorus-Legierungen (On the Melting Equilibria of the Iron-Aluminum and Iron-Phosphorus Alloys), Arch. Eisenhüttenw., 1980, 51, p 325-327
G. Inden and W. Pepperhoff, Experimental study of the order: disorder transition in bcc Fe-Al alloys, Z. Metall., 1990, 81, p 770-773
F. Stein and M. Palm, Re-determination of Transition Temperatures in the Fe-Al System by Differential Thermal Analysis, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2007, 98, p 580-588
P. Rocquet, G. Jegaden, and J. Petit, The Gamma Loop in the Fe-Al System, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1967, 205, p 437-441
E. Schürmann and H.-P. Kaiser, Thermodynamik der Eisen-Aluminum-Legierungen (Thermodynamics of the Iron-Aluminum Alloys), Arch. Eisenhüttenw., 1981, 52, p 127-130, in German
J. Chipman and T. Floridis, Activity of Aluminium in Liquid Ag-AlFe-Al, Fe-Al-C, and Fe-Al-C-Si alloys, Acta Metall., 1955, 3, p 456-459
P. Gross, D. Levi, E. Dewning, G. Wilson, Physical Chemistry of Process Metallurgy, Vol 1., G.R. St Pierre, Ed., New York, 1961, p 403-412
F. Woolley and J. Elliott, Heats of Solution of Aluminum, Copper, Silicon in Liquid Iron, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 1967, 239, p 1872-1883
H. Mitani and H. Nagai, Determination of the Activities of Aluminum in Liquid Aluminum-Iron Binary Alloys by the Bubbling Method, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1968, 32, p 752-755
G. Belton and R. Fruehan, Spectrometric Determination of Activities in Iron-Aluminum and Silver-Aluminum Liquid Alloys, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 1969, 245, p 113-117
R. Hultgren, D. Desai, D. Hawkins, M. Gleiser, and K. Kelley, Selected Values of Thermodynamic Properties of Binary Alloys, American Society for Metals, Materials Park, OH, 1973
E. Ichise, T. Yamauchi, and T. Mori, Knudsen Cell-Mass Spectrometric Study of the Thermodynamics of Fe-Al Alloys, Tetsu to Hagane, 1977, 63, p 417-424, in Japan
K. Rzyman, Z. Moser, A. Miodownik, L. Kaufman, R. Watson, and M. Weinert, Enthalpies or Formation of AlFe: Experiment Versus Theor, CALPHAD, 2000, 24, p 309-318
J. Breuer, A. Grün, F. Sommer, and E. Mittemeijer, Enthalpy of Formation of B2-Fe1−x Alx and B2-(Ni, Fe)1−x Al x , Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, 32B, p 913-918
L. Bencze, D. Raj, W. Oates, J. Herrmann, L. Singheiser, and K. Hilpert, Thermodynamic Investigation of the A2/B2 Region of the Fe-Al System by Knudsen effusion Mass Spectrometry, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34A, p 2409-2419
D. Raj, L. Bencze, D. Kath, W. Dates, J. Herrmann, and L. Singheiser, Thermodynamic Activity Measurements in the B2 Phases of the Fe-Al and Ni-Al Systems, Intermetallics, 2003, 11, p 1119-1124
S. Radcliffe, B. Averbach, and M. Cohen, Relative Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Iron-Aluminum Alloys, Acta Metall., 1961, 9, p 169-176
J. Eldrich and K. Komarek, Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Iron-Aluminum Alloys, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 1964, 230, p 226-233
N. Jacobson and C. Mehrotra, Thermodynamics of Iron-Aluminum Alloys at 1573K, Metall. Trans. B, 1993, 24B, p 481-486
H. Kleykamp and H. Glasbrenner, Thermodynamic Properties of Solid Aluminum-Iron Alloys, Z. Metall., 1997, 88, p 230-235
F. Körber, W. Oelsen, and H. Lichtenberg, Auf der Thermochemie von Legierungen. II. Direkte Bestimmung der Bildungswärme von ternären Legierungen des Systems Fe-Ni-Al, Fe-Co-Al, Cu-Ni-Al, Fe-Al-Si, sowie bestimmte Legierungen der Cu-Mn-Al-System (On the thermochemistry of alloys. II. Direct determination of the heat of formation of ternary alloys of the system Fe-Ni-Al, Fe-Co-Al, Cu-Ni-Al, Fe-Al-Si, as well as Certain Alloys of the Cu-Mn-Al System). Mitt. KWI für Eisenforsch., 1937, 19, p 131-159 [in German]
A. Sinha and L. Balasundaram, Curie temperature of Iron-Aluminum and Iron-Silicon Alloys, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 1967, 20, p 21-24
W. Köster and T. Gödecke, Physikalische Messungen an Eisen-Aluminum-Legierungen mit 10 bis 50 at.% Al (Physical Measurements of Fe-Al Alloys with 10 to 50 at.% Al), Z. Metall., 1980, 71, p 765-769, in German
S. Beer, The Solution of Aluminum Phosphide in Aluminum, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1969, 116, p 263-265
A. McAllster, The Al-P (Aluminum-Phosphorus) System, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr., 1985, 6, p 222-224
H. Lescuyer, M. Allibert, and G. Laslaz, Solubility and Precipitation of AlP in Al-Si Melts Studied with a Temperature Controlled Filtration Technique, J. Alloys Compd., 1998, 279, p 237-244
E. Turkdogan, Physical Chemistry of High Temperature Technology, Academic Press, New York, 1980
I. Barin, F. Sauert, E. Schultze-Rhonhof, and W. Sheng, Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, VCH Verlagesellchaft mbH, Weinheim, Germany, 1989
C. Wang and M. Zaheervuddin, Preparation and Properties of Aluminum Phosphide, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 1963, 25, p 326-327
W. Kischio, Bildungsentalpie von Aluminumphosphid (Enthalpy of Formation of the Aluminium Phosphide), J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 1965, 27, p 750-751, in German
S. Martosudirdjo and J. Pratt, Calorimetric Studies on the Heats of Formation of IIIB-VB Adamantine Phases, Thermochim. Acta, 1974, 10, p 23-31
S. Peviak and A. Sandulova, Tepмoдинaмичecкиe xapaктepиcтики фocфидa aлюминия (Thermodynamic Characteristics of Aluminum Phosphide), Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Neorg. Mater., 1974, 10, p 146-147, in Russian
R. Vogel and H. Klose, Das Zustandsschaubild Eisen-Eisenphosphid-Aluminumphosphid-Aluminum (The Phase Diagram of Iron-Iron Phosphide–Aluminum Phosphide-Aluminum System), Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1952, 23, p 287-291, in German
H. Kaneko, T. Nishizawa, K. Tamaki, and A. Tanifuji, Solubility of Phosphorus in α and γ Iron, Nippon Kinzoku Gakkai Shi, 1965, 29, p 166-171, in Japanese
K. Yamada and E. Kato, Mass Spectrometric Determination of Activities of Phosphorus in Liquid Fe-P-Si, Al, Ti, V, Cr Co, Ni, Nb And Mo Alloys, Tetsu to Hagane, 1979, 65, p 273-280
K. Yamada and E. Kato, Effect of Dilute Concentrations of Si, Al, Ti, V, Cr Co, Ni, Nb and Mo on the Activity Coefficient of P in Liquid Iron, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1983, 23, p 51-55
A. Dinsdale, SGTE Data for Pure Elements, CALPHAD, 1991, 15, p 317-425
J.-O. Andersson, T. Helander, L. Höglund, P. Shi, and B. Sundman, Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, Computational Tools for Materials Science, CALPHAD, 2002, 26, p 273-312
I. Edgar, Solubility of Iron in Solid Aluminum, Trans. AIME, 1948, 180, p 225-229
C. Crussard and F. Aubertin, Etude thermo´electrique et thermodynamique d’alliage `a base d’aluminum contenant Mg, Si, Fe ou Ti (Thermoelectric and Thermodynamic Investigation of Aluminium Based Alloys Containing Mg, Si, Fe or Ti), Rev. Met., 1949, 46, p 661-675, in French
A. Oscarsson, W. Hutchinson, H. Ekström, D. Dickson, C. Simensen, and G. Raynaud, A Comparison of Different Procedures for Determination of Iron in Solid Solution in Aluminum, Z. Metall., 1988, 79, p 600-604
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (TEKES) is gratefully acknowledged by Dr J. Miettinen and Prof. S. Louhenkilpi. The research was carried out as part of the Finnish Metals and Engineering Competence Cluster (FIMECC)’s SIMP program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miettinen, J., Louhenkilpi, S. & Vassilev, G. Thermodynamic Description of Ternary Fe-X-P Systems. Part 9: Fe-Al-P. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 36, 317–326 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-015-0383-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-015-0383-5