Abstract
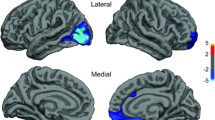
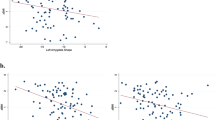
We aimed to investigate the relationship between BMI (body mass index) and the volumes of the structures of the reward system (hippocampus, amygdala, accumbens, caudatum, putamen, and orbitofrontal cortex). The right and left structures were examined separately. Their volumes were assessed using a 3-T MRI scanner and Freesurfer software. Ninety-two healthy subjects were involved (mean BMI: 22.3 ± 3.4 kg/m2, mean age: 23.2 ± 2.7). We found that the volume of the right amygdala positively correlated with the BMI in men but not in women. Moreover, we could demonstrate this association only in the overweight male sub-population. We suggest that an association between body weight and the morphological variability of the reward system can be demonstrated by MRI. This may be further evidence for a different body-weight regulation in the two sexes. The potential relationship between the volume of the right amygdala and the BMI in heavier individuals requires further studies with larger samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer, T., Barsi, P., Bone, B., Angyalosi, A., Aradi, M., Szalay, C., et al. (2008). History of simple febrile seirures is associated with hippocampal abnormlaities in adults. Epilepsia, 49, 1562–1569.
Baker, K. B., & Kim, J. J. (2004). Amygdalar lateralization in fear conditioning: evidence for greater involvement of the right amygdala. Behavioral Neuroscience, 118, 15–23.
Bruce-Keller, A. J., Keller, J. N., & Morrison, C. D. (2009). Obesity and vulnerability of the CNS. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1792, 395–400.
CDC: Centers for disease control and prevention. Percentile Data Files with LMS Values. http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/percentile_data_files.htm (Last accessed: 12-04-2010)
Chen, H., Zhang, S. M., Schwarzschild, M. A., Hernán, M. A., Willett, W. C., & Ascherio, A. (2004). Obesity and the risk of Parkinson's disease. American Journal of Epidemiology, 159, 547–555.
Clegg, D. J., Riedy, C. A., Smith, K. A., Benoit, S. C., & Woods, S. C. (2003). Differential sensitivity to central leptin and insulin in male and female rats. Diabetes, 52, 682–687.
Draganski, B., Gaser, C., Busch, V., Schuierer, G., Bogdahn, U., & May, A. (2004). Neuroplasticity: changes in grey matter induced by training. Nature, 427(6972), 311–312.
Druce, M., & Bloom, S. R. (2003). Central regulators of food intake. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 6(4), 361–367.
Durston, S., Hulshoff Pol, H. E., Casey, B. J., Giedd, J. N., Buitelaar, J. K., & van Engeland, H. (2001). Anatomical MRI of the developing human brain: what have we learned? Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40(9), 1012–1020.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33, 341–355.
Gazdzinski, S., Kornak, J., Winer, M. W., & Meyerhoff, D. J. (2008). Body mass index and magnetic resonance markers of brain integrity in adults. Ann Neurol, 63(5), 652–657.
Giordano, G. D., Renzetti, P., Parodi, R. C., et al. (2001). Volume measurement with magnetic resonance imaging of hippocampus-amygdala formation in patients with anorexia nervosa. J Endocrinol Invest, 24(7), 510–514.
Grabenhorst, F., Rolls, E. T., Parris, B. A., & d’Souza, A. A. (2010). How the brain represents the reward value of fat in the mouth. Cerebral Cortex, 20(5), 1082–1091.
Gustafson, D., Rothenberg, E., Blennow, K., Steen, B., & Skoog, I. (2003). An 18-year follow-up of overweight and risk of Alzheimer disease. Archives of Internal Medicine, 163, 2524–2528.
Gustafson, D., Lissner, L., Bengtsson, C., Björkelund, C., & Skoog, I. (2004). A 24-year follow-up of body mass index and cerebral atrophy. Neurology, 63, 1876–1881.
Haapaniemi, H., Hillbom, M., & Juvela, S. (1997). Lifestyle-associated risk factors for acute brain infarction among persons of working age. Stroke, 28, 26–30.
Hahn, Z., Karádi, Z., Sándor, P., & Lénárd, L. (1988). Sex-related differences in food and water intake and body weight changes with prolonged administration of adrenaline in the rat. Acta Physiologica Hungarica, 72(1), 103–109.
Hajnal, A., Sándor, P., Jandó, G., Vida, I., Czurkó, A., Karádi, Z., et al. (1992). Feeding disturbances and EEG activity changes after amygdaloid kainate lesions in the rat. Brain Research Bulletin, 29(6), 909–916.
Haltia, L. T., Viljanen, A., Parkkola, R., Kemppainen, N., Rinne, J. G., Nuutila, P., et al. (2009). Brain white matter expansion in human obesity and the recovering effect of dieting. J Clin Endocrin Metabol, 92, 3278–3284.
Heijer, T., Geerlings, M. I., Hoebeek, F. E., Hofman, A., Koudstaal, P. J., & Breteler, M. M. B. (2006). Use of hippocampal and amygdalar volumens on magnetic resonance imaging to predict dementia in cognitively intact elderly people. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63, 57–62.
Hoffmans, M. D. A. F., Kromhout, D., & De Lezenne Coulander, C. (1985). The impact of body mass index of 78 612 18-year old Dutch men on 32-year mortality from all causes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 41, 749–756.
Holsen, L. M., & Zarcone, J. R. (2005). Neural mechanisms underlying food motivation in children and adolescents. Neuroimage, 27, 669–676.
Holsen, L. M., Zarcone, J. R., Brooks, W. M., et al. (2006). Neural mechanisms underlying hyperphagia in Prader-Willi syndrome. Obesity, 14, 1028–1037.
Janszky, J., Szűcs, A., Halász, P., Borbély, C., Holló, A., Barsi, P., et al. (2002). Orgasmic aura originates from the right hemisphere. Neurology, 58, 302–304.
Karádi, Z., Scott, T. R., Oomura, Y., Nishino, H., Aou, A., & Lénárd, L. (1998). Complex functional attributes of amygdaloid gustatory neurons in the rhesus monkey. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 855, 488–493.
Karas, G. B., Burton, E. J., Rombouts, S. A., et al. (2003). A comprehensive study of gray matter loss in patients with Alzheimer’s disease using optimized voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage, 18, 895–907.
King, B. M., Rollins, B. L., Stines, S. G., Cassis, S. A., McGuire, H. B., & Lagarde, M. L. (1999). Sex differences in body weight gains following amygdaloid lesions in rats. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 277, R975–R980.
Lapidus, L., Bengtsson, C., Larsson, B., Pennert, K., Rybo, E., & Sjostrom, L. (1984). Distribution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 12-year follow up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden. British Medical Journal, 289, 1257–1261.
Larsson, B., Svardsudd, K., Welin, L., Wilhelmsen, L., Bjbmtorp, P., & Tlbblin, G. (1984). Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: a 13-year follow-up of participants in the study of men born in 1913. British Medical Journal, 288, 1401–1404.
Lénárd, L., & Hahn, Z. (1982). Amygdalar noradrenergic and dopaminergic mechanisms in the regulation of hunger and thirst-motivated behavior. Brain Research, 233, 115–132.
Lénárd, L., Hahn, Z., & Karádi, Z. (1982). Body weight changes after neurochemical manipulations of lateral amygdala: noradrenergic and dopaminergic mechanisms. Brain Research, 249, 95–101.
Lukáts, B., Egyed, R., Lénárd, L., & Karádi, Z. (2005). Homeostatic alterations induced by interleukin-1beta microinjection into the orbitofrontal cortex in the rat. Appetite, 45, 137–147.
Maguire, E. A., Gadian, D. G., Johnsrude, I. S., Good, C. D., Ashburner, J., Frackowiak, R. S., et al. (2000). Navigation-related structural change in the hippocampi of taxi drivers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 4398–4403.
Manson, J. E., Golditz, G. A., Stampfer, M. J., et al. (1990). A prospective study of obesity and risk of coronary heart disease in women. New Engl J Med, 322, 882–889.
Markowitsch, H. J. (1998). Differential contribution of right and left amygdala to affective information processing. Behavioural Neurology, 11, 233–244.
Mietus-Snyder, M. L., & Lustig, R. H. (2008). Childhood obesity: adrift in the “limbic triagnle”. Annual Review of Medicine, 59, 147–162.
Miyake, Y., Okamoto, Y., Onoda, K., Shirao, N., Okamoto, Y., Otagaki, Y., et al. (2010). Neural processing of negative word stimuli concerning body image in patients with eating disorders: an fMRI study. Neuroimage, 50, 1333–1339.
Morey, R. A., Petty, C. M., Xu, Y., et al. (2009). A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. Neuroimage, 45, 855–866.
Nielsen, S. J., Siega-Riz, A. M., & Popkin, B. M. (2002). Trends in energy intake in U.S. between 1977 and 1996: similar shifts seen across age groups. Obesity Research, 10, 370–378.
Pannacciulli, N., Del Parigi, A., Chen, K., & Le, D. S. (2006). Brain abnormalities in human obesity: a voxel-based morphometric study. Neuroimage, 31, 1419–1425.
Pardoe, H. R., Pell, G. S., Abbott, D. F., & Jackson, G. D. (2009). Hippocampal volume assessment in temporal lobe epilepsy: how good is automated segmentation? Epilepsia, 50, 2586–2592.
Passamonti, L., Rowe, J. B., Schwarzbauer, C., Ewbank, M. P., Hagen, E., & Calder, A. (2009). Personality predicts the brain´s response to viewing appetizing foods: the neural basis of a risk factor for overeating. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 43–51.
Pereno, G. L., & Beltramino, C. A. (2009). Differential role of gonadal hormones on kainic acid-induced neurodegeneration in medial amygdaloid nucleus of female and male rats. Neuroscience, 163, 952–963.
Raz, N., Rodrigue, K. M., & Acker, J. D. (2003). Hypertension and the brain: vulnerability of the prefrontal regions and executive functions. Behavioral Neuroscience, 117, 1169–1180.
Stice, E., Spoor, S., Bohon, C., & Small, D. M. (2008). Relation between obesity and bluntedstriatal response to food is moderated by TaqIA A1 allele. Science, 322, 449–452.
Stoeckel, L. E., Weller, R. E., Cook, E. W., 3rd, Twieg, D. B., Knowlton, R. C., & Cox, J. E. (2008). Widespread reward-system activation in obese women in response to pictures of high-calorie foods. Neuroimage, 41(2), 636–647.
Stoeckel, L. E., Kim, J., Weller, R. E., Cox, J. E., Cook, E. W., 3rd, & Horwitz, B. (2009). Effective connectivity of a reward network in obese women. Brain Research Bulletin, 79(6), 388–395.
Sundquist, J., & Johansson, S. E. (1998). The influence of socioeconomic status, ethnicity and lifestyle on body mass index in a longitudinal study. International Journal of Epidemiology, 27, 57–63.
Taki, Y., Goto, R., Evans, A., et al. (2004). Voxel-based morphometry of human brain with age and cerebrovascular risk factors. Neurobiology of Aging, 25, 455–463.
Taki, Y., Kinomura, S., Kazunori, S., Inoue, K., Goto, R., Okada, K., et al. (2008). Relationship between body mass index and gray matter volume in 1,428 healthy individuals. Obesity, 16, 119–124.
Tomasi, D., Wang, G. J., Wang, R., et al. (2009). Association of body mass and brain activation during gastric distention: implications for obesity. Brain Activation, 4, 1–11.
van der Laan, L. N., de Ridder, D. T., Viergever, M. A., Smeets, P. A. (2010). The first taste is always with the eyes: a meta-analysis on the neural correlates of processing visual food cues. Neuroimage, 2010 Nov 25. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 21111829.
Vocks, S., Herpertz, S., Rosenberger, C., Senf, W., Gizewski, E. R. (2010). Effects of gustatory stimulation on brain activity during hunger and satiety in females with restricting-type anorexia nervosa: an fMRI study. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 2010 Aug 13. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 20709330.
Walther, K., Birdsill, A. C., Glisky, E. L., & Ryan, L. (2010). Structural brain differences and cognitive functioning related to body mass index in older females. Human Brain Mapping, 31(7), 1052–1064.
Wang, G. J., Volkow, N. D., Telang, F., et al. (2009). Evidence of gender differences in the ability to inhibit brain activation alicited by food stimulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 1249–1254.
Ward, M. A., Carlsson, C. M., Trivedi, M. A., Sager, M. A., & Johnson, S. C. (2005). The effect of body mass index on global brain volume in middle-aged adults: a cross sectional study. BMC Neurology, 5, 23.
Winter, Y., Rohrmann, S., Linseisen, J., et al. (2008). Contribution of obesity and abdominal fat mass to risk of stroke and transient ischemic attacks. Stroke, 39, 3145–3151.
Witte, A. V., Savli, M., Holik, A., Kasper, S., & Lanzenberger, R. (2010). Regional sex differences in grey matter volume are associated with sex hormones in the young adult brain. Neuroimage, 49, 1205–1212.
Woods, S. C., Gotoh, K., & Clegg, D. J. (2003). Gender differences in the control of energy homeostasis. Expl Biol Med, 228, 1175–1180.
Yang, X., Yan, J., Lu, B., Hao, X., Lei, W., Yang, D., et al. (2009). Fos expression and hormone changes following electrical stimulation of the posterodorsal amygdala and the effects on food intake in conscious female rats. Brain Research, 1273, 83–91.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Bolyai Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Science (JJ, NK and AS: helped in the preparation, design and conduct of this study); and grants from the Hungarian Research Fund (OTKA-NKTH F68720: helped in conduction of this study); the Norwegian Financial Mechanism (HU00114: helped in the conduction and analysis process of this study), Hungarian Research Council (ETT 272/2009: helped in the preparation, design and conduction of this study).
Declaration of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orsi, G., Perlaki, G., Kovacs, N. et al. Body weight and the reward system: the volume of the right amygdala may be associated with body mass index in young overweight men. Brain Imaging and Behavior 5, 149–157 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-011-9119-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-011-9119-2