Abstract
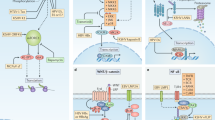
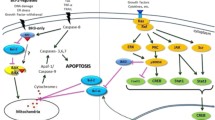
Cancer is not rare anywhere in the world now, and the global burden of cancer continues to increase largely every year. Previous research on infections and cancers reported that, about 17.8 % of the cancers worldwide, which are over 1.9 million cases of cancer, are related to viral infections. At least six oncoviruses, cancer-causing viruses, have been known so far, which include hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, Epstein–Barr virus (EBV or HHV-4), human papillomavirus, human T lymphotropic virus type 1, Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV or HHV-8), but the pathogenic mechanism is far from being completely understood. In this study, assuming that finding human proteins significantly similar to viral oncoproteins leads to a categorization of the cancer-related pathways that are currently not clearly known, we analyzed different types of virus-caused cancers based on their similarity in order to clarify the unknown cancer mechanisms. As a result, we obtained several potential tumor pathways that may be significant and essential in oncogenic cancer process, which will be helpful for further study on cancer mechanisms and the development of new drug targets.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcami A (2003) Viral mimicry of cytokines, chemokines and their receptors. Nat Rev Immunol 3(1):36–50
Arvanitakis L, Yaseen N, Sharma S (1995) Latent membrane protein-1 induces cyclin D2 expression, pRb hyperphosphorylation, and loss of TGF-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition in EBV-positive B cells. J Immunol 155(3):1047–1056
Bader GD, Donaldson I, Wolting C et al (2001) BIND—the biomolecular interaction network database. Nucleic Acids Res 29(1):242–245
Bhairavabhotla RK, Verm V, Tongaonkar H et al (2007) Role of IL-10 in immune suppression in cervical cancer. Indian J Biochem Biophys 44(5):350–356
Boccardo E, Villa LL (2007) Viral origins of human cancer. Curr Med Chem 14(24):2526–2539
Boudny V, Kovarik J (2002) JAK/STAT signaling pathways and cancer. Janus kinases/signal transducers and activators of transcription. Neoplasma 49(6):349–355
Brown KD, Hostager BS, Bishop GA (2001) Differential signaling and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) degradation mediated by CD40 and the Epstein–Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). J Exp Med 193(8):943–954
Burýsek L, Yeow WS, Lubyová B, Kellum M, Schafer SL, Huang YQ, Pitha PM (1999) Functional analysis of human herpesvirus 8-encoded viral interferon regulatory factor 1 and its association with cellular interferon regulatory factors and p300. J Virol 73(9):7334–7342
Bustamante CI, Wade JC (1991) Herpes simplex virus infection in the immunocompromised cancer patient. J Clin Oncol 9(10):1903–1915
Choudhury AD, Choudhury MD, Chetia P, Chowdhury A, Talukdar AD (2014) An in silico appraisal of azoic and disulphide derivatives for anticancer activity against HPV E6 oncoprotein to medicate cervical cancer. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 17(1):38–46
Durbin R, Eddy S, Krogh A, Mitchison G (1998) Biological sequence analysis: probabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acids. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F et al (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127(12):2893–2917
Finn RD, Mistry J, Tate J et al (2010) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 38(1):D211–D222
George RA, Liu JY, Feng LL et al (2006) Analysis of protein sequence and interaction data for candidate disease gene prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 34(19):e130
Heger A, Holm L (2003) Exhaustive enumeration of protein domain families. J Mol Biol 328(3):749–767
Hembruff SL, Cheng N (2009) Chemokine signaling in cancer: Implications on the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic targeting. Cancer Ther 7(A):254–267
Huang Y, Zhang J, Cui ZM et al (2013) Expression of the CXCL12/CXCR4 and CXCL16/CXCR6 axes in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer. Chin J Cancer 32(5):289–296
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Furumichi M et al (2010) KEGG for representation and analysis of molecular networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D355–D360
Kilger E, Kieser A, Baumann M, Hammerschmidt W (1998) Epstein–Barr virus-mediated B-cell proliferation is dependent upon latent membrane protein 1, which simulates an activated CD40 receptor. EMBO J 17(6):1700–1709
Luker KE, Pica CM, Schreiber RD, Piwnica-Worms D (2001) Overexpression of IRF9 confers resistance to antimicrotubule agents in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(17):6540–6547
Matsuda NM, Miller SM, Evora PR (2009) The chronic gastrointestinal manifestations of Chagas disease. Clinics 64(12):1219–1224
McCabe RE (1990) Current diagnosis and management of toxoplasmosis in cancer patients. Oncology 4(10):81–90
McGivern DR, Lemon SM (2011) Virus-specific mechanisms of carcinogenesis in hepatitis C virus associated liver cancer. Oncogene 30(17):1969–1983
McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Munger K (2008) Viruses associated with human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782(3):127–150
Moore PS, Chang Y (2010) Why do viruses cause cancer? Highlights of the first century of human tumour virology. Nat Rev Cancer 10(12):878–889
Moore PS, Boshoff C, Weiss RA, Chang Y (1996) Molecular mimicry of human cytokine and cytokine response pathway genes by KSHV. Science 274(5293):1739–1744
Mosialos G, Birkenbach M, Yalamanchili R et al (1995) The Epstein–Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell 80(3):389–399
Mulder NJ, Apweiler R, Attwood TK et al (2005) InterPro, progress and status in 2005. Nucleic Acids Res 33(Database issue):D201–D205
Parkin DM (2006) The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer 118(12):3030–3044
Pruitt KD, Brown GR, Hiatt SM et al (2014) RefSeq: an update on mammalian reference sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 42(1):D756–D763
Russo JJ, Bohenzky RA, Chien MC et al (1996) Nucleotide sequence of the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (HHV8). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(25):14862–14867
Seo T, Park J, Lee D, Hwang SG, Choe J (2001) Viral interferon regulatory factor 1 of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus binds to p53 and represses p53-dependent transcription and apoptosis. J Virol 75(13):6193–6198
Turner FS, Clutterbuck DR, Semple CA (2003) POCUS: mining genomic sequence annotation to predict disease genes. Genome Biol 4(11):R75
Vande Pol SB, Brown MC, Turner CE (1998) Association of bovine papillomavirus Type 1 E6 oncoprotein with the focal adhesion protein paxillin through a conserved protein interaction motif. Oncogene 16(1):43–52
Vento S, Lanzafame M (2011) Tuberculosis and cancer: a complex and dangerous liaison. Lancet Oncol 12(6):520–522
Veyssier-Belot C, Couderc LJ, Desgranges C et al (1990) Kaposi’s sarcoma and HTLV-I infection. Lancet 336(8714):575
Weinberg RA (2006) The biology of cancer. Garland Science, Routledge
Xie Y, Ruan B, Chen Y et al (2011) Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol 83(5):879–883
Xu D, Coleman T, Zhang J et al (2007) Epstein–Barr virus inhibits Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic replication in primary effusion lymphomas. J Virol 81(11):6068–6078
Acknowledgments
Computational resources were provided by the Bioinformatics Center and Supercomputer system, Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University. Funding from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and the Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Kotera, M. & Goto, S. Virus proteins similar to human proteins as possible disturbance on human pathways. Syst Synth Biol 8, 283–295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-014-9141-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-014-9141-y