Abstract
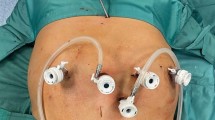
The da Vinci Xi Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been released in 2014 to facilitate minimally invasive surgery. Novel features are targeted towards facilitating complex multi-quadrant procedures, but data is scarce so far. Perioperative data of patients who underwent robotic general surgery with the da Vinci Xi system within the first 6 month after installation were collected and analyzed. The gastric bypass procedures performed with the da Vinci Xi Surgical System were compared to an equal amount of the last procedures with the da Vinci Si Surgical System. Thirty-one foregut (28 Roux-en-Y gastric bypasses), 6 colorectal procedures and 1 revisional biliary procedure were performed. The mean operating room (OR) time was 221.8 (±69.0) minutes for gastric bypasses and 306.5 (±48.8) for colorectal procedures with mean docking time of 9.4 (±3.8) minutes. The gastric bypass procedure was transitioned from a hybrid to a fully robotic approach. In comparison to the last 28 gastric bypass procedures performed with the da Vinci Si Surgical System, the OR time was comparable (226.9 versus 230.6 min, p = 0.8094), but the docking time significantly longer with the da Vinci Xi Surgical System (8.5 versus 6.1 min, p = 0.0415). All colorectal procedures were performed with a single robotic docking. No intraoperative and two postoperative complications occurred. The da Vinci Xi might facilitate single-setups of totally robotic gastric bypass and colorectal surgeries. However, further comparable research is needed to clearly determine the significance of this latest version of the da Vinci Surgical System.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hagen ME, Inan I, Pugin F, Morel P (2007) The da Vinci surgical system in digestive surgery. Rev Med Suisse 3:1622–1626
Baek SK, Carmichael JC, Pigazzi A (2013) Robotic surgery: colon and rectum. Cancer J 19:140–146
Satava RM (2003) Robotic surgery: from past to future—a personal journey. Surg Clin N Am 83:1491–1500
http://www.intuitivesurgical.com. Accessed 30 July 2016
Buchs NC, Bucher P, Pugin F, Hagen ME, Morel P (2010) Robot-assisted oncologic resection for large gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a preliminary case series. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 20:411–415
Hagen ME, Pugin F, Chassot G et al (2012) Reducing cost of surgery by avoiding complications: the model of robotic Roux-en-Y gastric Bypass. Obes Surg 22(1):52–61
Morel P, Buchs NC, Iranmanesh P et al (2014) Robotic single-site cholecystectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21(1):18–25. doi:10.1002/jhbp.36
Buchs NC, Hagen ME, Pugin F et al (2012) Intra-operative fluorescent cholangiography using indocyanin green during robotic single site cholecystectomy. Int J Med Robot 8:436–440
Buchs NC, Pugin F, Volonte F, Hagen ME, Morel P, Ris F (2013) Robotic transanal endoscopic microsurgery: technical details for the lateral approach. Dis Colon Rectum 56:1194–1198
Trinh QD, Sammon J, Sun M et al (2012) Perioperative outcomes of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy compared with open radical prostatectomy: results from the nationwide inpatient sample. Eur Urol 61:679–685
Gandaglia G, Sammon JD, Chang SL et al (2014) Comparative effectiveness of robot-assisted and open radical prostatectomy in the postdissemination era. J Clin Oncol 32:1419–1426
Ficarra V, Novara G, Ahlering TE et al (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting potency rates after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 62:418–430
Ficarra V, Sooriakumaran P, Novara G et al (2012) Systematic review of methods for reporting combined outcomes after radical prostatectomy and proposal of a novel system: the survival, continence, and potency (SCP) classification. Eur Urol 61:541–548
Novara G, Ficarra V, Mocellin S et al (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting oncologic outcome after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 62:382–404
Excellence NNIfHaC (2014). Prostate cancer: diagnosis and treatment. http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/14348/66226/66226.pdf. 2014
Jung M, Morel P, Buehler L, Buchs NC, Hagen ME (2015) Robotic general surgery: current practice, evidence, and perspective. Langenbecks Arch Surg 400:283–292
Iranmanesh P, Morel P, Wagner OJ, Inan I, Pugin F, Hagen ME (2010) Set-up and docking of the da Vinci surgical system: prospective analysis of initial experience. Int J Med Robot 6:57–60
Iranmanesh P, Morel P, Buchs NC et al (2013) Docking of the da Vinci Si Surgical System® with single-site technology. Int J Med Robot 9:12–16
Acknowledgements
We thank Francoise Bernardi for the data collection and Jona Misasa Mendoza for the assistance with the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Hagen received personal fees by Intuitive Surgical Inc. outside this project. Dr. Jung, Dr. Ris, DR. Buchs, Dr. Fakhro, Prof. Buehler and Prof. Morel have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
M. E. Hagen and M. K. Jung contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagen, M.E., Jung, M.K., Ris, F. et al. Early clinical experience with the da Vinci Xi Surgical System in general surgery. J Robotic Surg 11, 347–353 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-016-0662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-016-0662-0