Abstract
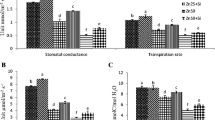
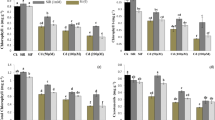
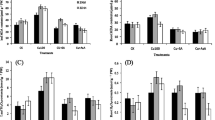
Accumulation of excess copper (Cu) in agricultural soils can decrease growth and quality of crops grown on these soils and a little information is available on the role of silicon (Si) in reducing Cu toxicity in plants. A hydroponic study was conducted to investigate the effects of Si (1.0 mM) on growth and physiology of cotton seedlings grown on different Cu (0, 25, and 50 µM) concentrations. Elevated levels of Cu decreased growth, biomass, photosynthetic pigments, and gas exchange characteristics, and increased the electrolyte leakage (EL), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) contents in leaf, stem, and roots of cotton seedlings. Cu stress alone decreased the activities of key antioxidant enzymes in cotton seedlings. Exogenous application of Si alleviated the toxic effects of Cu on cotton seedlings by improving growth, photosynthetic pigments, and gas exchange characteristics under Cu stress. The Si application decreased Cu concentrations in leaves, stem, and roots as compared with the control plants. Furthermore, Si decreased oxidative stress as evidenced by decreased EL, H2O2, and TBARS contents, and increased the antioxidant enzyme activities in cotton seedlings. This study provides evidences of Si-mediated reduction of Cu toxicity in cotton seedlings at physiological and biochemical levels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Rehman MZ, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015a) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MK, Irshad MK (2015b) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ali B, Tao Q, Zhou Y, Gill RA, Ali S, Rafiq MT, Xu L, Zhou W (2013a) 5-Aminolevolinic acid mitigates the cadmium-induced changes in Brassica napus as revealed by the biochemical and ultra-structural evaluation of roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:271–280
Ali B, Wang B, Ali S, Ghani MA, Hayat MT, Yang C, Xu L, Zhou W (2013b) 5-Aminolevulinic acid ameliorates the growth, photosynthetic gas exchange capacity, and ultrastructural changes under cadmium stress in Brassica napus L. J Plant Growth Regul 32:604–614
Ali B, Qian P, Jin R, Ali S, Khan M, Aziz R, Tian T, Zhou W (2014) Physiological and ultra-structural changes in Brassica napus seedlings induced by cadmium stress. Biol Plant 58:131–138
Ando Y, Nagata S, Yanagisawa S, Yoneyama T (2013) Copper in xylem and phloem saps from rice (Oryza sativa): the effect of moderate copper concentrations in the growth medium on the accumulation of five essential metals and a speciation analysis of copper-containing compounds. Funct Plant Biol 40:89–100
Angelova V, Ivanova R, Delibaltova V, Ivanov K (2004) Bio-accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in fibre crops (flax, cotton and hemp). Indus Crops Prod 19:197–205
Bokor B, Vaculik M, Slováková L, Masarovič D, Lux A (2014) Silicon does not always mitigate zinc toxicity in maize. Acta Physiol Plant 36:733–743
Bravin MN, Le Merrer B, Denaix L, Schneider A, Hinsinger P (2010) Copper uptake kinetics in hydroponically-grown durum wheat (Triticum turgidum durum L.) as compared with soil’s ability to supply copper. Plant Soil 331:91–104
Chen J, Shafi M, Li S, Wang Y, Wu J, Ye Z, Peng D, Yan W, Liu D (2015) Copper induced oxidative stresses, antioxidant responses and phytoremediation potential of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep13554
Christiansen KS, Borggaard OK, Holm PE, Vijver MG, Hauschild MZ, Peijnenburg WJ (2015) Experimental determinations of soil copper toxicity to lettuce (Lactuca sativa) growth in highly different copper spiked and aged soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5283–5292
Collin B, Doelsch E, Keller C, Panfili F, Meunier JD (2012) Distribution and variability of silicon, copper and zinc in different bamboo species. Plant Soil 351:377–387
Collin B, Doelsch E, Keller C, Cazevieille P, Tella M, Chaurand P, Panfili F, Hazemann JL, Meunier JD (2014) Copper distribution and speciation in bamboo exposed to a high Cu concentration and Si supplementation. First evidence on the presence of reduced copper bound to sulfur compounds in Poaceae. Environ Pollut 187:22–30
Daud MK, Variath MT, Ali S, Jamil M, Khan MT, Shafi M, Shuijin Z (2009) Genetic transformation of bar gene and its inheritance and segregation behavior in the resultant transgenic cotton germplasm (br001). Pak J Bot 41:2167–2178
de Freitas TA, França MGC, de Almeida AAF, de Oliveira SJR, de Jesus RM, Souza VL, Mangabeira PA (2015) Morphology, ultrastructure and mineral uptake is affected by copper toxicity in young plants of Inga subnuda subs. luschnathiana (Benth.) TD Penn. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15479–15494
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorne TA (1981) Leaf senescence correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Dresler S, Hanaka A, Bednarek W, Maksymiec W (2014) Accumulation of low-molecular-weight organic acids in roots and leaf segments of Zea mays plants treated with cadmium and copper. Acta Physiol Plant 36:1565–1575
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Ishaque W, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 96:242–249
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Ishaque W, Farid M, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2016) Cadmium stress in cotton seedlings: physiological, photosynthesis and oxidative damages alleviated by glycinebetaine. South Afr J Bot 104:61–68
Feigl G, Kumar D, Lehotai N, Pető A, Molnár Á, Rácz É, Ördög A, Erdei L, Kolbert ZS, Laskay G (2015) Comparing the effects of excess copper in the leaves of Brassica juncea (L. Czern) and Brassica napus (L.) seedlings: growth inhibition, oxidative stress and photosynthetic damage. Acta Biol Hung 66:205–221
Feng J, Shi Q, Wang X, Wei M, Yang F, Xu H (2010) Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Sci Hort 123:521–530
Gajewska E, SkŁodowska M (2010) Differential effect of equal copper, cadmium and nickel concentration on biochemical reactions in wheat seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:996–1003
Gu HH, Zhan S, Wang SZ, Tang YT, Chaney RL, Fang XH, Cai XD, Qiu RL (2012) Silicon-mediated amelioration of zinc toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant Soil 350:193–204
Habiba U, Shafaqat Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbasi GH, Hayat T, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Kang W, Bao J, Zheng J, Hu H, Du J (2015) Distribution and chemical forms of copper in the root cells of castor seedlings and their tolerance to copper phytotoxicity in hydroponic culture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:7726–7734
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier JD (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM Cu. Planta 241:847–860
Khaliq A, Ali S, Hameed A, Farooq MA, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Mahmood K, Ishaque W, Rizwan M (2016) Silicon alleviates nickel toxicity in cotton seedlings through enhancing growth, photosynthesis and suppressing Ni uptake and oxidative stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:633–647
Khandekar S, Leisner S (2011) Soluble silicon modulates expression of Arabidopsis thaliana genes involved in copper stress. J Plant Physiol 168:699–705
Kopittke PM, Menzies NW (2006) Effect of Cu toxicity on growth of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Plant Soil 279:287–296
Kumar P, Tewari RK, Sharma PN (2008) Modulation of copper toxicity induced oxidative damage by excess supply of iron in maize plants. Plant Cell Rep 27:399–409
Kumar S, Kumar S, Prakash P, Singh M (2014) Antioxidant defense mechanisms in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under copper and arsenic toxicity. Int J Plant Physiol Biochem 6:40–43
Li J, Leisner SM, Frantz J (2008) Alleviation of copper toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana by silicon addition to hydroponic solutions. J Am Soc Hort Sci 133:670–677
Li P, Song A, Li Z, Fan F, Liang Y (2013a) Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating manganese transport and antioxidant reactions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 354:407–419
Li P, Song A, Li Z, Fan F, Liang Y (2013b) Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating manganese transport and antioxidant reactions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 354:407–419
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids—pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 148. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 350–382
Lin CY, Trinh NN, Fu SF, Hsiung YC, Chia LC, Lin CW, Huang HJ (2013) Comparison of early transcriptome responses to copper and cadmium in rice roots. Plant Mol Biol 81:507–522
Liu JJ, Wei Z, Li JH (2014a) Effects of copper on leaf membrane structure and root activity of maize seedling. Bot Stud 55:1–6
Liu L, Sun H, Chen J, Zhang Y, Li D, Li C (2014b) Effects of cadmium (Cd) on seedling growth traits and photosynthesis parameters in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Omics J 7:284–290
Lukatkin A, Egorova I, Michailova I, Malec P, Strzałka K (2014) Effect of copper on pro-and antioxidative reactions in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) in vitro and in vivo. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28:80–86
Madejon P, Ramírez-Benítez JE, Corrales I, Barceló J, Poschenrieder C (2009) Copper-induced oxidative damage and enhanced antioxidant defenses in the root apex of maize cultivars differing in Cu tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 67:415–420
Mateos-Naranjo E, Gallé A, Florez-Sarasa I, Perdomo JA, Galmés J, Ribas-Carbó M, Flexas J (2015) Assessment of the role of silicon in the Cu-tolerance of the C 4 grass Spartina densiflora. J Plant Physiol 178:74–83
Mei L, Daud MK, Ullah N, Ali S, Khan M, Malik Z, Zhu SJ (2015) Pretreatment with salicylic acid and ascorbic acid significantly mitigate oxidative stress induced by copper in cotton genotypes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9922–9931
Metzner H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungenzur Synchronisierbakeiteinzelner Pigmentmangel-Mutation von Chlorella. Planta 65:186–194 (in German)
Michaud AM, Chappellaz C, Hinsinger P (2008) Copper phytotoxicity affects root elongation and iron nutrition in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum durum L.). Plant Soil 310:151–165
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Oliva SR, Mingorance MD, Leidi EO (2011) Effects of silicon on copper toxicity in Erica andevalensis Cabezudo and Rivera: a potential species to remediate contaminated soils. J Environ Monit 13:591–596
Ramzani PMA, Khan WD, Iqbal M, Kausar S, Ali S, Rizwan M, Virk ZA (2016) Effect of different amendments on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth, yield, nutrient uptake and grain quality in Ni-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res doi:10.1007/s11356-016-7038-x
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soil and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Hélène M, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209–210:326–334
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ibrahim M, Farid M, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Rehman MZ, Qayyum MF, Abbas F (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15416–15431
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016a) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016b) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2230–2248
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Rehman MZ, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016c) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6436-4
Sanchez-Pardo B, Fernandez-Pascual M, Zornoza P (2014) Copper microlocalisation and changes in leaf morphology, chloroplast ultrastructure and antioxidative response in white lupin and soybean grown in copper excess. J Plant Res 127:119–129
Shen X, Xiao X, Dong Z, Chen Y (2014) Silicon effects on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of peanut under aluminum stress. Acta Physiol Plant 36:3063–3069
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma G, Sahoo L, Panda S (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39
Vaculik M, Landberg T, Greger M, Luxova M, Stolarikova M, Lux A (2012) Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize. Ann Bot 110:433–443
Vaculik M, Pavlovič A, Lux A (2015) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity by enhanced photosynthetic rate and modified bundle sheath’s cell chloroplasts ultrastructure in maize. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:66–73
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecol. doi:10.5402/2011/402647
Yruela I (2009) Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 36:409–430
Yruela I (2013) Transition metals in plant photosynthesis. Metallomics 5:1090–1109
Zhang XZ (1992) Themeasurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD POD and CAT activities in biological system. In: Zhang XZ (ed) Research Methodology of Crop Physiology, Beijing Agriculture Press, pp 208–211
Zhang J, Kirkham MB (1994) Drought-stress induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidases in wheat leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 35:785–791
Acknowledgments
Financial support from Government College University Faisalabad, Pakistan, and higher education commission (HEC) of Pakistan is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. G. dos Santos.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Rizwan, M., Ullah, N. et al. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of silicon-induced copper stress tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Acta Physiol Plant 38, 262 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2279-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2279-3