Abstract
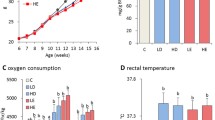
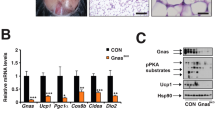
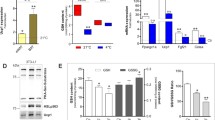
The aim of this study was to evaluate thermogenesis in the interscapular brown adipose tissue (IBAT) of rats submitted to low-protein, high-carbohydrate (LPHC) diet and the involvement of adrenergic stimulation in this process. Male rats (~100 g) were submitted to LPHC (6 %-protein; 74 %-carbohydrate) or control (C; 17 %-protein; 63 %-carbohydrate) isocaloric diets for 15 days. The IBAT temperature was evaluated in the rats before and after the administration of noradrenaline (NA) (20 µg 100 g b w−1 min−1). The expression levels of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) and other proteins involved in the regulation of UCP1 expression were determined by Western blot (Student’s t test, P ≤ 0.05). The LPHC diet promoted a 1.1 °C increase in the basal temperature of IBAT when compared with the basal temperature in the IBAT of the C group. NA administration promoted a 0.3 °C increase in basal temperature in the IBAT of the C rats and a 0.5 °C increase in the IBAT of the LPHC group. The level of UCP1 increased 60 % in the IBAT of LPHC-fed rats, and among the proteins involved in its expression, such as β3-AR and α1-AR, there was a 40 % increase in the levels of p38-MAPK and a 30 % decrease in CREB when compared to the C rats. The higher sympathetic flux to IBAT, which is a consequence of the administration of the LPHC diet to rats, activates thermogenesis and increases the expression of UCP1 in the tissue. Our results suggest that the increase in UCP1 content may occur via p38 MAPK and ATF2.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon B, Nedergaard J (1986) Brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in neonatal and cold-adapted animals. Biochem Soc Trans 14(2):233–236
Nedergaard J, Cannon B (1985) [3H]GDP binding and thermogenin amount in brown adipose tissue mitochondria from cold-exposed rats. Am J Physiol 248(3 Pt 1):C365–C371
Himms-Hagen J, Hogan S, Zaror-Behrens G (1986) Increased brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in obese (ob/ob) mice fed a palatable diet. Am J Physiol 250(3 Pt 1):E274–E281
Rothwell NJ, Stock MJ (1979) A role for brown adipose tissue in diet-induced thermogenesis. Nature 281(5726):31–35
Rothwell NJ, Stock MJ (1997) A role for brown adipose tissue in diet-induced thermogenesis. Obes Res 5:650–656
Sell H, Deshaies Y, Richard D (2004) The brown adipocyte: update on its metabolic role. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(11):2098–2104
Saito M (2014) Human brown adipose tissue: regulation and anti-obesity potential. Endocr J 61(5):409–416
Cypess AM, Lehman S, Williams G, Tal I, Rodman D, Goldfine AB, Kuo FC, Palmer EL, Tseng YH, Doria A, Kolodny GM, Kahn CR (2009) Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans. N Engl J Med 360:1509–1517
van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Schrauwen P (2011) Implications of nonshivering thermogenesis for energy balance regulation in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R285–R296
Nedergaard J, Bengtsson T, Cannon B (2007) Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E444–E452
Seale P, Lazar MA (2009) Brown fat in humans: turning up the heat on obesity. Diabetes 58(7):1482–1484
Cannon B, Nedergaard J (2004) Brown adipose tissue: function and physiological significance. Physiol Rev 84(1):277–359
Lafontan M, Berlan M (1993) Fat cell adrenergic receptors and the control of white and brown fat cell function. J Lipid Res 34(7):1057–1091
Holm C (2003) Molecular mechanisms regulating hormone-sensitive lipase and lipolysis. Biochem Soc Trans 31(Pt 6):1120–1124
Rim JS, Xue B, Gawronska-Kozak B, Kozak LP (2004) Sequestration of thermogenic transcription factors in the cytoplasm during development of brown adipose tissue. J Biol Chem 279(24):25916–25926
Thonberg H, Fredriksson JM, Nedergaard J, Cannon B (2002) A novel pathway for adrenergic stimulation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation: mediation via alpha1-adrenoceptors and protein kinase C activation. Biochem J 364(Pt 1):73–79
Canettieri G, Celi FS, Baccheschi G, Salvatori L, Andreoli M, Centanni M (2000) Isolation of human type 2 deiodinase gene promoter and characterization of a functional cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element. Endocrinology 141(5):1804–1813
Golozoubova V, Gullberg H, Matthias A, Cannon B, Vennstrom B, Nedergaard J (2004) Depressed thermogenesis but competent brown adipose tissue recruitment in mice devoid of all hormone-binding thyroid hormone receptors. Mol Endocrinol 18(2):384–401
Cao W, Daniel KW, Robidoux J, Puigserver P, Medvedev AV, Bai X, Floering LM, Spiegelman BM, Collins S (2004) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is the central regulator of cyclic AMP-dependent transcription of the brown fat uncoupling protein 1 gene. Mol Cell Biol 24(7):3057–3067
Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR (2007) Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell 131(2):242–256
Seale P, Kajimura S, Yang W, Chin S, Rohas LM, Uldry M, Tavernier G, Langin D, Spiegelman BM (2007) Transcriptional control of brown fat determination by PRDM16. Cell Metab 6(1):38–54
Aparecida de Franca S, Dos Santos MP, Garofalo MA, Navegantes LC, Kettelhut Ido C, Lopes CF, Kawashita NH (2009) Low protein diet changes the energetic balance and sympathetic activity in brown adipose tissue of growing rats. Nutrition 25(11–12):1186–1192
Buzelle SL, Santos MP, Baviera AM, Lopes CF, Garofalo MA, Navegantes LC, Kettelhut IC, Chaves VE, Kawashita NH (2010) A low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet increases the adipose lipid content without increasing the glycerol-3-phosphate or fatty acid content in growing rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88(12):1157–1165
Santos MP, Franca SA, Santos JT, Buzelle SL, Bertolini GL, Garófalo MA, Kettelhut IC, Frasson D, Chaves VE, Kawashita NH (2012) A low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet increases fatty acid uptake and reduces norepinephrine-induced lipolysis in rat retroperitoneal white adipose tissue. Lipids 47(3):279–289
Menezes AL, Pereira MP, Buzelle SL, Santos MP, França SA, Baviera AM, Andrade CM, Garófalo MA, do Carmo Kettelhut I, Chaves VE, Kawashita NH (2013) A low protein, high-carbohydrate diet increases de novo fatty acid synthesis from glycerol and glycerokinase content in the liver of growing rats. Nutr Res 33(6):494–502
Feres DD, Dos Santos MP, Buzelle SL, Pereira MP, de Franca SA, Garófalo MA, Andrade CM, Froelich M, de Almeida FJ, Frasson D, Chaves VE, Kawashita NH (2013) In vitro TNF-alpha- and noradrenaline-stimulated lipolysis is impaired in adipocytes from growing rats fed a low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet. Lipids 48(8):779–786
Aparecida de Franca S, Pavani Dos Santos M, Queiroz Nunes, da Costa RV, Froelich M, Buzelle SL, Chaves VE, Giordani MA, Pereira MP, Colodel EM, Marlise Balbinotti Andrade C, Kawashita NH (2014) Low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet increases glucose uptake and fatty acid synthesis in brown adipose tissue of rats. Nutrition 30(4):473–480
Batistela E, Pereira MP, Siqueira JT, Paula-Gomes S, Zanon NM, Oliveira EB, Navegantes LC, Kettelhut IC, Andrade CM, Kawashita NH, Baviera AM (2014) Decreased rate of protein synthesis, caspase-3 activity, and ubiquitin-proteasome proteolysis in soleus muscles from growing rats fed a low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 92(6):445–454
Pereira MP, Buzelle SL, Batistela E, Doneda DL, França SA, Santos MP, Andrade CM, Garófalo MA, do Carmo Kettelhut I, Navegantes LC, Chaves VE, Bertolini GL, Kawashita NH (2014) High glucose uptake in growing rats adapted to a low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet determines low fasting glycemia even with high hepatic gluconeogenesis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 92(6):460–466
Patel MS, Srinivasan M (2011) Metabolic programming in the immediate postnatal life. Ann Nutr Metab 58:18–28
Steyn NP, Mchiza Z, Hill J, Davids YD, Hinrichsen E, Opperman M, Rumbelow J, Jacobs P (2013) Nutritional contribution of street foods to the diet of people in developing countries: a systematic review. Public Health Nutr 17:1–12
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123(11):1939–1951
Patel VM, Heinel LA, Provencio JJ, Vinall PE, Kramer MS, Rosenwasser RH (2002) Validation of image analysis for enzyme histochemical and immunocytochemical staining. Biotech Histochem 77(4):213–221
Siegrist-Kaiser CA, Pauli V, Juge-Aubry CE, Boss O, Pernin A, Chin WW, Cusin I, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Burger AG, Zapf J, Meier CA (1997) Direct effects of leptin on brown and white adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 100(11):2858–2864
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bordicchia M, Liu A, Amri EZ, Ailhaud G, Fulgheri PD, Zhang C, Takahashi N, Sarzani R, Collins S (2012) Cardiac natriuretic peptides act via p38 MAPK to induce the brown fat thermogenic program in mouse and human adipocytes. J Clin Invest 122(3):1022–1036
Chen HY, Liu Q, Salter AM, Lomax MA (2013) Synergism between cAMP and PPARγ Signalling in the Initiation of UCP1 Gene Expression in HIB1B Brown Adipocytes. PPAR Res 2013:476049
Sell H, Berger JP, Samson P, Castriota G, Lalonde J, Deshaies Y, Richard D (2004) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonism increases the capacity for sympathetically mediated thermogenesis in lean and ob/ob mice. Endocrinology 145(8):3925–3934
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Celso Roberto Afonso for his technical assistance. This work was supported by Grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Mato Grosso (FAPEMAT) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and funding was also provided by the European Union 7th Framework Program (FP7-PEOPLE-2013-IRSES Grant No. 612547).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
de França, S.A., dos Santos, M.P., Przygodda, F. et al. A Low-Protein, High-Carbohydrate Diet Stimulates Thermogenesis in the Brown Adipose Tissue of Rats via ATF-2. Lipids 51, 303–310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4119-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4119-z