Abstract
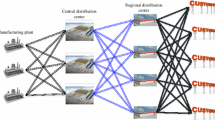
In this paper, a multi-period logistics network redesign problem arising in the context of strategic supply chain planning is studied. Several aspects of practical relevance are captured, namely, multiple echelons with different types of facilities, product flows between facilities in the same echelon, direct shipments to customers, and facility relocation. A two-phase heuristic approach is proposed to obtain high-quality feasible solutions to the problem, which is initially modeled as a large-scale mixed-integer linear program. In the first phase of the heuristic, a linear programming rounding strategy is applied to find initial values for the binary location variables. The second phase of the heuristic uses local search to correct the initial variable choices when a feasible solution is not identified, or to improve the initial feasible solution when its quality does not meet given criteria. The results of a computational study are reported for randomly generated instances comprising a variety of logistics networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Sahinidis NV (2003) An approximate scheme for stochastic integer programming arising in capacity expansion. Oper Res 51:461–471
Ahmed S, King A, Parija G (2003) A multi-stage stochastic integer programming approach for capacity expansion under uncertainty. J Glob Optim 26:3–24
Alonso-Ayuso A, Escudero LF, Garín A, Ortuño MT, Pérez G (2003) An approach for strategic supply chain planning under uncertainty based on stochastic 0–1 programming. J Glob Optim 26:97–124
Ambrosino D, Scutellà MG (2005) Distribution network design: new problems and related models. Eur J Oper Res 165:610–624
Ballou RH (1968) Dynamic warehouse location analysis. J Mark Res 5:271–276
Canel C, Khumawala BM, Law J, Loh A (2001) An algorithm for the capacitated, multi-commodity multi-period facility location problem. Comput Oper Res 28:411–427
Chudak F, Shmoys D (2004) Improved approximation algorithms for the uncapacitated facility location problem. SIAM J Comput 33:1–25
Cordeau JF, Pasin F, Solomon MM (2006) An integrated model for logistics network design. Ann Oper Res 144:59–82
Daskin M, Snyder L, Berger R (2005) Facility location in supply chain design. In: Langevin A, Riopel D (eds) Logistics systems: design and optimization. Springer, Berlin, pp 39–65. Chap 2
Goetschalckx M, Vidal CJ, Dogan K (2002) Modeling and design of global logistics systems: a review of integrated strategic and tactical models and design algorithms. Eur J Oper Res 143:1–18
Gonzalez TF (ed) (2007) Handbook of approximation algorithms and metaheurististics. Chapman & Hall/CRC, London/Boca Raton
Hammami R, Frein Y, Hadj-Alouane AB (2008) Supply chain design in the delocalization context: relevant features and modeling tendencies. Int J Prod Econ 113:641–656
Harrison TP (2004) Principles for the strategic design of supply chains. In: Harrison TP, Lee HL, Neale JJ (eds) The practice of supply chain management: where theory and application converge. Springer, New York, pp 3–12. Chap 1
Hinojosa Y, Puerto J, Fernández FR (2000) A multiperiod two-echelon multi-commodity capacitated plant location problem. Eur J Oper Res 123:271–291
Hinojosa Y, Kalcsics J, Nickel S, Puerto J, Velten S (2008) Dynamic supply chain design with inventory. Comput Oper Res 35:373–391
ILOG Concert Technology 2.0 User’s Manual (2003) ILOG, Inc, Incline Village, Nevada: www.ilog.com/products/optimization/tech/concert.cfm
ILOG CPLEX User’s Manual (2007) ILOG, Inc, Incline Village, Nevada: www.ilog.com/products/cplex
Julka N, Baines T, Tjahjono B, Lendermann P, Vitanov V (2007) A review of multi-factor capacity expansion models for manufacturing plants: searching for a holistic decision aid. Int J Prod Econ 106:607–621
Ko HJ, Evans GW (2007) A genetic algorithm-based heuristic for the dynamic integrated forward/reverse logistics network for 3PLs. Comput Oper Res 34:346–366
Meixell MJ, Gargeya VB (2005) Global supply chain design: a literature review and critique. Transp Res, Part E, Logist Transp Rev 41:531–550
Melachrinoudis E, Min H (2000) The dynamic relocation and phase-out of a hybrid, two-echelon plant/warehousing facility: a multiple objective approach. Eur J Oper Res 123:1–15
Melkote S, Daskin MS (2001) Capacitated facility location/network design problems. Eur J Oper Res 129:481–495
Melo MT, Nickel S, Saldanha da Gama F (2003) Large-scale models for dynamic multi-commodity capacitated facility location. Technical Report 58, Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics (ITWM), Kaiserslautern, Germany. Available at www.itwm.fraunhofer.de/fileadmin/ITWM-Media/Zentral/Pdf/Berichte_ITWM/2003/bericht58.pdf
Melo MT, Nickel S, Saldanha da Gama F (2006) Dynamic multi-commodity capacitated facility location: a mathematical modeling framework for strategic supply chain planning. Comput Oper Res 33:181–208
Melo MT, Nickel S, Saldanha da Gama F (2009a) Facility location and supply chain management—a review. Eur J Oper Res 196:401–412
Melo MT, Nickel S, Saldanha da Gama F (2009b) An LP-rounding heuristic to solve a multi-period facility relocation problem. Technical Report 168, Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics (ITWM), Kaiserslautern, Germany. Available at www.itwm.fraunhofer.de/fileadmin/ITWM-Media/Zentral/Pdf/Berichte_ITWM/2009/bericht_168.pdf
Mitra G, Poojari C, Sen S (2006) Strategic and tactical planning models for supply chains: an application of stochastic mixed integer programming. In: Appa G, Pitsoulis L, Williams HP (eds) Handbook on modelling for discrete optimization. Springer, Berlin, pp 227–264. Chap 8
Santoso T, Ahmed S, Goetschalckx M, Shapiro A (2005) A stochastic programming approach for supply chain network design under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 167:96–115
Schütz P, Tomasgard A, Ahmed S (2009) Supply chain design under uncertainty using sample average approximation and dual decomposition. Eur J Oper Res 199:409–419
Shmoys D (2004) The design and analysis of approximation algorithms: facility location as a case study. In: Hosten S, Lee J, Thomas R (eds) Trends in optimization, proceedings of symposia in applied mathematics, vol 61. American Mathematical Society, Providence, pp 85–97
Simchi-Levi D, Chen X, Bramel J (2005) The logic of logistics: theory, algorithms and applications for logistics and supply chain management. Springer series in operations research and financial engineering. Springer, New York
Srivastava SK (2008) Network design for reverse logistics. Omega 36:535–548
Thanh PN, Bostel N, Péton O (2008a) A dynamic model for facility location in the design of complex supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 113:678–693
Thanh PN, Bostel N, Péton O (2008b) A linear relaxation-based heuristic for logistics network design. In: 7e Conférence Francophone de MOdélisation et SIMulation—MOSIM’08, 31 March–2 April, Paris, France
Troncoso JJ, Garrido RA (2005) Forestry production and logistics planning: an analysis using mixed-integer programming. For Policy Econ 7:625–633
Vazirani V (2001) Approximation algorithms. Springer, New York
Vila D, Martel A, Beauregard R (2006) Designing logistics networks in divergent process industries: a methodology and its application to the lumber industry. Int J Prod Econ 102:358–378
Wilhelm W, Liang D, Rao B, Warrier D, Zhu X, Bulusu S (2005) Design of international assembly systems and their supply chains under NAFTA. Transp Res, Part E, Logist Transp Rev 41:467–493
Wolf S, Merz P (2007) A hybrid method for solving large-scale supply chain problems. In: Cotta C, van Hemert J (eds) Proceedings of the 7th European conference on evolutionary computation in combinatorial optimization. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4446. Springer, Berlin, pp 219–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melo, M.T., Nickel, S. & Saldanha-da-Gama, F. An efficient heuristic approach for a multi-period logistics network redesign problem. TOP 22, 80–108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-011-0235-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11750-011-0235-3