Abstract
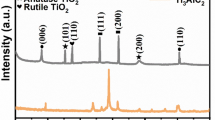
ZnO/TiO2 composites were synthesized by using the solvothermal method and ultrasonic precipitation followed by heat treatment in order to investigate their photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange (MO) in aqueous suspension under UV irradiation. The composition and surface structure of the catalyst were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The degradation efficiencies of MO at various pH values were obtained. The highest degradation efficiencies were obtained before 30 min and after 60 min at pH 11.0 and pH 2.0, respectively. A sample analysis was conducted using liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization ion-trap mass spectrometry. Six intermediates were found during the photocatalytic degradation process of quinonoid MO. The degradation pathway of quinonoid MO was also proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinheiro H M, Touraud E, Thomas O. Aromatic amines from azo dye reduction: status review with emphasis on direct UV spectrophotometric detection in textile industry wastewaters. Dyes Pigment, 2004, 61: 121–139
Gong R M, Li M, Yang C, Sun Y Z, Chen J. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull. J Hazard Mater B, 2005, 121: 247–250
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol, 2001, 77: 247–255
Bianco-Prevot A, Basso A, Baiocchi C, Pazzi M, Marci G, Augugliaro V, Palmisano L, Pramauro E. Analytical control of photocatalytic treatments: degradation of a sulfonated azo dye. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2004, 378: 214–220
Kansal S K, Singh M, Sud D. Studies on photodegradation of two commercial dyes in aqueous phase using different photocatalysts. J Hazard Mater, 2007, 141: 581–590
Liu Y, Chen X, Li J, Burda C. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts. Chemosphere, 2005, 61: 11–18
Kostedt IVWL, Ismail A A, Mazyck DW. Impact of heat treatment and composition of ZnO-TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic oxidation of an azo dye. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2008, 47: 1483–1487
Yu X D, Wu Q Y, Jiang S C, Guo Y H. Nanoscale ZnS/TiO2 composites: preparation, characterization, and visible-light photocatalytic activity. Mater Charact, 2006, 57: 333–341
Rachel A, Subrahmanyam M, Boule P. Comparison of photocatalytic efficiencies of TiO2 in suspended and immobilised form for the photocatalytic degradation of nitrobenzenesulfonic acids. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2002, 37: 301–308
Shephard G S, Stochenström S, Villiers D D, Engelbrecht W J, Wessels G F S. Degradation of microcystin toxins in a falling film photocatalytic reactor with immobilized titanium dioxide catalyst. Water Res, 2002, 36: 140–146
Stokke J M, Mazyck D W, Wu C Y, Sheahan R. Photocatalytic oxidation of methanol using silica-titania composites in a packedbed reactor. Environ Prog, 2006, 25: 312–318
Ansorgova D, Holcapek M, Jandera P. Ion-pairing high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of impurities and reduction products of sulphonated azo dyes. J Sep Sci, 2003, 26: 1011–1027
Gosetti F, Gianotti V, Polati S, Gennaro M C. HPLC-MS degradation study of E110 Sunset Yellow FCF in a commercial beverage. J Chromatogr A, 2005, 1090: 107–115
Liao D L, Badour C A, Liao B Q. Preparation of nanosized TiO2/ZnO composite catalyst and its photocatalytic activity for degradation of methyl orange. J Photochem Photobio A: Chem, 2008, 194: 11–19
Yang S G, Quan X, Li X Y, Liu Y Z, Chen S, Chen G H. Preparation, characterization and photoelectrocatalytic properties of nanocrystalline Fe2O3/TiO2, ZnO/TiO2, and Fe2 O3/ZnO/TiO2 composite film electrodes towards pentachlorophenol degradation. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2004, 6: 659–664
Chen S F, Zhao W, Liu W, Zhang S J. Preparation, characterization and activity evaluation of p-n junction photocatalyst p-ZnO/n-TiO2. Appl Surf Sci, 2008, 255: 2478–2484
Evgenidou E, Fytianos K, Poulios I. Semiconductor-sensitized photodegradation of dichlorvos in water using TiO2 and ZnO as catalysts. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2005, 59: 81–89
Tang W Z, An H R. Photocatalytic degradation kinetics and mechanism of acid blue 40 by TiO2/UV in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 1995, 31: 4171–4183
Serpone N, Maruthamuthu P, Pichat P, Pelizzetti E, Hidaka H. Exploiting the interparticle electron transfer process in the photocatalysed oxidation of phenol, 2-chlorophenol and pentachlorophenol: Chemical evidence for electron and hole transfer between coupled semiconductors. J Photochem Photobio A: Chem, 1995, 85: 247–252
Sukharev V, Kershaw R. Concerning the role of oxygen in photocatalytic decomposition of salicylic acid in water. J Photochem Photobio A: Chem, 1996, 98: 165–169
So C M, Cheng M Y, Yu J C, Wong P K. Degradation of azo dye procion Red MX-5B by photocatalytic oxidation. Chemosphere, 2002, 46: 905–912
Hu C, Tang Y H, Jiang Z, Hao Z P, Tang H X, Wong P K. Characterization and photocatalytic activity of noble-metalsupported surface TiO2/SiO2. Appl Catal A, 2003, 253: 389–396
Kostedt IV W L, Drwiega J, Mazyck D W, Lee S W, Sigmund W, Wu C Y, Chadik P. Magnetically agitated photocatalytic reactor for photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous phase organic pollutions. Environ Sci Technol, 2005, 39: 8052–8056
Hasnat M A, Agrios A G, Gray K A, Rajh T, Thurnauer M C. Explaining the enhanced photocatalytic activity of Degussa P25 mixedphase TiO2 using EPR. J Phys Chem B, 2003, 107: 4545–4549
Zhu C M, Wang L Y, Kong L R, Yang X, Wang L S, Zheng S J, Chen F L, Feng M Z, Zong H. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by supports TiO2+ UV in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 2000, 41: 303–309
Parks G A. The isoelectric points of solids oxides, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex system. Chem Rev, 1965, 65: 177–198
Wang Y B, Hong C S. Effect of hydrogen peroxide, periodate and persulfate on photocatalysis of 2-chlorobiphenyl in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Water Res, 1999, 33: 2031–2036
Rafols C, Barcelo D. Determination of mono- and disulphonated azo dyes by liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A, 1997, 777: 177–192
Augugliaro V, Baiocchi C, Bianco-Prevot A, Lopez E G, Loddo V, Malato S, Marci G, Palmisano L, Pazzi M, Pramauro E. Azo-dyes photocatalytic degradation in aqueous suspension of TiO2 under solar irradiation. Chemosphere, 2002, 49: 1223–1230
Baiocchi C, Brussino M C, Pramauro E, Bianco-Prevot A, Palmisano L, Marci G. Characterization of methyl orange and its photocatalytic degradation products by HPLC/UV-VIS diode array and atmospheric pressure ionization quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom, 2002, 214: 247–256
Bianco-Prevot A, Basso A, Baiocchi C, Pazzi M, Marci G, Augugliaro V, Palmisano L, Pramauro E. Analytical control of photocatalytic treatments: Degradation of a sulfonated azo dye. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2004, 378: 214–220
Dai K, Chen H, Peng T Y, Ke D N, Yi H B. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous suspension of mesoporous titania nanoparticles. Chemosphere, 2007, 69: 1361–1367
Sabljic A, Peijnenburg W. Recommendations on modeling lifetime and degradability of organic compounds in air, soil and water systems. Pure Appl Chem, 2001, 73: 1331–1348
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, M., Guo, C., Zhu, X. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using ZnO/TiO2 composites. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 3, 271–280 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-009-0035-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-009-0035-2