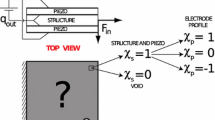
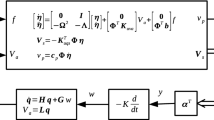
Abstract
Piezoelectric materials are those having the ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical one, and vice versa. Often surface bonded to structures, they are commonly used for sensing, acting and even for reducing noise and structural vibrations as part of active control systems. And, further, they can isolate specific mode shapes of structures when working as spatial filters in the frequency domain (i.e. modal transducers) by shaping properly the piezoelectric layers. This article is intended to revise that concept, initially conceived for beam-type structures only, and explain how it has been extended to plates and shells by means of optimization techniques.








































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreassen E, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2014) Design of manufacturable 3D extremal elastic microstructure. Mech Mater 69(1):1–10
Bathe K, Wilson E (1976) Numerical methods in finite element analysis, 1st edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization: theory, methods, and applications. No. 724 in 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69(9–10):635–654
Bourdin B (2001) Filters in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(9):2143–2158
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2001) Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(26–27):3443–3459
Carbonari RC, Silva ECN, Nishiwaki S (2007) Optimum placement of piezoelectric material in piezoactuator design. Smart Mater Struct 16(1):207–220
Clark RL, Burke SE (1996) Practical limitations in achieving shaped modal sensors with induced strain materials. J Vib Acoust 118(4):668–675
Clarke F (1990) Optimization and nonsmooth analysis, 1st edn. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia
Dailey RL (1987) Eigenvector derivatives with repeated eigenvalues. AIAA J 27(4):486–491
Deaton JD, Grandhi RV (2014) A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(1):1–38
Díaz AR, Kikuchi N (1992) Solutions to shape and topology eigenvalue optimization problems using a homogenization method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 35(7):1487–1502
Donoso A, Bellido JC, Chacón JM (2010) Numerical and analytical method for the design of piezoelectric modal sensors/actuators for shell-type structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 81:1700–1712
Donoso A, Bellido JC (2009) Distributed piezoelectric modal sensors for circular plates. J Sound Vib 319:50–57
Donoso A, Bellido JC (2009) Systematic design of distributed piezoelectric modal sensors/actuators for rectangular plates by optimizing the polarization profile. Struct Multidiscip Optim 38(4):347–356
Donoso A, Bellido JC (2009) Tailoring distributed modal sensors for in-plane modal filtering. Smart Mater Struct 18(3):037,002
Donoso A, Sigmund O (2016) Topology optimization of piezo modal transducers with null-polarity phases. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53
Du J, Olhoff N (2007) Topological design of freely vibrating continuum structures for maximum values of simple and multiple eigenfrequencies and frequency gaps. Struct Multidiscip Optim 34(2):91–110
Friswell MI (1996) The derivatives of repeated eigenvalues and their associated eigenvectors. J Vib Acoust 118(3):390–397
Guest JK, Prevost JH, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238–254
Guest JK (2015) Optimizing the layout of discrete objects in structures and materials: a projection-based topology optimization approach. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 283:330–351
Hansen LV (2005) Topology optimization of free vibrations of fiber laser packages. Struct Multidiscip Optim 29(5):341–348
IEEE: Standard on Piezoelectricity (1988) ANSI/IEEE, pp 176–1987. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.1988.79638
Jaffe J, Roth RS, Marzullo S (1954) Piezoelectric properties of lead Zirconate-lead Titanate solid-solution ceramics. J Appl Phys 25(25):809–810
Jakob SJ, Niels LP (2006) On maximal eigenfrequency separation in two-material structures: the 1D and 2D scalar cases. J Sound Vib 289(45):967–986
Jensen J, Sigmund O (2011) Topology optimization for nano-photonics. Laser Photonics Rev 5(2):308–321
Jian K, Friswell MI (2006) Designing distributed modal sensors for plate structures using finite element analysis. Mech Syst Signal Process 20(8):2290–2304
Jian K, Friswell MI (2007) Distributed modal sensors for rectangular plate structures. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 18(9):939–948
Kang Z, Wang X, Luo Z (2012) Topology optimization for static shape control of piezoelectric plates with penalization on intermediate actuation voltage. J Mech Des 134(5):051,006
Kang Z, Tong L (2008) Topology optimization-based distribution design of actuation voltage in static shape control of plates. Comput Struct 86(19–20):1885–1893
Kawai H (1969) The piezoelectricity of poly (vinylidene fluoride). Jpn J Appl Phys 8:975–976
Kim J, Hwang JS, Kim SJ (2001) Design of modal transducers by optimizing spatial distribution of discrete gain weights. AIAA J 39:1969–1976
Kim TS, Kim YY (2000) MAC-based mode-tracking in structural topology optimization. Comput Struct 74(3):375–383
Kögl M, Silva ECN (2005) Topology optimization of smart structures: design of piezoelectric plate and shell actuators. Smart Mater Struct 14(2):387–399
Kucera M, Manzaneque T, Sánchez-Rojas JL, Bittner A, Schmid U (2013) Q-factor enhancement for self-actuated self-sensing piezoelectric MEMS resonators applying a lock-in driven feedback loop. J Micromech Microeng 23(8):085,009
Lazarov BS, Wang F, Sigmund O (2016) Length scale and manufacturability in density-based topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 86:189–218
Lee I (1996) Numerical method for sensitivity analysis of eigensystems with non-repeated and repeated eigenvalues. J Sound Vib 195(1):17–32
Lee CK, Moon FC (1990) Modal sensors/actuators. J Appl Mech 57(2):434–441
Lema MA (2016) Diseño de microsensores piezoeléctricos mediante formulación robusta (2016). Master thesis, Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha
Lin R, Wang Z, Lim MK (1996) A practical algorithm for the efficient computation of eigenvector sensitivities. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 130(3):355–367
Luo Z, Gao W, Song C (2010) Design of multi-phase piezoelectric actuators. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 21(18):1851–1865
Ma ZD, Cheng HC, Kikuchi N (1994) Structural design for obtaining desired eigenfrequencies by using the topology and shape optimization method. Comput Syst Eng 5(1):77–89
Maeda Y, Nishiwaki S, Izui K, Yoshimura M, Matsui K, Terada K (2006) Structural topology optimization of vibrating structures with specified eigenfrequencies and eigenmode shapes. Int J Numer Methods Eng 67(5):597–628
Moheimani SO, Fleming AJ (2006) Piezoelectric transducers for vibration control and damping, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Nakasone PH, Silva ECN (2010) Dynamic design of piezoelectric laminated sensors and actuators using topology optimization. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 21(16):1627–1652
Nelson RB (1976) Simplified calculation of eigenvector derivatives. AIAA J 14(9):1201–1205
Pedersen NL (2000) Maximization of eigenvalues using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 20(1):2–11
Porn S, Nasser H, Coelho RF, Belouettar S, Deraemaeker A (2016) Level set based structural optimization of distributed piezoelectric modal sensors for plate structures. Int J Sol Struct 80:348–358
Preumont A, François A, De Man P, Piefort V (2003) Spatial filters in structural control. J Sound Vib 265(1):61–79
Pulskamp JS, Bedair SS, Polcawich RG, Smith GL, Martin J, Power B, Bhave SA (2012) Electrode-shaping for the excitation and detection of permitted arbitrary modes in arbitrary geometries in piezoelectric resonators. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 59(5):1043–1060
Ruiz D (2015) Optimal design of piezoelectric microtransducers. Ph.D. thesis, Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha
Ruiz D, Bellido JC, Donoso A, Sánchez-Rojas JL (2013) Design of in-plane piezoelectric sensors for static response by simultaneously optimizing the host structure and the electrode profile. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(5):1023–1026
Ruiz D, Bellido JC, Donoso A (2016) Design of piezoelectric modal filters by simultaneously optimizing the structure layout and the electrode profile. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53:715–730
Ruiz D, Donoso A, Bellido JC, Kucera M, Schmid U, Sánchez-Rojas JL (2016) Design of piezoelectric microtransducers based on the topology optimization method. Microsyst Technol 22(7):1733–1740
Ruiz D, Díaz-Molina A, Sigmund O, Donoso A, Bellido JC, Sánchez-Rojas JL. Optimal design of robust piezoelectric unimorph microgrippers. Sens Act A Phys (submitted for publication)
Ruiz D, Sigmund O. Optimal design of robust piezoelectric microgrippers under large displacements (work in progress)
Sánchez-Rojas JL, Hernando J, Donoso A, Bellido JC, Manzaneque T, Ababneh A, Seidel H, Schmid U (2010) Modal optimization and filtering in piezoelectric microplate resonators. J Micromech and Microeng 20(5):055027
Schevenels M, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2011) Robust topology optimization accounting for spatially varying manufacturing errors. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(4952):3613–3627
Seyranian AP, Lund E, Olhoff N (1994) Multiple eigenvalues in structural optimization problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 8:207–227
Sigmund O (1997) On the design of compliant mechanisms using topology optimization. Mech Struct Mach 25(4):493–524
Sigmund O, Torquato S, Aksay IA (1998) On the design of 1–3 piezo-composites using topology optimization. J Mater Res 13(4):1038–1048
Sigmund O (2007) Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4–5):401–424
Sigmund O (2009) Manufacturing tolerant topology optimization. Acta Mech Sin 25(2):227–239
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches: a comparative review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Silva ECN, Fonseca JSO, Kikuchi N (1997) Optimal design of piezoelectric microstructures. Comput Mech 19(5):397–410
Silva ECN, Fonseca JSO, de Espinosa FMC, Crumm AT, Brady GA, Halloran JW, Kikuchi N (1999) Design of piezocomposite materials and piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization—part I. Arch Comput Methods Eng 6(2):117–182
Silva ECN, Nishiwaki S, Kikuchi N (1999) Design of piezocomposite materials and piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization—part II. Arch Comput Methods Eng 6(3):191–215
Silva ECN, Kikuchi N (1999) Design of piezocomposite materials and piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization—part III. Arch Comput Methods Eng 6(4):305–329
Silva ECN, Kikuchi N (1999) Design of piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization. Smart Mater Struct 8(3):350–364
Stolpe M, Svanberg K (2001) An alternative interpolation scheme for minimum compliance topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 22(2):116–124
Sun D, Tong L, Wang D (2002) Modal actuator/sensor by modulating thickness of piezoelectric layers for smart plates. AIAA J 40:1676–1679
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Tcherniak D (2002) Topology optimization of resonating structures using SIMP method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 54(11):1605–1622
Tsai TD, Cheng CC (2013) Structural design for desired eigenfrequencies and mode shapes using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47(5):673–686
Wang F, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2011) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):767–784
Wang B, Caldwell S (1993) An improved approximate method for computing eigenvector derivatives. Finite Elem Anal Des 14(4):381–392
Zhang X, Kang Z, Li M (2014) Topology optimization of electrode coverage of piezoelectric thin-walled structures with CGVF control for minimizing sound radiation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50:799–814
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the kind invitation from ARCME Editors-in-Chief to write this survey paper. Authors acknowledge financial support form the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad through Grant MTM2013-47053-P, the Junta de Castilla-La Mancha and the European Fund for Regional Development through Grant PEII-2014-010-P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human Participants and Animals
This research does not involve neither human participants nor animals.
Informed Consent
All the authors are informed and provided their consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz, D., Bellido, J.C. & Donoso, A. Optimal Design of Piezoelectric Modal Transducers. Arch Computat Methods Eng 25, 313–347 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-016-9200-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-016-9200-5