Abstract
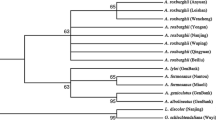
In order to develop an efficient identification method for Fallopia plants and drugs, molecular analysis of the partial matK gene sequences was performed on 6 Fallopia species. Based on the matK sequences, a phylogenetic tree was constructed, which showed that different populations of inter- and intra-species could be specified and distinguished. The matK gene sequences of the 6 Fallopia species were all found to be of 1 271 bp in length, with some nucleotide variations throughout the entire sequences. The nucleotide difference at position 1 041 could distinguish F. denticulata from others, while specific nucleotide at position 1 154 became identification markers for F. aubertii. Moreover, four specific marker sites for F. multiflora var. ciliinerve at positions 216, 224, 1 060 and 1 179, seven for F. convolvulus at 318, 765, 772, 874, 936, 952 and 1 036, and seven for F. dentate alata at 111, 192, 366, 450, 457, 1 032 and 1 074 were also observed. By detecting the marker nucleotides and analyzing the phylogenetic relationship, the botanical origins of five inspected drugs were determined, suggesting that matK sequences can be used for authenticating Fallopia plants and drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Editorial commission of FRPS. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005, 25(1): 96–103 (Ch).
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (1)[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 122 (Ch).
Lü L, Shao X, Wang L, et al. Stilbene glucoside from Polygonum multiflorum Thunb: A novel natural inhibitor of advanced glycation end product formation by trapping of methylglyoxal[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2010, 58(4): 2239–2245(Ch).
Cheng Xiyin, Liu Wan. Empirical identification of Heshouwu and its common adulterants[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Drug Application, 2007, 1(11): 19(Ch).
Ruan Xifa. Identification of Heshouwu based on the physical and chemical characters[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2007, 19(9): 68–69(Ch).
Carles M, Lee T, Moganti S, et al. Chips and Qi: microcosmponent-based analysis in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Fresenius J Anal Chem, 2001, 371(2): 190–194.
Joshi K, Chavan P, Warude D, et al. Molecular markers in herbal drug technology[J]. Curr Sci, 2004, 87(2): 159–165.
Pang Qihuu, Yan Ping, Zhao Xuan. Identification of Alpinia officinarum Hance and its adulterant based on matK gene sequences[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 26: 11–15 (Ch).
Zhang Qun. Sequence analysis of chloroplast maturase K gene of Chinese medical plant Eucommia ulmoides[J]. Ecol Sci, 2004, 23: 141–143(Ch).
Liu Jing, He Tao, Chun Ze. Analysis and authentication of chloroplast matK gene sequences of Herba dendrobii[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2009, 44(9):1051–1055(Ch).
Chen K S, Li F, Xu C J, et al. An efficient macro-method of genomic DNA isolation from Actinidia chinensis leaves[J]. Hereditas, 2004, 26(4): 529–531(Ch).
Ooi K, Endo Y, Yokoyama J, et al. Useful primer designs to amplify DNA fragments of the plastid gene matK from angiosperm plants [J]. J Jap Bot, 1995, 70: 328–331.
Yang D Y, Fushimi H, Cai S Q, et al. Molecular analysis of Rheum species used as Rhei Rhizoma based on the chloroplast matK gene sequence and its application for identification[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2004, 27(3): 375–383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(06019716)
Biography: SHENG Shujing, female, Ph.D. candidate, research direction: molecular identification of Chinese herbal medicines.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, S., Yan, P., Zheng, C. et al. Identification of Fallopia species based on the chloroplast matK gene sequences. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 15, 521–526 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-010-0695-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-010-0695-6