Abstract
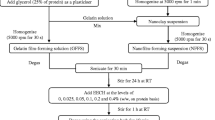
The effects of several agents in two different concentrations and pH values (5.0 and 8.0) on the functional properties of tilapia (Oreochromis urolepis hornorum) skin gelatin were evaluated and compared using a control tilapia skin gelatin and a commercial mammalian gelatin. The addition of the agents (sucrose 4 % and 8 % (w/v), glycerol 5 % and 10 % (v/v), NaCl 0.3 and 0.8 mol/L, MgCl2 0.3 and 0.8 mol/L, MgSO4 0.3 and 0.8 mol/L, KCl 0.3 and 0.8 mol/L, and transglutaminase 10 and 15 mg/mL) slightly increased the turbidity. There were different ratios of rheological properties depending on the agent, concentration, and pH. The addition of all agents increased the viscosity of the gelatin solution, mainly at pH 5.0. The addition of glycerol (10 % (v/v)) raised viscosity up to 7.45 cP. The setting time was prolonged by incorporating the agents. The gelatin samples with the addition of MgSO4 0.8 mol/L showed higher gel strength than the mammalian gelatin, exhibiting values of 298 and 295gf at pH 5.0 and 8.0, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aewsiri, T., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., Encarnacion, A. B., Wierenga, P. A., & Gruppen, H. (2011). Enhancement of emulsifying properties of cuttlefish skin gelatin by modification with hydroxysuccinimide esters of fatty acids. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-011-0553-3.
Alfaro, A. T., Fonseca, G. G., Costa, C. S., & Prentice, C. (2009). Effect of extraction parameters on the properties of gelatin from King weakfish (Macrodon ancylodon) bones. Food Science and Technology International, 15(6), 553–562.
AOAC. (2000). Official methods of the Association of Official Agricultural Chemist’s International. Gaithersburg: AOAC International.
Arvanitoyannis, I. S., & Kassaveti, A. (2008). Fish industry waste: treatments, environmental impacts, current and potential uses. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 43(4), 726–745.
Arvanitoyannis, I. S., & Ladas, D. (2008). Meat waste treatment methods and potential uses. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 43(3), 543–559.
Asghar, A., & Henrickson, R. L. (1982). Chemical, biochemical, functional, and nutritional characteristics of collagen food systems. In C. O. Chichester, E. M. Mrata, & B. S. Schweigert (Eds.), Advances in food research (pp. 232–272). London: Academic Press.
Boran, G., Mulvaney, S. J., & Regenstein, J. M. (2010). Rheological properties of gelatin from silver carp skin compared to commercially available gelatins from different sources. Journal of Food Science, 75(8), E565–E571.
BSI. (1975). Methods for sampling and testing gelatin (physical and chemical methods). London: British Standards Institution.
Bueno, C. M., Alvim, I. D., Koberstein, T. C. R. D., Portella, M. C., & Grosso, C. (2011). Production of tilapia skin gelatin and its use in the production of micro-particles containing salmon oil. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology, 14(1), 65–73.
Chiou, B., Avena-Bustillos, R. J., Shey, J., Yee, E., Bechtel, P. J., Imam, S. H., Glenn, G. M., & Orts, W. J. (2006). Rheological and mechanical properties of cross-linked fish gelatins. Polymer, 47(18), 6379–6386.
Cho, S. M., Gu, Y. S., & Kim, S. B. (2004). Extracting optimization and physical properties of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) skin gelatin compared to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocolloids, 19(2), 221–229.
Choi, S. S., & Regenstein, J. M. (2000). Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of fish gelatin. Journal of Food Science, 65(2), 194–199.
Cole, C. G. B. (2011). Gelatin food science. Available at: www.gelatin.co.za. Accessed 26 April 2011.
Cole, C. G. B., & Roberts, J. J. (1996). Changes in the molecular composition of gelatin due to the manufacturing process and animal age, as shown by electrophoresis. Journal of the Society of the Leather Technologists and Chemists, 80(5), 136–141.
Duan, R., Zhang, J., Xing, F., Konno, K., & Xu, B. (2011). Study on the properties of gelatins from skin of carp (Cyprinus carpio) caught in winter and summer season. Food Hydrocolloids, 25, 368–373.
Elysée-Collen, B., & Lencki, R. W. (1996). Effect of ethanol, ammonium sulfate, and temperature on the phase behaviour of type B gelatin. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 44(7), 1651–1657.
Fernández-Díaz, M. D., Montero, P., & Gómez-Guillén, M. C. (2001). Gel properties of collagens from skins of cod (Gadus morhua) and hake (Merluccius merluccius) and their modification by the coenhancers magnesium sulphate, glycerol and transglutaminase. Food Chemistry, 74(2), 161–167.
Fernández-Díaz, M. D., Montero, P., & Gómez-Guillén, M. C. (2003). Effect of freezing fish skins on molecular and rheological properties of extracted gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids, 17(3), 281–286.
Gildberg, A., Arnesen, J. A., & Carlehög, M. (2002). Utilisation of cod backbone by biochemical fractionation. Process Biochemistry, 38(4), 475–480.
Gilsenan, P. M., & Ross-Murphy, S. B. (2000). Rheological characterisation of gelatins from mammalian and marine sources. Food Hydrocolloids, 14(3), 191–195.
Gómez-Guillén, M. C., Turnay, J., Fernández-Díaz, M. D., Ulmo, N., Lizarbe, M. A., & Montero, P. (2002). Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: a comparative study. Food Hydrocolloids, 16(1), 25–34.
Gudmundsson, M. (2002). Rheological properties of fish gelatin. Journal of Food Science, 67(6), 2172–2176.
Gudmundsson, M., & Hafsteinsson, H. (1997). Gelatin from cod skins as affected by chemical treatments. Journal of Food Science, 62(1), 37–39.
Harrington, W. F., & von Hippel, P. H. (1962). The structure of collagen and gelatin. In C. B. Anfinsen Jr., M. L. Anson, K. Bailey, & J. T. Edsall (Eds.), Advances in protein chemistry (pp. 1–138). London: Elsevier.
Haug, I. J., Draget, K. I., & Smidsrød, O. (2004). Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocolloids, 18(2), 203–213.
Jamilah, B., & Harvinder, K. G. (2002). Properties of gelatins from skins of fish—black tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and red tilapia (Oreochromis nilotica). Food Chemistry, 77, 81–84.
Johns, P., & Courts, A. (1977). Relationship between collagen and gelatin. In A. G. Ward & A. Courts (Eds.), The science and technology of gelatin (pp. 138–177). London: Academic Press.
Jongjareonrak, A., Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., & Tanaka, M. (2006). Skin gelatin from bigeye snapper and brownstripe red snapper: chemical compositions and effect of microbial transglutaminase on gel properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 20, 1216–1222.
Jongjareonrak, A., Rawdkuen, S., Chaijan, M., Benjakul, S., Osako, K., & Tanaka, M. (2010). Chemical compositions and characterisation of skin gelatin from farmed giant catfish (Pangasianodon gigas). LWT- Food Science and Technology, 43, 161–165.
Kunz, W., Lo Nostro, P., & Ninham, B. W. (2004). The present state of affairs with Hofmeister effects. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science, 9, 1–18.
Ledward, D. A. (1986). Gelation of gelatin. In J. R. Mitchell & D. A. Ledward (Eds.), Functional properties of food macromolecules (pp. 171–201). London: Elsevier.
Leuenberger, B. H. (1991). Investigation of viscosity and gelation properties of different mammalian and fish gelatins. Food Hydrocolloids, 5(4), 353–361.
Mohtar, N. F., Perera, C., & Quek, S. (2010). Optimisation of gelatine extraction from hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae) skins and measurement of gel strength and SDS-PAGE. Food Chemistry, 122, 307–313.
Montero, P., Fernández-Díaz, M. D., & Gómez-Guillén, M. C. (2002). Characterization of gelatin gels induced by high pressure. Food Hydrocolloids, 16(3), 197–205.
Naftalian, R. J., & Symons, M. C. R. (1974). The mechanism of sugar-dependent stabilization of gelatin gels. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 352(1), 173–176.
Nagl, S., Tichy, H., Mayer, W. E., Samonte, I. E., Mcandrew, B. J., & Klein, J. (2001). Classification and phylogenetic relationships of African tilapiine fishes inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 20(3), 361–374.
Norland, R. E. (1990). Fish gelatin. In M. N. Voight & J. K. Botta (Eds.), Advances in fisheries technology and biotechnology for increased profitability (pp. 325–333). Lancaster: Technomic Publishing Co.
Piotrowska, B., Sztuka, K., Kolodziejska, I. L., & Dobrosielska, E. (2008). Influence of transglutaminase or 1-ethyl-3-(3- imethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) on the properties of fish-skin gelatin films. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(7), 1362–1371.
Sai-Ut, S., Jongjareonrak, A., & Rawdkuen, S. (2011). Re-extraction, recovery, and characteristics of skin gelatin from farmed giant catfish. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-010-0408-3.
Sarabia, A. I., Gómez-Guillén, M. C., & Montero, P. (2000). The effect of added salt on the viscoelastic properties of fish skin gelatin. Food Chemistry, 70(1), 71–76.
Zhang, Y., & Cremer, P. S. (2006). Interactions between macromolecules and ions: the Hofmeister series. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 10, 658–663.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by Ajinomoto, Limeira (SP), for supplying the enzyme transglutaminase ACTIVA MP®; and Embrapa–Agricultural Research Corporation, Embrapa Swine and Poultry, Concórdia (SC), for the lyophilizing of the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Trindade Alfaro, A., Fonseca, G.G. & Prentice-Hernández, C. Enhancement of Functional Properties of Wami Tilapia (Oreochromis urolepis hornorum) Skin Gelatin at Different pH Values. Food Bioprocess Technol 6, 2118–2127 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0859-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0859-9