Abstract
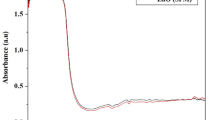
In recent years, the biosynthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been projected as an alternative to traditional antibiotics for their superior antimicrobial properties and significant inhibition of the biofilm formation. Particularly, it is found that the effectiveness of AgNPs varies greatly with the biomaterial used in their synthesis. Mushrooms are natural resources for excellent antioxidants and bioactive compounds. Nevertheless, there are few reports on the application of mushrooms in AgNPs biosynthesis. In this study, AgNPs were successfully synthesized using Flammulina velutipes extract as reductants and stabilizing agents. The following analyses of UV-visible spectroscopy showed typical absorbance peak at 450 nm. Transmission electron microscope analysis indicated that the prepared AgNPs were monodispersed spheres with an average size of approximately 22 nm. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the face-centered cubic (fcc) crystalline structure of metallic silver. Furthermore, the synthesized AgNPs exhibited high stability and antibacterial activities against 6 aquatic pathogens. A subsequent challenge experiment showed that the prepared AgNPs significantly reduced the mortality rate of Ruditapes philippinarum clam infected with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Notably, AgNPs treatment could inhibit the biofilm formation of the pathogen, indicating that the extracellular synthesis of AgNPs using mushroom can be developed into a novel effective antimicrobial agent to overcome the multidrug-resistant microorganisms in aquaculture. This study will open a new way for edible mushroom processing and wide application in aquaculture.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzohairy, M. A., Ansari, M. A., Cameotra, S. S., Khan, H. M., & Khan, A. A. (2015). Antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles against MRSA and MRSE isolated from wounds in a tertiary care hospital. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology, 33(1), 101–109.
Ashokkumar, S., Ravi, S., Kathiravan, V., & Velmurugan, S. (2015). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using A. indicum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 134(139C), 34–39.
Bankar, A., Joshi, B., Kumar, A. R., & Zinjarde, S. (2010). Banana peel extract mediated novel route for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 368(1-3), 58–63.
Bazargani, M. M., & Rohloff, J. (2016). Antibiofilm activity of essential oils and plant extracts against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli biofilms. Food Control, 61, 156–164.
Chen, Z., Wang, Z., Ren, J., & Qu, X. (2018). Enzyme mimicry for combating bacteria and biofilms. Accounts of Chemical Research, 51(3), 789–799.
Dal Lago, V., Luciane, F. D. O., Kaliandra, D. A. G., Kobarg, J., & Borba Cardoso, M. (2011). Size-selective silver nanoparticles: future of biomedical devices with enhanced bactericidal properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21(33), 12267.
Dehnavi, A. S., Raisi, A., & Aroujalian, A. (2013). Control size and stability of colloidal silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity prepared by a green synthesis method. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Metal-Organic, and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 43(5), 543–551.
Dubey, S. P., Lahtinen, M., & Sillanp, M. (2010a). Green synthesis and characterizations of silver and gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rosa rugosa. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 364(1-3), 34–41.
Dubey, S. P., Lahtinen, M., & Sillanpaeae, M. (2010b). Tansy fruit mediated greener synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Process Biochemistry, 45(7), 1065–1071.
Emiliane, A. A., de Andrade, N. J., Silva, L. H. M. D., Carvalho, A. F. D., et al. (2010). Control of microbial adhesion as a strategy for food and bioprocess technology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3(3), 321–332.
Fayaz, A. M., Balaji, K., Girilal, M., Yadav, R., Kalaichelvan, P. T., & Venketesan, R. (2010). Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: a study against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomedicine, 6(1), 103–109.
Flemming, H. C., & Wingender, J. (2010). The biofilm matrix. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(9), 623–633.
Gavade, N. L., Kadam, A. N., Suwarnkar, M. B., Ghodake, V. P., & Garadkar, K. M. (2015). Biogenic synthesis of multi-applicative silver nanoparticles by using Ziziphus jujuba leaf extract. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 136, 953–960.
Hassan, H. (2017). Nanomaterials for alternative antibacterial therapy. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 12, 8211–8225.
Hwang, I., Lee, J., Hwang, J. H., Kim, K.-J., & Lee, D. G. (2012). Silver nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death in Candida albicans through the increase of hydroxyl radicals. The FEBS Journal, 279(7), 1327–1338.
Jing, P., Zhao, S. J., Lu, M. M., Cai, Z., Pang, J., & Song, L. H. (2014). Multiple-fingerprint analysis for investigating quality control of Flammulina velutipes, fruiting body polysaccharides. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(50), 12128–12133.
Klug, T. V., Novello, J., Laranja, D. C., Aguirre, T. A. S., Alessandro, D. O. R., Tondo, E. C., et al. (2017). Effect of tannin extracts on biofilms and attachment of Escherichia coli on lettuce leaves. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(2), 275–283.
Li, Q., Mahendra, S., Lyon, D. Y., Brunet, L., Liga, M. V., Li, D., & Alvarez, P. J. (2008). Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential applications and implications. Water Research, 42(18), 4591–4602.
Li, Q., Zhang, Z., Haque, S. S., Zhang, M., & Xia, L. (2010). Localized surface plasmon resonance effects by naturally occurring Chinese yam particles. Journal of Applied Physics, 108(12), 1102.
Li, K., Ma, C., Jian, T., Sun, H., Wang, L., Xu, H., Li, W., Su, H., & Cheng, X. (2017). Making good use of the byproducts of cultivation: green synthesis and antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles using the leaf extract of blueberry. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(11), 3569–3576.
Liu, S., Guo, J., Cao, S., Zhou, Y., Luo, L., Lin, C., et al. (2018). Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites modulate the biofilm formation and extracellular polymeric substances (eps) production. Nanoscale, 41, 19603–19611.
Loo, C. Y., Rohanizadeh, R., Young, P. M., Traini, D., Cavaliere, R., Whitchurch, C., et al. (2015). Combination of silver nanoparticles and curcumin nanoparticles for enhanced anti-biofilm activities. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64(12), 2513–2522.
Lúcia, S., & Ramos, F. (2018). Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 52(2), 135–143.
Machul, A., Mikolajczyk, D., Regiel-Futyra, A., Heczko, P. B., Strus, M., Arruebo, M., et al. (2015). Study on inhibitory activity of chitosan-based materials against biofilm producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 30(3), 269–278.
Matamp, N., & Bhat, S. G. (2020). Genome characterization of novel lytic myoviridae bacteriophage vp-1 enhances its applicability against mdr-biofilm-forming vibrio parahaemolyticus. Archives of Virology, 165(2), 387–396.
Miri, A., Sarani, M., Rezazade Bazaz, M., & Darroudi, M. (2015). Plant-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Prosopis farcta extract and its antibacterial properties. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 141, 287–291.
Mizan, M. F. R., Jahid, I. K., Kim, M., Lee, K. H., Kim, T. J., & Ha, S. D. (2016). Variability in biofilm formation correlates with hydrophobicity and quorum sensing among vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from food contact surfaces and the distribution of the genes involved in biofilm formation. Biofouling, 32(3-4), 497–509.
Múgica-Vidal, R., Sainz-García, E., Álvarez-Ordóñez, A., Prieto, M., González-Raurich, M., López, M., López, M., Rojo-Bezares, B., Sáenz, Y., & Alba-Elías, F. (2019). Production of antibacterial coatings through atmospheric pressure plasma: a promising alternative for combatting biofilms in the food industry. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(8), 1251–1263.
Neethirajan, S., & Jayas, D. S. (2011). Nanotechnology for the food and bioprocessing industries. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 4(1), 39–47.
Niemira, B. A. (2010). Irradiation sensitivity of planktonic and biofilm-associated listeria monocytogenes and L. innocua as influenced by temperature of biofilm formation. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3(2), 257–264.
Olson, M. E., Ceri, H., Morck, D. W., Buret, A. G., & Read, R. R. (2002). Biofilm bacteria: formation and comparative susceptibility to antibiotics. Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research, 66(2), 86–92.
Pimprikar, P. S., Joshi, S. S., Kumar, A. R., Zinjarde, S. S., & Kulkarni, S. K. (2009). Influence of biomass and gold salt concentration on nanoparticle synthesis by the tropical marine yeast Yarrowia lipolytica NCIM 3589. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 74(1), 309–316.
Ramasamy, M., Lee, J. H., & Lee, J. (2016). Potent antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of bacteriogenically synthesized gold-silver nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria and their physiochemical characterizations. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 31(3), 366–378.
Sahu, N., Soni, D., Chandrashekhar, B., Sarangi, B. K., Satpute, D., & Pandey, R. A. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Cynodon dactylon leaves and assessment of their antibacterial activity. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 36(7), 999–1004.
Shavel, A., Cadavid, D., Ibáñez, M., Carrete, A., & Cabot, A. (2012). Continuous production of Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals in a flow reactor. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 134(3), 1438–1441.
Shi, M., Yang, Y., Guan, D., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2012). Bioactivity of the crude polysaccharides from fermented soybean curd residue by Flammulina velutipes. Carbohydrate Polymers, 89(4), 1268–1276.
Singh, P., Kim, Y. J., Zhang, D., & Yang, D. C. (2016). Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends in Biotechnology, 34(7), 588–599.
Swain, P., Nayak, S. K., Sasmal, A., Behera, T., Barik, S. K., Swain, S. K., Mishra, S. S., Sen, A. K., Das, J. K., & Jayasankar, P. (2014). Antimicrobial activity of metal based nanoparticles against microbes associated with diseases in aquaculture. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30(9), 2491–2502.
Taghavizadeh Yazdi, M. E., Khara, J., Sadeghnia, H. R., Esmaeilzadeh Bahabadi, S., & Darroudi, M. (2017). Biosynthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Rheum turkestanicum shoots extract. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 44, 1325–1334.
Vijayakumar, M., Priya, K., Nancy, F. T., Noorlidah, A., & Ahmed, A. (2013). Biosynthesis, characterisation and anti-bacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Artemisia nilagirica. Industrial Crops and Products, 41, 235–240.
Wang, L., Liu, C. C., Wang, Y. Y., Xu, H., Su, H., & Cheng, X. (2016a). Antibacterial activities of the novel silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using Cordyceps militaris extract. Current Applied Physics, 16(9), 969–973.
Wang, L., Xu, H., Gu, L., Han, T. T., Wang, S., & Meng, F. B. (2016b). Bioinspired synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using purple sweet potato root extract. Materials and Processing Report, 31(8), 437–442.
Yang, W., Fang, Y., Liang, J., & Hu, Q. (2011). Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharides and evaluation of its acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. Food Research International, 44(5), 1269–1275.
Yang, N., Li, F. Y., Jian, T. C., Liu, C. C., Sun, H. S., Wang, L., et al. (2017). Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract and their antibacterial properties against aquatic pathogens. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(12), 95–100.
Zafar, N., Shamaila, S., Nazir, J., Sharif, R., Rafique, M. S., Hasan, J., Ammara, S., & Khalid, H. (2016). Antibacterial action of chemically synthesized and laser-generated silver nanoparticles against human pathogenic bacteria. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 32(8), 721–728.
Zhang, Z., Lv, G., He, W., Shi, L., & Fan, L. (2013). Effects of extraction methods on the antioxidant activities of polysaccharides obtained from Flammulina velutipes. Carbohydrate Polymers, 98(2), 1524–1531.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong (No. 2019GSF107091; 2019GSF109114) and the Marine and Fisheries Science and Technology Innovation Program of Shandong (No. 2017YY04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wei, Y., Wang, H. et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Mushroom Flammulina velutipes Extract and Their Antibacterial Activity Against Aquatic Pathogens. Food Bioprocess Technol 13, 1908–1917 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02533-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02533-7