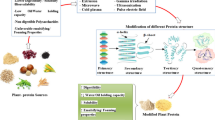
Abstract
Plant-based proteins have shown great potential as an alternative substitute for animal proteins to meet the increasing global demand. Nevertheless, several limitations mitigate plant-based protein application and utilization. As a panacea to meeting the market demand, it is imperative to modify plant-based proteins to produce improved quality and techno-functionalities compared to conventional animal protein ingredients. Enzymatic, chemical, and physical modifications have been used for plant-based proteins, which have shown exciting results in improving their techno-functional properties, digestibility, and inherent allergenicity. Among these modification methods, the low-cost, limited time, high sensitivity, and high reproducibility give enzymatic modification leverage over chemical and physical methods. This review gave a concise summary of the advantages and disadvantages of enzymatic modifications. The efficacy of enzymatic modification in producing protein ingredients from plant sources with improved techno-functional properties, digestibility, and alleviated allergenicity was discussed. Furthermore, the application of enzymatic modification in the production of bioactive compounds with health-beneficial properties adds in no small measure to the novelty of this review.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmadifard, N., Murueta, J. H. C., Abedian-Kenari, A., Motamedzadegan, A., & Jamali, H. (2016). Comparison the effect of three commercial enzymes for enzymatic hydrolysis of two substrates (rice bran protein concentrate and soy-been protein) with SDS-PAGE. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(2), 1279–1284.
Akharume, F. U., Aluko, R. E., & Adedeji, A. A. (2021). Modification of plant proteins for improved functionality: A review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(1), 198–224.
Al-Ruwaih, N., Ahmed, J., Mulla, M. F., & Arfat, Y. A. (2019). High-pressure assisted enzymatic proteolysis of kidney beans protein isolates and characterization of hydrolysates by functional, structural, rheological and antioxidant properties. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 100, 231–236.
Aluko, R. E. (2008). Determination of nutritional and bioactive properties of peptides in enzymatic pea, chickpea, and mung bean protein hydrolysates. Journal of AOAC International, 91(4), 947–956.
Aluko, R. E. (2015). Structure and function of plant protein-derived antihypertensive peptides. Current Opinion in Food Science, 4, 44–50.
Aluko, R. E. (2018). Food protein-derived peptides: Production, isolation, and purification. In R. Y. Yada (Ed.), Proteins in Food Processing (Second Edition) (pp. 389–412). Woodhead Publishing.
Aondona, M. M., Ikya, J. K., Ukeyima, M. T., Gborigo, T. W. J., Aluko, R. E., & Girgih, A. T. (2021). In vitro antioxidant and antihypertensive properties of sesame seed enzymatic protein hydrolysate and ultrafiltration peptide fractions. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 45(1), e13587.
Arte, E., Huang, X., Nordlund, E., & Katina, K. (2019). Biochemical characterization and technofunctional properties of bioprocessed wheat bran protein isolates. Food Chemistry, 289, 103–111.
Arte, E., Rizzello, C. G., Verni, M., Nordlund, E., Katina, K., & Coda, R. (2015). Impact of enzymatic and microbial bioprocessing on protein modification and nutritional properties of wheat bran. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 63(39), 8685–8693.
Bandara, N., Akbari, A., Esparza, Y., & Wu, J. (2018). Canola protein: A promising protein source for delivery, adhesive, and material applications. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 95(8), 1075–1090.
Barać, M., Čabrilo, S., Pešić, M., Stanojević, S., Pavlićević, M., Maćej, O., & Ristić, N. (2011). Functional properties of pea (Pisum sativum, L.) protein isolates modified with chymosin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(12), 8372–8387.
Baugreet, S., Kerry, J. P., Brodkorb, A., Gomez, C., Auty, M., Allen, P., & Hamill, R. M. (2018). Optimisation of plant protein and transglutaminase content in novel beef restructured steaks for older adults by central composite design. Meat Science, 142, 65–77.
Beaubier, S., Albe-Slabi, S., Aymes, A., Bianeis, M., Galet, O., & Kapel, R. (2021). A rational approach for the production of highly soluble and functional sunflower protein hydrolysates. Foods, 10(3), 664.
Biscola, V., de Olmos, A. R., Choiset, Y., Rabesona, H., Garro, M. S., Mozzi, F., Chobert, J.-M., Drouet, M., Haertlé, T., & Franco, B. (2017). Soymilk fermentation by Enterococcus faecalis VB43 leads to reduction in the immunoreactivity of allergenic proteins β-conglycinin (7S) and glycinin (11S). Beneficial Microbes, 8(4), 635–643.
Boohaker, R. J., Lee, M. W., Vishnubhotla, P., Perez, J. M., & Khaled, A. R. (2012). The use of therapeutic peptides to target and to kill cancer cells. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 19(22), 3794–3804.
Boutureira, O., & Bernardesa. J., G. (2015). Advances in chemical protein modification. Chemical Reviews, 115(5), 2174–2195.
Brückner-Gühmann, M., Heiden-Hecht, T., Sözer, N., & Drusch, S. (2018). Foaming characteristics of oat protein and modification by partial hydrolysis. European Food Research and Technology, 244(12), 2095–2106.
Buchert, J., Ercili Cura, D., Ma, H., Gasparetti, C., Monogioudi, E., Faccio, G., Mattinen, M., Boer, H., Partanen, R., & Selinheimo, E. (2010). Crosslinking food proteins for improved functionality. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 1, 113–138.
Budseekoad, S., Yupanqui, C. T., Sirinupong, N., Alashi, A. M., Aluko, R. E., & Youravong, W. (2018). Structural and functional characterization of calcium and iron-binding peptides from mung bean protein hydrolysate. Journal of Functional Foods, 49, 333–341.
Cabanillas, B., Pedrosa, M. M., Rodríguez, J., Gonzalez, A., Muzquiz, M., Cuadrado, C., Crespo, J. F., & Burbano, C. (2010). Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on lentil allergenicity. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, 54(9), 1266–1272.
Cabanillas, B., Pedrosa, M. M., Rodriguez, J., Muzquiz, M., Maleki, S. J., Cuadrado, C., Burbano, C., & Crespo, J. F. (2012). Influence of enzymatic hydrolysis on the allergenicity of roasted peanut protein extract. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 157(1), 41–50.
Caetano-Silva, M. E., Netto, F. M., Bertoldo-Pacheco, M. T., Alegría, A., & Cilla, A. (2021). Peptide-metal complexes: Obtention and role in increasing bioavailability and decreasing the pro-oxidant effect of minerals. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 61(9), 1470–1489.
Calderón-chiu, C., Calderón-santoyo, M., Damasceno-gomes, S., & Ragazzo-Sánchez, J. A. (2021). Use of jackfruit leaf (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) protein hydrolysates as a stabilizer of the nanoemulsions loaded with extract-rich in pentacyclic triterpenes obtained from Coccoloba uvifera L. leaf. Food Chemistry: X, 12, 100138.
Campbell-Platt, G. (1994). Fermented foods—a world perspective. Food Research International, 27(3), 253–257.
Chen, D., & Campanella, O. H. (2022). Limited enzymatic hydrolysis induced pea protein gelation at low protein concentration with less heat requirement. Food Hydrocolloids, 128, 107547.
Chen, L., Chen, J., Ren, J., & Zhao, M. (2011). Modifications of soy protein isolates using combined extrusion pre-treatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis for improved emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 887–897.
Chen, Z., Wang, J., Liu, W., & Chen, H. (2017). Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant and anticancer activities of proteins from four legume species. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 54(4), 964–972.
Chunkao, S., Youravong, W., Yupanqui, C. T., Alashi, A. M., & Aluko, R. E. (2020). Structure and function of mung bean protein-derived iron-binding antioxidant peptides. Foods, 9(10), 1406.
Coda, R., Melama, L., Rizzello, C. G., Curiel, J. A., Sibakov, J., Holopainen, U., Pulkkinen, M., & Sozer, N. (2015). Effect of air classification and fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum VTT E-133328 on faba bean (Vicia faba L.) flour nutritional properties. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 193, 34–42.
Cui, P., Lin, S., Jin, Z., Zhu, B., Song, L., & Sun, N. (2018). In vitro digestion profile and calcium absorption studies of a sea cucumber ovum derived heptapeptide–calcium complex. Food and Function, 9(9), 4582–4592.
Curiel, J. A., Coda, R., Centomani, I., Summo, C., Gobbetti, M., & Rizzello, C. G. (2015). Exploitation of the nutritional and functional characteristics of traditional Italian legumes: The potential of sourdough fermentation. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 196, 51–61.
del Mar Yust, M., Pedroche, J., del Carmen Millán-Linares, M., Alcaide-Hidalgo, J. M., & Millán, F. (2010). Improvement of functional properties of chickpea proteins by hydrolysis with immobilised Alcalase. Food Chemistry, 122(4), 1212–1217.
Dias, D. R., Abreu, C. M. P. D., Silvestre, M. P. C., & Schwan, R. F. (2010). In vitro protein digestibility of enzymatically pre-treated bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flour using commercial protease and Bacillus sp. protease. Food Science and Technology, 30(1), 94–99.
Djoullah, A., Husson, F., & Saurel, R. (2018). Gelation behaviors of denaturated pea albumin and globulin fractions during transglutaminase treatment. Food Hydrocolloids, 77, 636–645.
Dube, M., Schäfer, C., Neidhart, S., & Carle, R. (2007). Texturisation and modification of vegetable proteins for food applications using microbial transglutaminase. European Food Research and Technology, 225(2), 287–299.
Eckert, E., Han, J., Swallow, K., Tian, Z., Jarpa-Parra, M., & Chen, L. (2019). Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis and ultrafiltration on physicochemical and functional properties of faba bean protein. Cereal Chemistry, 96(4), 725–741.
El Mecherfi, K.-E., Lupi, R., Cherkaoui, M., Albuquerque, M. A., Todorov, S. D., Tranquet, O., Klingebiel, C., Rogniaux, H., Denery-Papini, S., & Onno, B. (2021). Fermentation of gluten by Lactococcus lactis LLGKC18 reduces its antigenicity and allergenicity. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 1–13.
Fadimu, G. J., Olatunde, O. O., Bandara, N., & Truong, T. (2022). Reducing allergenicity in plant-based proteins. In B. B. S. Prakash, & C. Gaiani (Ed.), Engineering Plant-based Food Systems.).
Galante, M., De Flaviis, R., Boeris, V., & Spelzini, D. (2020). Effects of the enzymatic hydrolysis treatment on functional and antioxidant properties of quinoa protein acid-induced gels. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 118, 108845.
Gao, Y., Zhang, X., Ren, G., Wu, C., Qin, P., & Yao, Y. (2020). Peptides from extruded lupin (Lupinus albus L.) regulate inflammatory activity via the p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 68(42), 11702–11709.
Garcia-Mora, P., Penas, E., Frias, J., Zielinski, H., Wiczkowski, W., Zielinska, D., & Martinez-Villaluenga, C. (2016). High-pressure-assisted enzymatic release of peptides and phenolics increases angiotensin converting enzyme I inhibitory and antioxidant activities of pinto bean hydrolysates. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64(8), 1730–1740.
García Arteaga, V., Apéstegui Guardia, M., Muranyi, I., Eisner, P., & Schweiggert-Weisz, U. (2020a). Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on molecular weight distribution, techno-functional properties and sensory perception of pea protein isolates. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 65, 102449.
García Arteaga, V., Leffler, S., Muranyi, I., Eisner, P., & Schweiggert-Weisz, U. (2020b). Sensory profile, functional properties and molecular weight distribution of fermented pea protein isolate. Current Research in Food Science, 4, 1–10.
Gençdağ, E., Görgüç, A., & Yılmaz, F. M. (2021). Recent advances in the recovery techniques of plant-based proteins from agro-industrial by-products. Food Reviews International, 37(4), 447–468.
Girgih, A. T., Alashi, A. M., He, R., Malomo, S. A., Raj, P., Netticadan, T., & Aluko, R. E. (2014). A novel hemp seed meal protein hydrolysate reduces oxidative stress factors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nutrients, 6(12), 5652–5666.
Görgüç, A., Gençdağ, E., & Yılmaz, F. M. (2020). Bioactive peptides derived from plant origin by-products: Biological activities and techno-functional utilizations in food developments – A review. Food Research International, 136, 109504.
Großmann, K. K., Merz, M., Appel, D., Thaler, T., & Fischer, L. (2020). Impact of peptidase activities on plant protein hydrolysates regarding bitter and umami taste. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69(1), 368–376.
Guan, H., Diao, X., Jiang, F., Han, J., & Kong, B. (2018). The enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein isolate by Corolase PP under high hydrostatic pressure and its effect on bioactivity and characteristics of hydrolysates. Food Chemistry, 245, 89–96.
Hewage, A., Olatunde, O. O., Nimalaratne, C., Malalgoda, M., Aluko, R. E., & Bandara, N. (2022). Novel Extraction technologies for developing plant protein ingredients with improved functionality. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 129, 492–511.
Humiski, L., & Aluko, R. (2007). Physicochemical and bitterness properties of enzymatic pea protein hydrolysates. Journal of Food Science, 72(8), S605–S611.
Ibrahim, H. R., Isono, H., & Miyata, T. (2018). Potential antioxidant bioactive peptides from camel milk proteins. Animal Nutrition, 4(3), 273–280.
Idowu, A. O., Famuwagun, A. A., Fagbemi, T., & N, & Aluko, R. E. (2021). Antioxidant and enzyme-inhibitory properties of sesame seed protein fractions and their isolate and hydrolyzate. International Journal of Food Properties, 24(1), 780–795.
Idowu, A. T., & Benjakul, S. (2019). Bitterness of fish protein hydrolysate and its debittering prospects. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 43(9), e12978.
Ismail, B. P., Senaratne-Lenagala, L., Stube, A., & Brackenridge, A. (2020). Protein demand: Review of plant and animal proteins used in alternative protein product development and production. Animal Frontiers, 10(4), 53–63.
Ivanova, P., Kalaydzhiev, H., Dessev, T. T., Silva, C. L. M., Rustad, T., & Chalova, V. I. (2018). Foaming properties of acid-soluble protein-rich ingredient obtained from industrial rapeseed meal. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 55(9), 3792–3798.
Jia, N., Zhang, F., Liu, Q., Wang, L., Lin, S., & Liu, D. (2019). The beneficial effects of rutin on myofibrillar protein gel properties and related changes in protein conformation. Food Chemistry, 301, 125206.
Joshi, P., & Varma, K. (2016). Effect of germination and dehulling on the nutritive value of soybean. Nutrition and Food Science.
Kasera, R., Singh, A., Lavasa, S., Prasad, K. N., & Arora, N. (2015). Enzymatic hydrolysis: A method in alleviating legume allergenicity. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 76, 54–60.
Kieliszek, M., Pobiega, K., Piwowarek, K., & Kot, A. M. (2021). Characteristics of the proteolytic enzymes produced by lactic acid bacteria. Molecules, 26(7), 1858.
Lammi, C., Zanoni, C., Arnoldi, A., & Vistoli, G. (2016). Peptides derived from soy and lupin protein as dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors: In vitro biochemical screening and in silico molecular modeling study. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64(51), 9601–9606.
Li, H., & Aluko, R. E. (2010). Identification and inhibitory properties of multifunctional peptides from pea protein hydrolysate. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(21), 11471–11476.
Li, H., Yu, J., Ahmedna, M., & Goktepe, I. (2013). Reduction of major peanut allergens Ara h 1 and Ara h 2, in roasted peanuts by ultrasound assisted enzymatic treatment. Food Chemistry, 141(2), 762–768.
Li, J., Xiang, Q., Liu, X., Ding, T., Zhang, X., Zhai, Y., & Bai, Y. (2017). Inactivation of soybean trypsin inhibitor by dielectric-barrier discharge (DBD) plasma. Food Chemistry, 232, 515–522.
Li, M., Blecker, C., & Karboune, S. (2021). Molecular and air-water interfacial properties of potato protein upon modification via laccase-catalyzed cross-linking and conjugation with sugar beet pectin. Food Hydrocolloids, 112, 106236.
Li, Y., Yu, J., Goktepe, I., & Ahmedna, M. (2016). The potential of papain and alcalase enzymes and process optimizations to reduce allergenic gliadins in wheat flour. Food Chemistry, 196, 1338–1345.
Lu, Q., Zuo, L., Wu, Z., Li, X., Tong, P., Wu, Y., Fan, Q., Chen, H., & Yang, A. (2022). Characterization of the protein structure of soymilk fermented by Lactobacillus and evaluation of its potential allergenicity based on the sensitized-cell model. Food Chemistry, 366, 130569.
Lv, Y., Wei, K., Meng, X., Huang, Y., Zhang, T., & Li, Z. (2017). Separation and identification of iron-chelating peptides from defatted walnut flake by nanoLC-ESI–MS/MS and de novo sequencing. Process Biochemistry, 59, 223–228.
M’hir, S., Aldric, J.-M., El-Mejdoub, T., Destain, J., Mejri, M., Hamdi, M., & Thonart, P. J. (2008). Proteolytic breakdown of gliadin by Enterococcus faecalis isolated from Tunisian fermented dough. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 24(12), 2775–2781.
Ma, F.-F., Wang, H., Wei, C.-K., Thakur, K., Wei, Z.-J., & Jiang, L. (2019). Three novel ACE inhibitory peptides isolated from Ginkgo biloba seeds: Purification, inhibitory kinetic and mechanism. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 1579.
Matsuura, M., Sasaki, M., Sasaki, A., & Takeuchi, T. J. P. U. (2000). Production for producing packed tofu. 6042851.
Meinlschmidt, P., Schweiggert-Weisz, U., & Eisner, P. (2016). Soy protein hydrolysates fermentation: Effect of debittering and degradation of major soy allergens. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 71, 202–212.
Meinlschmidt, P., Sussmann, D., Schweiggert-Weisz, U., & Eisner, P. (2015). Enzymatic treatment of soy protein isolates: Effects on the potential allergenicity, technofunctionality, and sensory properties. Food Science and Nutrition, 4(1), 11–23.
Mills, E. C., & Shewry, P. R. (2004). Plant food allergens: Wiley Online Library.
Mojica, L., Luna-Vital, D. A., & de Mejia, E. G. (2018). Black bean peptides inhibit glucose uptake in Caco-2 adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the expression and translocation pathway of glucose transporters. Toxicology Reports, 5, 552–560.
Montemurro, M., Pontonio, E., Gobbetti, M., & Rizzello, C. G. (2019). Investigation of the nutritional, functional and technological effects of the sourdough fermentation of sprouted flours. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 302, 47–58.
Nadeeshani, H., Senevirathne, N., Somaratne, G., & Bandara, N. (2022). Recent trends in the utilization of pulse protein in food and industrial applications. ACS Food Science & Technology, 2(5), 722–737.
Nasrabadi, M. N., Doost, A. S., & Mezzenga, R. (2021). Modification approaches of plant-based proteins to improve their techno-functionality and use in food products. Food Hydrocolloids, 118, 106789.
Nisov, A., Ercili-Cura, D., & Nordlund, E. (2020). Limited hydrolysis of rice endosperm protein for improved techno-functional properties. Food Chemistry, 302, 125274.
Nonaka, M., Soeda, T., Yamagiwa, K., Kowata, H., Motogi, M., & Toiguchi, S. (1991). Process of preparing shelf-stable" tofu" at normal temperature for long term. In: Google Patents.
Nwachukwu, I. D., & Aluko, R. E. (2019). Structural and functional properties of food protein-derived antioxidant peptides. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 43(1), e12761.
Olagunju, A. I., Omoba, O. S., Enujiugha, V. N., Alashi, A. M., & Aluko, R. E. (2021). Thermoase-hydrolysed pigeon pea protein and its membrane fractions possess in vitro bioactive properties (antioxidative, antihypertensive, and antidiabetic). Journal of Food Biochemistry, 45(3), e13429.
Olatunde, O. O., & Benjakul, S. J. (2018). Natural preservatives for extending the shelf-life of seafood: A revisit. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 17(6), 1595–1612.
Oparil, S., Acelajado, M., Bakris, G., Berlowitz, D., Cífková, R., Dominiczak, A., Grassi, G., Jordan, J., Poulter, N., & Rodgers, A. (2018). Hypertension. Nature reviews. Disease primers, 4, 18014. In).
Pal, R., Bhartiya, A., ArunKumar, R., Kant, L., Aditya, J., & Bisht, J. (2016). Impact of dehulling and germination on nutrients, antinutrients, and antioxidant properties in horsegram. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 53(1), 337–347.
Pan, X., Fang, Y., Wang, L., Xie, M., Hu, B., Zhu, Y., Zhao, E., Pei, F., Shen, F., & Li, P. (2019). Effect of enzyme types on the stability of oil-in-water emulsions formed with rice protein hydrolysates. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(15), 6731–6740.
Pearson, K. M., Pannell, L. K., & Fales, H. M. (2002). Intramolecular cross-linking experiments on cytochrome c and ribonuclease A using an isotope multiplet method. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 16(3), 149–159.
Perreault, V., Hénaux, L., Bazinet, L., & Doyen, A. (2017). Pretreatment of flaxseed protein isolate by high hydrostatic pressure: Impacts on protein structure, enzymatic hydrolysis and final hydrolysate antioxidant capacities. Food Chemistry, 221, 1805–1812.
Pinterits, A., & Arntfield, S. D. (2008). Improvement of canola protein gelation properties through enzymatic modification with transglutaminase. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 41(1), 128–138.
Pontonio, E., Verni, M., Dingeo, C., Diaz-de-Cerio, E., Pinto, D., & Rizzello, C. G. (2020). Impact of enzymatic and microbial bioprocessing on antioxidant properties of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Antioxidants, 9(12), 1258.
Rizzello, C. G., De Angelis, M., Coda, R., & Gobbetti, M. (2006). Use of selected sourdough lactic acid bacteria to hydrolyze wheat and rye proteins responsible for cereal allergy. European Food Research and Technology, 223(3), 405–411.
Ruíz-Henestrosa, V. P., Carrera Sánchez, C., del Mar Yust, M., Pedroche, J., Millán, F., & Rodríguez Patino, J. M. (2007). Limited enzymatic hydrolysis can improve the interfacial and foaming characteristics of β-conglycinin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(4), 1536–1545.
Sah, W. I., & Alisha, N. (2018). The Influences of transglutaminase enzyme dosage on the meat characteristic from restructuring the animal and vegetable protein sources. In E3S Web of Conferences, vol. 67 (pp. 03043): EDP Sciences.
Samtiya, M., Acharya, S., Pandey, K. K., Aluko, R. E., Udenigwe, C. C., & Dhewa, T. (2021). Production, purification, and potential health applications of edible seeds’ bioactive peptides: A concise review. Foods, 10(11), 2696.
Sandoval-Sicairos, E. S., Milán-Noris, A. K., Luna-Vital, D. A., Milán-Carrillo, J., & Montoya-Rodríguez, A. (2021). Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of peptides released from germinated amaranth during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chemistry, 343, 128394.
Schettino, R., Pontonio, E., & Rizzello, C. G. (2019). Use of fermented hemp, chickpea and milling by-products to improve the nutritional value of semolina pasta. Foods, 8(12), 604.
Schlegel, K., Leidigkeit, A., Eisner, P., & Schweiggert-Weisz, U. (2019a). Technofunctional and sensory properties of fermented lupin protein isolates. Foods, 8(12), 678.
Schlegel, K., Sontheimer, K., Hickisch, A., Wani, A. A., Eisner, P., & Schweiggert-Weisz, U. (2019b). Enzymatic hydrolysis of lupin protein isolates-Changes in the molecular weight distribution, technofunctional characteristics, and sensory attributes. Food Science and Nutrition, 7(8), 2747–2759.
Segura-Campos, M., Espinosa-García, L., Chel-Guerrero, L., & Betancur-Ancona, D. (2012). Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on solubility, hydrophobicity, and in vivo digestibility in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). International Journal of Food Properties, 15(4), 770–780.
Seo, W. H., Lee, H. G., & Baek, H. H. (2008). Evaluation of bitterness in enzymatic hydrolysates of soy protein isolate by taste dilution analysis. Journal of Food Science, 73(1), S41–S46.
Shekarforoush, E., Jiang, X., Kedir Muhammed, M., Whitehead, K. A., Arneborg, N., & Risbo, J. (2022). Enzymatic modification and adsorption of hydrophobic zein proteins on lactic acid bacteria stabilize pickering emulsions. Food Research International, 161, 111783.
Shen, P., Zhou, F., Zhang, Y., Yuan, D., Zhao, Q., & Zhao, M. (2020). Formation and characterization of soy protein nanoparticles by controlled partial enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocolloids, 105, 105844.
Shi, X., Guo, R., White, B. L., Yancey, A., Sanders, T. H., Davis, J. P., Burks, A. W., & Kulis, M. (2013). Allergenic properties of enzymatically hydrolyzed peanut flour extracts. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 162(2), 123–130.
Silva, C. S., Moutinho, C., Ferreira da Vinha, A., & Matos, C. (2019). Trace minerals in human health: Iron, zinc, copper, manganese and fluorine. International Journal of Science and Research Methodology, 13(3), 57–80.
Singh, T. P., Siddiqi, R. A., & Sogi, D. S. (2021). Enzymatic modification of rice bran protein: Impact on structural, antioxidant and functional properties. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 138, 110648.
Sonklin, C., Alashi, A. M., Laohakunjit, N., & Aluko, R. E. (2021). Functional characterization of mung bean meal protein-derived antioxidant peptides. Molecules, 26(6), 1515.
Starzynska-Janiszewska, A., & Stodolak, B. (2011). Effect of inoculated lactic acid fermentation on antinutritional and antiradical properties of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus' Krab') flour. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 61(4).
Sung, D.-E., Lee, J., Han, Y., Shon, D.-H., Ahn, K., Oh, S., & Do, J.-R. (2014). Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis of buckwheat protein on antigenicity and allergenicity. Nutrition Research and Practice, 8(3), 278–283.
Taniya, M., Reshma, M., Shanimol, P., Krishnan, G., & Priya, S. (2020). Bioactive peptides from amaranth seed protein hydrolysates induced apoptosis and antimigratory effects in breast cancer cells. Food Bioscience, 35, 100588.
Tapal, A., & Tiku, P. K. (2019). Nutritional and nutraceutical improvement by enzymatic modification of food proteins. In M. Kuddus (Ed.), Enzymes in food biotechnology (pp. 471–481). Elsevier.
Trester-Zedlitz, M., Kamada, K., Burley, S. K., Fenyö, D., Chait, B. T., & Muir, T. W. (2003). A modular cross-linking approach for exploring protein interactions. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 125(9), 2416–2425.
Trigui, I., Yaich, H., Sila, A., Cheikh-Rouhou, S., Krichen, F., Bougatef, A., Attia, H., & Ayadi, M. (2021). Physical, techno-functional and antioxidant properties of black cumin seeds protein isolate and hydrolysates. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 15(4), 3491–3500.
Udenigwe, C. C., & Aluko, R. E. (2012). Food protein-derived bioactive peptides: Production, processing, and potential health benefits. Journal of Food Science, 77(1), R11–R24.
Urbizo-Reyes, U., San Martin-González, M. F., Garcia-Bravo, J., Vigil, A. L. M., & Liceaga, A. M. (2019). Physicochemical characteristics of chia seed (Salvia hispanica) protein hydrolysates produced using ultrasonication followed by microwave-assisted hydrolysis. Food Hydrocolloids, 97, 105187.
Vásquez-Villanueva, R., Muñoz-Moreno, L., Carmena, M. J., Marina, M. L., & García, M. C. (2018). In vitro antitumor and hypotensive activity of peptides from olive seeds. Journal of Functional Foods, 42, 177–184.
Venuste, M., Zhang, X., Shoemaker, C. F., Karangwa, E., Abbas, S., & Kamdem, P. E. (2013). Influence of enzymatic hydrolysis and enzyme type on the nutritional and antioxidant properties of pumpkin meal hydrolysates. Food and Function, 4(5), 811–820.
Vilcacundo, R., Martínez-Villaluenga, C., & Hernández-Ledesma, B. (2017). Release of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Journal of Functional Foods, 35, 531–539.
Vilcacundo, R., Miralles, B., Carrillo, W., & Hernández-Ledesma, B. (2018). In vitro chemopreventive properties of peptides released from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein under simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Research International, 105, 403–411.
Wang, B., Meng, T., Ma, H., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Jin, J., & Ye, X. (2016). Mechanism study of dual-frequency ultrasound assisted enzymolysis on rapeseed protein by immobilized Alcalase. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 32, 307–313.
Wang, J., Wang, T., Yu, G., Li, X., Liu, H., Liu, T., & Zhu, J. (2022). Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the physicochemical and emulsification properties of rice bran albumin and globulin fractions. LWT, 156, 113005.
Wang, L., Ding, Y., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Wang, R., Luo, X., Li, Y., Li, J., & Chen, Z. (2018). Isolation of a novel calcium-binding peptide from wheat germ protein hydrolysates and the prediction for its mechanism of combination. Food Chemistry, 239, 416–426.
Wine, R. N., Dial, J. M., Tomer, K. B., & Borchers, C. H. (2002). Identification of components of protein complexes using a fluorescent photo-cross-linker and mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 74(9), 1939–1945.
Wu, W., Zhang, M., Sun, C., Brennan, M., Li, H., Wang, G., Lai, F., & Wu, H. (2016). Enzymatic preparation of immunomodulatory hydrolysates from defatted wheat germ (Triticum Vulgare) globulin. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 51(12), 2556–2566.
Xu, N., Chen, G., & Liu, H. (2017). Antioxidative categorization of twenty amino acids based on experimental evaluation. Molecules, 22(12), 2066.
Yang, A., Zuo, L., Cheng, Y., Wu, Z., Li, X., Tong, P., & Chen, H. (2018). Degradation of major allergens and allergenicity reduction of soybean meal through solid-state fermentation with microorganisms. Food and Function, 9(3), 1899–1909.
Yarnpakdee, S., Benjakul, S., Kristinsson, H. G., & Kishimura, H. J. (2015). Antioxidant and sensory properties of protein hydrolysate derived from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by one-and two-step hydrolysis. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(6), 3336–3349.
Yu, J., Ahmedna, M., Goktepe, I., Cheng, H., & Maleki, S. (2011). Enzymatic treatment of peanut kernels to reduce allergen levels. Food Chemistry, 127(3), 1014–1022.
Yu, J., Goktepe, I., & Ahmedna, M. (2013). Enzymatic treatment of peanut butter to reduce the concentration of major peanut allergens. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 48(6), 1224–1234.
Yu, J., Hernandez, M., Li, H., Goktepe, I., Robinette, C., Auerbach, A., Peden, D., & Ahmedna, M. (2015). Allergenicity of roasted peanuts treated with a non-human digestive protease. Food Research International, 69, 341–347.
Zamani, A., Madani, R., Rezaei, M., & Benjakul, S. (2017). Antioxidative activitiy of protein hydrolysate from the muscle of common kilka (Clupeonella cultriventris caspia) prepared using the purified trypsin from common kilka intestine. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology, 26(1), 2–16.
Zhang, M., & Mu, T.-H. (2017). Identification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from sweet potato protein hydrolysates by Alcalase under high hydrostatic pressure. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 43, 92–101.
Zhang, Q., Cheng, Z., Wang, Y., Zheng, S., Wang, Y., & Fu, L. (2021). Combining Alcalase hydrolysis and transglutaminase-cross-linking improved bitterness and techno-functional properties of hypoallergenic soybean protein hydrolysates through structural modifications. LWT, 151, 112096.
Zhang, Z., Kobata, K., Pham, H., Kos, D., Tan, Y., Lu, J., & McClements, D. J. (2022). Production of plant-based seafood: Scallop analogs formed by enzymatic gelation of pea protein-pectin mixtures. Foods, 11(6), 851.
Zou, Z., Wang, M., Wang, Z., Aluko, R. E., & He, R. (2020). Antihypertensive and antioxidant activities of enzymatic wheat bran protein hydrolysates. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 44(1), e13090.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge funding support from the Canada Research Chairs Program to N. Bandara and R.E. Aluko and the NSERC Discovery Grant Program to N. Bandara (RGPIN 2020–07136) and R.E. Aluko (RGPIN 2018–06019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Oladipupo O. Olatunde, Iyiola O. Owolabi, Olamide S. Fadairo, Anujit Ghosal, and Oluwafemi J. Coker collected and compiled the data, wrote the manuscript, and revised it. Olugbenga P. Soladoye, Rotimi E. Aluko, and Nandika Bandara revised the manuscript. Oladipupo O. Olatunde and Nandika Bandara planned, drafted, and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Olatunde, O.O., Owolabi, I.O., Fadairo, O.S. et al. Enzymatic Modification of Plant Proteins for Improved Functional and Bioactive Properties. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 1216–1234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02971-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02971-5