Abstract
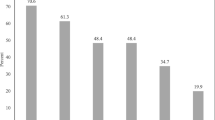
Organophosphate (OP) compounds are widely used in different applications including agriculture. The widespread use of OP insecticides, however, brings high risks of severe health problems. Besides occupational poisoning in industrial production and agricultural application, instances of acute organophosphate poisoning (OPP) also include suicide, homicide, and accidental overdose. Cardiovascular manifestations frequently accompany exposure to these organophosphorus compounds, but their exact nature is not fully elucidated. In this study, we evaluated 20 patients who presented to our emergency department with organophosphorus (OP) poisoning and discussed their associated electrocardiographic (ECG) abnormalities. Over 3 months, 20 patients with OP poisoning were included in this prospective study. ECG analysis included the rate, ST-T abnormalities, conduction defects, and measurement of PR and “QTc” intervals. Our results show that 12 patients were having prolonged QTc interval i.e., >0.43 s. Eight patients were having mild elevated ST segment and low-amplitude “T” waves. Most of the patients have shown increased heart rate, where as some has shown decreased value. From this study, we conclude that acute organophosphorus poisoning is associated with ventricular arrhythmias, tachycardia and bradycardia, and attributes mild myocardial ischemia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gagandeep, S., & Dheeraj, K. (2009). Neurology of acute organophosphate poisoning. Neurology India, 57, 119–125.
Vijayakumar, S., Fareedullah, M., Venkateswarlu, B., Sudhakar, Y., & Ashok kumar, E. (2010). Current review on organophosphorus poisoning. Archives of Applied Science Research., 2(4), 199–215.
Comroe, J. H., Todd, J., Gammon, G. D., Leopold, I. H., Koelle, G. B., & Bodansky, O. (1946). The effect of di-isopropyl-fluorphosphate (DFP) upon patients with myasthenia gravis. American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 212, 641–651.
Grob, D., & Harvey, A. M. (1949). Observations on the effects of tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) in man and on its use in treatment of myasthenia gravis. Bull Johns Hopkins Hospital, 84, 533–567.
Rider, J. A., Schulman, S., Richtern, R. B., Moeller, H. D., & Du Bois, K. P. (1951). Treatment of myasthenia gravis with octainethyl pyrophosphoramide. JAMA, 145, 967–972.
Khurram, S. R., Owais, F. M., Ahmad, B., Qurashi, F. S., & Shaheen, M. (2008). Organophosphorus compound poisoning; Epidemiology and management. Professional Medical Journal, 15(4), 518–523.
Ludomirsky, A., Klein, H. O., Sarelli, P., Becker, B., Hoffman, S., & Taitelman, U. (1982). Q-T prolongation and polymorphous (“Torsade de pointes”) Ventricular arrhythmias associated with OP insecticide poisoning. The American Journal of Cardiology, 49, 1654–1658.
Povoa, R., Cardoso, S. H., & Luna-Filho, B. (1997). Organophosphate poisoning and myocardial necrosis. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia, 68, 377–380.
Saadeh, A. M., Farsakh, N. A., & Al-Ali, M. K. (1997). Cardiac manifestations of acute carbamate and organophosphate poisoning. Heart, 77, 461–464.
Juliana, M. T., Nathan, D. M., Diana, A. M., Francisco, T. R., & Ana, L. K. (2009). Cardio-respiratory function and oxidative stress biomarkers in Nile-tilapia exposed to the organophosphate insecticide trichlorfon. Ecotoxichology and Environmental Safety, 72, 1413–1424.
Yusuf, Y., Yucel, Y., Hayrettin, S., Polat, D., Seda, O., & Okhan, A. (2009). Electrocardiographic findings of acute organophosphate poisoning. Journal of Emergency Medicine, 36, 39–42.
Kiss, Z., & Fazekas, T. (1979). Arrhythmias in organophosphate poisonings. Acta Cardiologica, 34, 323–330.
Cherian, M. A., Roshini, C., Peter, J. V., & Cherian, A. M. (2005). Oximes in organophosphorus poisoning. Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine, 9, 155–163.
Schwart, P. F., & Priori, S. G. (2004). Long QT syndrome: genotype-phenotype correlations. In D. P. Zipes & J. Jalife (Eds.), Cardiac electrophysiology from cell to bedside (4th ed., pp. 651–659). Philadelphia: Saunders.
Ford, G. A., Wood, S. M., & Daly, A. K. (2003). CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes of patients with terodiline cardiotoicity identified through the yellow card system. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 50, 77–80.
Priori, S. G., Schwartz, P. J., Napolitano, C., Bloise, R., Ronchetti, E., Grillo, M., et al. (2003). Risk stratification in the long-QT syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine, 348, 1866–1874.
Luzhnikov, E. A., Savina, A. S., & Shepelev, V. M. (1975). Pathogenesis of disorders of cardiac rhythm and conductivity in acute organophosphate insecticide poisoning. Kardiologia (U.S.S.R.), 15, 126–129.
Ludomirsky, A., Klein, H. O., Sarelli, P., Becker, B., Hoffman, S., Taitelman, U., et al. (1982). QT prolongation and polymorphous (torsade de pointes) ventricular arrhythmias associated with organophosphorus insecticide poisoning. American Journal of Cardiology, 49, 1654–1658.
Kumiko, T., Yoshiko, A., & Miwako, K. (2006). Long QT and ST-T change associated with organophosphate exposure by aerial spray. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 22, 40–45.
Thevenin, J., Da Costa, A., Roche, F., Romeyer, C., Messier, M., & Isaaz, K. (2003). Flecainide induced ventricular tachycardia (torsades de pointes). Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 26, 1907–1908.
Abraham, S., Oz, N., Sahar, R., & Kadar, T. (2001). QTc prolongation and cardiac lesions following acute organophosphate poisoning in rats. Proceedings of the Western Pharmacology Society, 44, 185–186.
Lovejoy, F. H., & Linden, C. H. (1991). Acute poison and drug overdosage. In: Harrison’s principles of internal medicine (12th ed., p. 2178) New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hayes, M. M., Van der Westhuizen, N. G., & Gelfand, M. (1978). Organophosphate poisoning in Rhodesia. A study of the clinical features and management of 105 patients. South African Medical Journal, 54, 230–234.
Bardin, P. G., Van Eeden, S. F., & Joubert, J. R. (1987). Intensive care management of acute organophosphate poisoning. A 7-year experience in the Western Cape. South African Medical, 72, 593–597.
Namba, T., Nolte, C. T., Jackrel, J., & Grob, D. (1971). Poisoning due to organophosphate insecticides. Acute and chronic manifestations. American Journal of Medicine, 50, 475–492.
Reigart, J. R., & Roberts, J. R. R. (1999). Recognition and management of pesticide poisonings (5th ed.). Washington: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Mr. R. Sunil and Mr. G. Prashanth, Cardio technicians of our hospital for their valuable support in spite of their busy schedule.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vijayakumar, S., Fareedullah, M., Ashok Kumar, E. et al. A Prospective Study on Electrocardiographic Findings of Patients with Organophosphorus Poisoning. Cardiovasc Toxicol 11, 113–117 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-011-9104-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-011-9104-4