Abstract
Objective
In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the relationship between the survival rate of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and expression of two biomarkers along with age, gender, tumor margin, depth of invasion, site of tumor, tumor diameter, tumor grade, number of involved nodes, and vascular invasion.
Materials and Methods
In this retrospective survey, medical records of patients referred to the Shohada-e Tajrish hospital during 2001 to 2005 were reviewed and subjects with definite diagnosis of SCC were included. Required data were extracted from the patients’ records, and their prepared paraffin-embedded tissue blocks were collected under supervision of two pathologists. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis was performed at the Firoozgar hospital in Tehran, Iran.
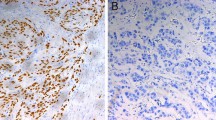
Results
The studied population included 20 men (74%) and 7 women (26%). The mean age at diagnosis was 58 ± 22. Results showed significantly higher survival rates in women compared to men (85.7 vs. 40%) (p = 0.001) and in patients with well-differentiated tumors compared to poor-differentiated cases (20 vs. 5%) (p = 0.004). No significant relationship was found between p53 expression and prognostic factors like age, gender, the site, grade, and size of the tumor, depth of invasion, involvement of lymph nodes, and vascular invasion.
Conclusion
Positivity of p53 and cyclin D1 was not found to be predictive of survival in patients with esophageal SCC which might be due to the small sample size of the present survey. Further investigations with larger sample populations and longer follow-ups are required to evaluate this correlation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Allameh A, Rasmi Y, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Tavangar SM, Sharifi R, Sadreddini M. Immunohistochemical analysis of selected molecular markers in esophagus precancerous, adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in Iranian subjects. Cancer Epidemiol. 2009;33(1):79–84.
Li H, Xiao W, Ma J, Zhang Y, Li R, Ye J, et al. Dual high expression of STAT3 and cyclinD1 is associated with poor prognosis after curative resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(11):7989–98.
Munoz N. Epidemiological aspects of oesophageal cancer. Endoscopy. 1993;25(09):609–12.
Parkin D, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide incidence of eighteen major cancers in 1985. Int J Cancer. 1993;54(4):594–606.
Pisani P, Parkin D, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from eighteen major cancers in 1985. Implications for prevention and projections of future burden. Int J Cancer. 1993;55(6):891–903.
Lam AKY. Molecular biology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2000;33(2):71–90.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–108.
Shadi Kolahdoozan MDM, Alireza Sadjadi MDM, Radmard AR, Hooman Khademi MDM. Five common cancers in Iran. Archives of Iranian medicine. 2010;13(2):143.
Chava S, Mohan V, Shetty P, Manolla M, Vaidya S, Khan I, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of p53, FHIT, and IGF2 gene expression in esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2012;25(1):81–7.
Ishikawa T, Furihata M, Ohtsuki Y, Murakami H, Inoue A, Ogoshi S. Cyclin D1 overexpression related to retinoblastoma protein expression as a prognostic marker in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1998;77(1):92.
Kawakubo H, Ozawa S, Ando N, Kitagawa Y, Mukai M, Ueda M, et al. Alterations of p53, cyclin D1 and pRB expression in the carcinogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2005;14(6):1453–60.
Vaninetti NM, Geldenhuys L, Porter GA, Risch H, Hainaut P, Guernsey DL, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitrotyrosine and p53 mutations in the molecular pathogenesis of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2008;47(4):275–85.
Wang G, Abnet C, Shen Q, Lewin K, Sun X, Roth M, et al. Histological precursors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: results from a 13 year prospective follow up study in a high risk population. Gut. 2005;54(2):187–92.
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote M, Pagano M, Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7(5):812–21.
Makino T, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Yoshioka S, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, et al. p53 mutation status predicts pathological response to chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(3):804–11.
Naganuma S, Whelan KA, Natsuizaka M, Kagawa S, Kinugasa H, Chang S, et al. Notch receptor inhibition reveals the importance of cyclin D1 and Wnt signaling in invasive esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 2012;2(4):459–475.
Nozoe T, Maehara Y. Over-expression of p53 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of women. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2005;53(67):73–6.
Nakajima Y, Nagai K, Miyake S, Ohashi K, Kawano T, Iwai T. Evaluation of an indicator for lymph node metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invading the submucosal layer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002;93(3):305–12.
Zhao J, Li L, Wei S, Gao Y, Chen Y, Wang G, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic role of cyclin D1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Dis Esophagus. 2012;25(6):520–6.
Mirinezhad SK, Somi MH, Jangjoo AG, Seyednezhad F, Dastgiri S, Mohammadzadeh M, et al. Survival rate and prognostic factors of esophageal cancer in East Azerbaijan province, north-west of Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(7):3451–4.
Hajian-Tilaki K. Factors affecting the survival of patients with oesophageal carcinoma under radiotherapy in the north of Iran. Br J Cancer. 2001;85(11):1671.
Van Andel J, Dees J, Dijkhuis C, Fokkens W, Van Houten H, De Jong P, et al. Carcinoma of the esophagus: results of treatment. Ann Surg. 1979;190(6):684.
Kinoshita Y, Endo M, Nakayama K, Sato H. Evaluation of ten-year survival after operation for upper-and mid-thoracic esophageal cancer. Int Adv Surg Oncol. 1977;1:173–200.
Shimada Y, Imamura M, Watanabe G, Uchida S, Harada H, Makino T, et al. Prognostic factors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma from the perspective of molecular biology. Br J Cancer. 1999;80(8)
Jeremic B, Shibamoto Y, Acimovic L, Matovic Z, Milicic B, Milisavljevic S, et al. Accelerated hyperfractionated radiation therapy and concurrent 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin chemotherapy for locoregional squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: a phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;40(5):1061–6.
Malhaire J-P, Lozac'h P, Simon H, Labat J-P, Topart P, Lucas B, et al. Split-course concomitant radiochemotherapy plus surgery vs. surgery alone in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. A non-randomized retrospective study of 184 patients. Bull Cancer. 1997;84(4):357–67.
Kolh P, Honore P, Gielen J, Degauque C, Azzam C, Legrand M, et al. Analysis of factors influencing long-term survival after surgical resection for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Chir Belg. 1998;99(3):113–8.
Launois B, Paul J, Lygidakis N, Campion J, Malledant Y, Grossetti D, et al. Results of the surgical treatment of carcinoma of the esophagus. Surgery, gynecology & obstetrics. 1983;156(6):753–60.
Petrequin P, Huguier M, Lacaine F, Houry S. Surgically treated esophageal cancers: predictive model of survival. Gastroenterologie clinique et biologique. 1996;21(1):12–6.
Slevin NJ, Stout R. Carcinoma of the oesophagus—a review of 108 cases treated by radical radiotherapy. Clin Radiol. 1989;40(2):200–3.
Giuli R, Gignoux M. Treatment of carcinoma of the esophagus: retrospective study of 2,400 patients. Ann Surg. 1980;192(1):44.
Roshandel G, Merat S, Sotoudeh M, Khoshnia M, Poustchi H, Lao-Sirieix P, et al. Pilot study of cytological testing for oesophageal squamous cell dysplasia in a high-risk area in northern Iran. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(12):2235–41.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Cancer Research Center of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences for their kind cooperation and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Cancer Research Center of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saemi, N., Khoshnevis, J., Akbari, M.E. et al. Evaluating the Correlation Between the Survival Rate of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Expression of p53 and Cyclin D1 Biomarkers Along with Other Prognostic Factors. J Gastrointest Canc 49, 35–40 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-016-9905-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-016-9905-6