Abstract
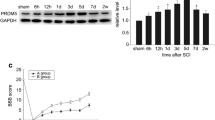
Wnt can induce signal transduction via the canonical pathway, which was involved in many processes in the nervous system. Nemo-like kinase (NLK) acts as a negative regulator of β-catenin/T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (LEF) and functions downstream of transforming growth factor β-activated kinase-1 in the Wnt signaling pathway. In this study, we performed a spinal cord injury (SCI) test in adult Sprague–Dawley rats and investigated the dynamic changes and role of NLK expression in the spinal cord. Western blot analysis revealed that NLK expression was low in normal spinal cord. It then increased markedly, peaked at 3 days, and declined to basal levels from 5 days after injury. Immunohistochemistry confirmed that NLK immunoactivity was expressed at low levels in gray and white matter under normal conditions and increased prominently in gray matter after the SCI test. Double immunofluorescent staining for NLK, caspase-3, β-catenin, and NeuN (neuronal nuclei) revealed that NLK and β-catenin were markedly increased and colocalized in apoptotic neurons. Coimmunoprecipitation data demonstrated that overexpression of NLK protein reduced β-catenin binding to LEF-1. Our results suggested that NLK was associated with neuronal apoptosis through attenuating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway after SCIs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- CDKs:
-
Cyclin-dependent protein kinases
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidin
- ERKs/MAPKs:
-
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinases/mitogen-associated protein kinases
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence system
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- LEF:
-
Lymphoid enhancer factor
- NeuN:
-
Neuronal nuclei
- NLK:
-
Nemo-like kinase
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TAK-1:
-
Transforming growth factor β-activated kinase-1
- TCF:
-
T-cell factor
- SCI:
-
Spinal cord injury
References
Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W (1996) Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382:638–642
Bracken MB, Freeman DJ, Hellenbrand K (1981) Incidence of acute traumatic hospitalized spinal cord injury in the United States, 1970-1977. Am J Epidemiol 113:615–622
Braun MM, Etheridge A, Bernard A, Robertson CP, Roelink H (2003) Wnt signaling is required at distinct stages of development for the induction of the posterior forebrain. Development 130:5579–5587
Brott BK, Pinsky BA, Erikson RL (1998) Nlk is a murine protein kinase related to Erk/MAP kinases and localized in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:963–968
Caraci F, Busceti C, Biagioni F, Aronica E, Mastroiacovo F, Cappuccio I, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Caricasole A, Copani A, Nicoletti F (2008) The Wnt antagonist, Dickkopf-1, as a target for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Res 33:2401–2406
Chen HL, Panchision DM (2007) Concise review: bone morphogenetic protein pleiotropism in neural stem cells and their derivatives–alternative pathways, convergent signals. Stem Cells 25:63–68
Chen RW, Qin ZH, Ren M, Kanai H, Chalecka-Franaszek E, Leeds P, Chuang DM (2003) Regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, p38 kinase and AP-1 DNA binding in cultured brain neurons: roles in glutamate excitotoxicity and lithium neuroprotection. J Neurochem 84:566–575
Chenn A, Walsh CA (2002) Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science 297:365–369
Chesnutt C, Burrus LW, Brown AM, Niswander L (2004) Coordinate regulation of neural tube patterning and proliferation by TGFbeta and WNT activity. Dev Biol 274:334–347
Chizhikov VV, Millen KJ (2004) Control of roof plate development and signaling by Lmx1b in the caudal vertebrate CNS. J Neurosci 24:5694–5703
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Hou J, Maiese K (2010) Wnt1 neuroprotection translates into improved neurological function during oxidant stress and cerebral ischemia through AKT1 and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3:153–165
Ciani L, Salinas PC (2005) WNTs in the vertebrate nervous system: from patterning to neuronal connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:351–362
Coyle-Rink J, Del VL, Sweet T, Khalili K, Amini S (2002) Developmental expression of Wnt signaling factors in mouse brain. Cancer Biol Ther 1:640–645
Emami KH, Brown LG, Pitts TE, Sun X, Vessella RL, Corey E (2009) Nemo-like kinase induces apoptosis and inhibits androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 69:1481–1492
Fernandez-Martos CM, Gonzalez-Fernandez C, Gonzalez P, Maqueda A, Arenas E, Rodriguez FJ (2011) Differential expression of Wnts after spinal cord contusion injury in adult rats. PLoS One 6:e27000
Gaulden J, Reiter JF (2008) Neur-ons and neur-offs: regulators of neural induction in vertebrate embryos and embryonic stem cells. Hum Mol Genet 17:R60–R66
Gruner JA (1992) A monitored contusion model of spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 9(123–126):126–128
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor cells. Development 131:2791–2801
Huelsken J, Birchmeier W (2001) New aspects of Wnt signaling pathways in higher vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11:547–553
Hyodo-Miura J, Urushiyama S, Nagai S, Nishita M, Ueno N, Shibuya H (2002) Involvement of NLK and Sox11 in neural induction in Xenopus development. Genes Cells 7:487–496
Ille F, Sommer L (2005) Wnt signaling: multiple functions in neural development. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:1100–1108
Ishitani T, Ishitani S (2013) Nemo-like kinase, a multifaceted cell signaling regulator. Cell Signal 25:190–197
Ishitani T, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Nagai S, Nishita M, Meneghini M, Barker N, Waterman M, Bowerman B, Clevers H, Shibuya H, Matsumoto K (1999) The TAK1-NLK-MAPK-related pathway antagonizes signalling between beta-catenin and transcription factor TCF. Nature 399:798–802
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, Ueno N, Yasuda J, Waterman M, Shibuya H, Moon RT, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K (2003a) The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23:131–139
Ishitani T, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K (2003b) Regulation of lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T-cell factor by mitogen-activated protein kinase-related Nemo-like kinase-dependent phosphorylation in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23:1379–1389
Jana A, Hogan EL, Pahan K (2009) Ceramide and neurodegeneration: susceptibility of neurons and oligodendrocytes to cell damage and death. J Neurol Sci 278:5–15
Jiang SD, Yan J, Jiang LS, Dai LY (2011) Down-regulation of the Wnt, estrogen receptor, insulin-like growth factor-I, and bone morphogenetic protein pathways in osteoblasts from rats with chronic spinal cord injury. Joint Bone Spine 78:488–492
Kalani MY, Cheshier SH, Cord BJ, Bababeygy SR, Vogel H, Weissman IL, Palmer TD, Nusse R (2008) Wnt-mediated self-renewal of neural stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16970–16975
Kaletta T, Schnabel H, Schnabel R (1997) Binary specification of the embryonic lineage in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 390:294–298
Karim R, Tse G, Putti T, Scolyer R, Lee S (2004) The significance of the Wnt pathway in the pathology of human cancers. Pathology 36:120–128
Kanei-Ishii C, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Tanikawa J, Nomura T, Ishitani T, Kishida S, Kokura K, Kurahashi T, Ichikawa-Iwata E, Kim Y, Matsumoto K, Ishii S (2004) Wnt-1 signal induces phosphorylation and degradation of c-Myb protein via TAK1, HIPK2, and NLK. Genes Dev 18:816–829
Kurahashi T, Nomura T, Kanei-Ishii C, Shinkai Y, Ishii S (2005) The Wnt-NLK signaling pathway inhibits A-Myb activity by inhibiting the association with coactivator CBP and methylating histone H3. Molr Biol Cell 16:4705–4713
Li Z, Cui G, Wang J, Yu Z, Zhao L, Lv Z (2012) Nemo-like kinase (NLK) involves in neuronal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:381–389
Megason SG, McMahon AP (2002) A mitogen gradient of dorsal midline Wnts organizes growth in the CNS. Development 129:2087–2098
Meneghini MD, Ishitani T, Carter JC, Hisamoto N, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Thorpe CJ, Hamill DR, Matsumoto K, Bowerman B (1999) MAP kinase and Wnt pathways converge to downregulate an HMG-domain repressor in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 399:793–797
Mirkovic I, Charish K, Gorski SM, McKnight K, Verheyen EM (2002) Drosophila nemo is an essential gene involved in the regulation of programmed cell death. Mech Dev 119:9–20
Molenaar M, van de Wetering M, Oosterwegel M, Peterson-Maduro J, Godsave S, Korinek V, Roose J, Destree O, Clevers H (1996) XTcf-3 transcription factor mediates beta-catenin-induced axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell 86:391–399
Muroyama Y, Fujihara M, Ikeya M, Kondoh H, Takada S (2002) Wnt signaling plays an essential role in neuronal specification of the dorsal spinal cord. Genes Dev 16:548–553
Ota S, Ishitani S, Shimizu N, Matsumoto K, Itoh M, Ishitani T (2012) NLK positively regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signalling by phosphorylating LEF1 in neural progenitor cells. Embo J 31:1904–1915
Rocheleau CE, Yasuda J, Shin TH, Lin R, Sawa H, Okano H, Priess JR, Davis RJ, Mello CC (1999) WRM-1 activates the LIT-1 protein kinase to transduce anterior/posterior polarity signals in C. elegans. Cell 97:717–726
See J, Zhang X, Eraydin N, Mun SB, Mamontov P, Golden JA, Grinspan JB (2004) Oligodendrocyte maturation is inhibited by bone morphogenetic protein. Mol Cell Neurosci 26:481–492
Smit L, Baas A, Kuipers J, Korswagen H, van de Wetering M, Clevers H (2004) Wnt activates the Tak1/Nemo-like kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 279:17232–17240
Tetsu O, McCormick F (1999) Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 398:422–426
Thorpe CJ, Moon RT (2004) nemo-like kinase is an essential co-activator of Wnt signaling during early zebrafish development. Development 131:2899–2909
Ulloa F, Marti E (2010) Wnt won the war: antagonistic role of Wnt over Shh controls dorso-ventral patterning of the vertebrate neural tube. Dev Dyn 239:69–76
Veeman MT, Axelrod JD, Moon RT (2003) A second canon. Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent Wnt signaling. Dev Cell 5:367–377
Verheyen EM, Mirkovic I, MacLean SJ, Langmann C, Andrews BC, MacKinnon C (2001) The tissue polarity gene nemo carries out multiple roles in patterning during Drosophila development. Mech Dev 101:119–132
Zechner D, Fujita Y, Hulsken J, Muller T, Walther I, Taketo MM, Crenshaw ER, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C (2003) Beta-Catenin signals regulate cell growth and the balance between progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the nervous system. Dev Biol 258:406–418
Zhuang B, Sockanathan S (2006) Dorsal-ventral patterning: a view from the top. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16:20–24
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China grant (no. 81300955), projects of Nantong (no. BK2011013 and no. BK2012075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dawei Xu and Wei Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Zhao, W., Pan, G. et al. Expression of Nemo-like kinase after spinal cord injury in rats. J Mol Neurosci 52, 410–418 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0191-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0191-5