Abstract
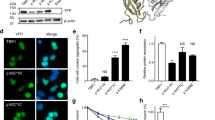
TBL1XR1 is a member of the WD40 repeat-containing gene family. Mutations of TBL1XR1 have been reported in neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs). Although the phenotypes of some patients have been described in single studies, few studies have reviewed the genotype and phenotype relationships using a relatively large cohort of patients with TBL1XR1 mutations. Herein, we report a new de novo frameshift mutation in TBL1XR1 (NM_024665.4, c.388_389delAC, p.T130Sfs*14) in a patient with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). To explore the correlations between genotypes and phenotypes for TBL1XR1 in NDDs, we manually curated and analyzed 38 variants and the associated phenotypes from 50 individuals with NDDs. TBL1XR1 mutations lead to a wide range of phenotypic defects. We conclude that the most common phenotypes associated with TBL1XR1 mutations were language and motor developmental delay, intellectual disabilities, facial deformity, hypotonia, and microcephaly. Our study provides a comprehensive spectrum of neurodevelopmental phenotypes caused by TBL1XR1 mutations, which is important for genetic diagnosis and precision clinical management.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Cadigan KM (2008) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: turning the switch. Dev Cell 14:322–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.006
Heinen CA et al (2016) A specific mutation in TBL1XR1 causes Pierpont syndrome. J Med Genet 53:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103233
Hu X, Lazar MA (2000) Transcriptional repression by nuclear hormone receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1043-2760(99)00215-5
Kobayashi Y et al (2016) High prevalence of genetic alterations in early-onset epileptic encephalopathies associated with infantile movement disorders. Brain Dev 38:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2015.09.011
Landrum MJ, Kattman BL (2018) ClinVar at five years: delivering on the promise. Hum Mutat 39:1623–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23641
Laskowski RA et al (2016) Integrating population variation and protein structural analysis to improve clinical interpretation of missense variation: application to the WD40 domain. Hum Mol Genet 25:927–935. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv625
Lek M et al (2016) Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19057
Lelieveld SH et al (2016) Meta-analysis of 2,104 trios provides support for 10 new genes for intellectual disability. Nat Neurosci 19:1194–1196. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4352
Noelanders R, Vleminckx K (2017) How Wnt signaling builds the brain: bridging development and disease. Neuroscientist 23:314–329. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858416667270
Oberoi J et al (2011) Structural basis for the assembly of the SMRT/NCoR core transcriptional repression machinery. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1983
O'Roak BJ et al (2012) Multiplex targeted sequencing identifies recurrently mutated genes in autism spectrum disorders. Science 338:1619–1622. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1227764
O'Roak BJ, Stessman HA, Boyle EA, Witherspoon KT, Martin B, Lee C, Vives L, Baker C, Hiatt JB, Nickerson DA, Bernier R, Shendure J, Eichler EE (2014) Recurrent de novo mutations implicate novel genes underlying simplex autism risk. Nat Commun 5:5595. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6595
Perissi V, Aggarwal A, Glass CK, Rose DW, Rosenfeld MG (2004) A corepressor/coactivator exchange complex required for transcriptional activation by nuclear receptors and other regulated transcription factors. Cell 116:511–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00133-3
Pierpont ME, Stewart FJ, Gorlin RJ (1998) Plantar lipomatosis, unusual facial phenotype and developmental delay: a new MCA/MR syndrome. Am J Med Genet 75:18–21
Pons L et al (2015) A new syndrome of intellectual disability with dysmorphism due to TBL1XR1 deletion. Am J Med Genet A 167A:164–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.36759
Richards S et al (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17:405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30
Riehmer V et al (2017) A heritable microduplication encompassing TBL1XR1 causes a genomic sister-disorder for the 3q26.32 microdeletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 173:2132–2138. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.38285
Saitsu H et al (2014) A girl with West syndrome and autistic features harboring a de novo TBL1XR1 mutation. J Hum Genet 59:581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2014.71
Stenson PD et al (2017) The Human Gene Mutation Database: towards a comprehensive repository of inherited mutation data for medical research, genetic diagnosis and next-generation sequencing studies. Hum Genet 136:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1779-6
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq603
Wang T, Guo H, Xiong B, Stessman HAF, Wu H, Coe BP, Turner TN, Liu Y, Zhao W, Hoekzema K, Vives L, Xia L, Tang M, Ou J, Chen B, Shen Y, Xun G, Long M, Lin J, Kronenberg ZN, Peng Y, Bai T, Li H, Ke X, Hu Z, Zhao J, Zou X, Xia K, Eichler EE (2016) De novo genic mutations among a Chinese autism spectrum disorder cohort. Nat Commun 7:13316. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13316
Yoon HG, Chan DW, Huang ZQ, Li J, Fondell JD, Qin J, Wong J (2003) Purification and functional characterization of the human N-CoR complex: the roles of HDAC3, TBL1 and TBLR1. EMBO J 22:1336–1346. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg120
Zhang XM, Chang Q, Zeng L, Gu J, Brown S, Basch RS (2006) TBLR1 regulates the expression of nuclear hormone receptor co-repressors BMC. Cell Biol 7:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2121-7-31
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the family who participated in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81330027, 81525007). H.G. was also supported by the China Hunan Provincial Science & Technology Department (2019RS2005), the Major Scientific and Technological Projects for collaborative prevention and control of birth defects in Hunan Province (2019SK1010) and Innovation-Driven Project of Central South University (2020CX042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of Center for Medical Genetics, Central South University.
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the family in the study.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the family in the study.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(XLSX 45 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, Y., Zhang, Q., Chen, M. et al. Genotype and Phenotype Correlations for TBL1XR1 in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. J Mol Neurosci 70, 2085–2092 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01615-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01615-7