Abstract
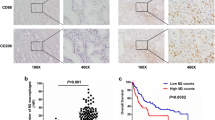
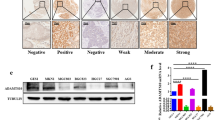
Patients with chronic pancreatitis with local inflammation have high risk for pancreatic cancer. The aim of this study was to examine the role of the inflammatory cells in the invasion of pancreatic cancer cells, focusing on the involvement of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 8 (ADAM8) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) proteins. ADAM8 expression is associated with worse survival of pancreatic cancer patients. Monocytes from healthy donors were differentiated into macrophages. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells were cultured either alone or with differentiated macrophages. The cancer cell migration rate in Matrigel was measured by imaging fluorescently stained cells for 24 h. After invasion, cells were sorted into CD14 positive/negative macrophages and cancer cells with magnetic separation. The expression of ADAM8 and MMP9 was measured by the real-time PCR. Protein-level expression of ADAM8 and MMP9 was analyzed by Western blotting. In two series, siRNA technique was used to reduce either ADAM8 or MMP9 expression in the cancer cells. The coculture with macrophages increased cancer cell migration rate in Matrigel, and increased ADAM8 and MMP9 mRNA expression and protein level in the cancer cells. Reduction of ADAM8 expression with siRNA in the cancer cells decreased macrophage-induced migration rate of the cancer cells from 11.7 ± 0.3 μm/h to 9.0 ± 0.2 μm/h (p < 0.01), and reduction of MMP9 expression decreased the migration rate to 10.1 ± 0.2 μm/h (p < 0.01). Anti-inflammatory macrophages increase pancreatic cancer cell migration rate in basement membrane matrix by inducing ADAM8 and MMP9 expression in cancer cells, thereby possibly enhancing the invasiveness of cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puolakkainen PA, Brekken RA, Muneer S, Sage EH. Enhanced growth of pancreatic tumors in SPARC-null mice is associated with decreased deposition of extracellular matrix and reduced tumor cell apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 2004;2:215–24.
Chong HC, Tan CK, Huang RL, Tan NS. Matricellular proteins: a sticky affair with cancers. J Oncol. (2012);351089.
McKay CJ, Glen P, McMillan DC. Chronic inflammation and pancreatic cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;22:65–73.
Arnold S, Rivera LB, Miller AF, Carbon JG, Dineen SP, Xie Y, Castrillon DH, Sage EH, Puolakkainen P, Bradshaw AD, Brekken RA. Lack of host SPARC enhances vascular function and tumor spread in an orthotopic murine model of pancreatic carcinoma. Dis Model Mech. 2010;3:57–72.
Pelli H, Juuti A, Mustonen H, Nordling S, Sirén J, Haglund C, Kiviluoto T. Results of 546 consecutive pancreatic operations at Helsinki University Hospital, Finland. Pancreatology. 2010;10:NLS33.
Mielgo A, Schmid MC. Impact of tumour associated macrophages in pancreatic cancer. BMB Rep. 2013;46:31–8.
Giraudo E, Inoue M, Hanahan D. An amino-bisphosphonate targets MMP-9-expressing macrophages and angiogenesis to impair cervical carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:623–33.
Shen Z, Kauttu T, Cao J, Seppänen H, Vainionpää S, Ye Y, Wang S, Mustonen H, Puolakkainen P. Macrophage coculture enhanced invasion of gastric cancer cells via TGF-β and BMP pathways. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:466–72.
Shen Z, Kauttu T, Seppänen H, Vainionpää S, Ye Y, Wang S, Mustonen H, Puolakkainen P. Both macrophages and hypoxia play critical role in regulating invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. Acta Oncol. 2013;52:852–60.
Lewis CE, Pollard JW. Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res. 2006;66:605–12.
Fukuda K, Kobayashi A, Watabe K. The role of tumor-associated macrophage in tumor progression. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012;4:787–98.
Bloomston M, Shafii A, Zervos E, Rosemurgy AS. TIMP-1 antisense gene transfection attenuates the invasive potential of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:668–74.
Schoppmann SF, Birner P, Stöckl J, Kalt R, Ullrich R, Caucig C, Kriehuber E, Nagy K, Alitalo K, Kerjaschki D. Tumor-associated macrophages express lymphatic endothelial growth factors and are related to peritumoral lymphangiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:947–56.
Murphy G. The ADAMs: signaling scissors in the tumor microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:929–41.
Grutzmann R, Luettges J, Sipos B, Dobrowolski F, Ammerpohi O, Alldinger I, Kersting S, Ockert D, Koch R, Kalthoff H, Schackert HK, Saeger HD, Klöppel G, Pilarsky C. ADAM9 expression in pancreatic cancer is associated with tumor type and is a prognostic factor in ductal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:1053–8.
Ringel J, Jesnowski R, Moniaux N, Luettges J, Ringel J, Choudhury A, Surinder BK, Klöppel G, Löhr M. Aberrant expression of disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17/tumornecrosis factor α converting enzyme increases malignant potential in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9045–53.
Valkovskaya N, Kayed H, Felix K, Hartmann D, Giese NA, Osinsky SP, Friess H, Kleeff J. ADAM8 expression is associated with increased invasiveness and reduced patient survival in pancreatic cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2007;11:1162–74.
van Uden P, Kenneth NS, Rocha S. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by NF-kappaB. Biochem J. 2008;412:477–84.
Mustonen H, Puolakkainen P, Kemppainen E, Kiviluoto T, Kivilaakso E. Taurocholate potentiates ethanol induced NF-kB activation and inhibits Caspase-3 activity in cultured rat gastric mucosal cells. Dic Dis Sci. 2009;54:928–36.
Terzić J, Grivennikov S, Karin E, Karin M. Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:2101–14.
Polk DB, Peek RM. Helicobacter pylori: gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:403–14.
Bingle L, Brown NJ, Lewis CE. The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: implications for new anticancer therapies. J Pathol. 2002;196:254–65.
Dirkx AEM, oude Egbrink MGA, Wagstaff J, Griffioen AW. Monocyte/macrophage infiltration in tumors: modulators of angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80:1183–96.
Lee CC, Liu KJ, Huang TS. Tumor-associated macrophage: its role in tumor angiogenesis. J Cancer Mol. 2006;2:135–40.
Morishita A, Gow CH, D’Armiento JM. Macrophages-specific matrix metalloproteinase-9 (mmp9) induces lung cancer metastasis in an animal model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:2440.
van Kempen LCL, Coussens LM. MMP9 potentiates pulmonary metastasis formation. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:251–2.
Sun HW, Li CJ, Chen HQ, Lin HL, Lv HX, Zhang Y, Zhang M. Involvement of integrins, MAPK, and NF-kappaB in regulation of the shear stress-induced MMP-9 expression in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;353:52–8.
Gordon GM, Dolena R, Ledee DR, Feuer W, Fini ME. Cytokines and signaling pathways regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression in corneal epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;221:402–11.
Okada Y, Eibl G, Duffy JP, Reber HA, Hines OJ. Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor upregulates the expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human pancreatic cancer. Surgery. 2003;134:293–9.
Esseghir S, Todd SK, Hunt T, Poulsom R, Plaza-Menacho I, Reis-Filho JS, Isacke CM. A role for glialcell derived neurotrophic factor induced expression by inflammatory cytokines and RET/GFR alpha 1 receptor up-regulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;15:11732–41.
Koshiba T, Hosotani R, Wada M, Miyamoto Y, Fujimoto K, Lee JU, Doa R, Arii S, Imamura M. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1998;82:642–50.
Graham CH, Connelly I, MacDougall JR, Kerbel RS, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Lala PK. Resistance of malignant trophoblast cells to both the anti-proliferative and anti-invasive effects of transforming growth factor-beta. Exp Cell Res. 1994;214:93–9.
Kuwada Y, Sasaki T, Morinaka K, Kitadai Y, Mukaida N, Chayama K. Potential involvement of IL-8 and its receptors in the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2003;22:765–71.
Bredin CG, Liu Z, Klominek J. Growth factor-enhanced expression and activity of matrix metalloproteases in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:4877–84.
Zhang D, Bar-Eli M, Meloche S, Brodt P. Dual regulation of MMP-2 expression by the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:19683–90.
Fritzsche FR, Jung M, Xu C, Rabien A, Schicktanz H, Stephan C, Dietel M, Jung K, Kristiansen G. ADAM8 expression in prostate cancer is associated with parameters of unfavorable prognosis. Surgery. 2003;134:293–9.
Zhang Y, Tan YF, Jiang C, Zhang K, Zha TZ, Zhang M. High ADAM8 Expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PatholOncol Res. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].
Fourie AM, Coles F, Moreno V, Karlsson L. Catalytic activity of ADAM8, ADAM15, and MDC-L (ADAM28) on synthetic peptide substrates and in ectodomain cleavage of CD23. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:30469–77.
Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Wolfson MF, Castner BJ, Stocking KL, Reddy P, Srinivasan S, Nelson N, Boiani N, Schooley KA, Gerhart M, Davis R, Fitzner JN, Johnson RS, Paxton RJ, March CJ, Cerretti DP. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-α from cells. Nature. 1997;385:729–33.
Blobel CP. ADAMS: key components in EGFR signalling and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:32–43.
Franovic A, Robert I, Smith K, Kurban G, Pause A, Gunaratnam L, Lee S. Multiple acquired renal carcinoma tumor capabilities abolished upon silencing of ADAM17. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8083–90.
Infante J, Burris HA, Lewis N, Donehower R, Redman J, Friedman S, Scherle P, Fridman J, Li J, Emm T, Troy S, Eckhardt SG. A multicenter phase Ib study of the safety, pharmacokinetics, biological activity and clinical efficacy of INCB7839, a potent and selective inhibitor of ADAM10 and ADAM17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106(Supp 1):S269.
Choi JY, Jang YS, Min SY, Song JY. Overexpression of MMP-9 and HIF-1α in breast cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. Breast Cancer. 2011;14:88–95.
Loging TW, Reisman D. Inhibition of the putative tumor suppressor gene TIMP-3 by tumor-derived p53 mutants and wild type p53. Oncogene. 1999;18:7608–15.
Acknowledgments
Georg C Ehrnrooth foundation, Sigrid Juselius Foundation, and Helsinki University Central Hospital Research Funds are acknowledged for supporting the study. None of the foundations have been involved in the study design.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Pauli Puolakkainen, Aino Koski, Harri Mustonen, and Hanna Seppänen share equal authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puolakkainen, P., Koski, A., Vainionpää, S. et al. Anti-inflammatory macrophages activate invasion in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by increasing the MMP9 and ADAM8 expression. Med Oncol 31, 884 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0884-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0884-9