Abstract
Background
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6 (HCV-6) is common in patients from Southeast Asia and the surrounding regions. Optimal treatment duration for HCV-6 is unknown given the inconclusive evidence from studies with varying methodologies and small sample sizes.
Methods
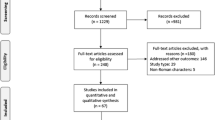
A literature search for ‘genotype 6’ in MEDLINE and EMBASE in October 2013 produced 161 and 251 articles, respectively. Additional abstracts were identified from four major international GI/liver conferences in 2012/2013. Inclusion criteria were original studies with ≥10 HCV-6 treatment-naïve patients treated with pegylated interferon + ribavirin (PEG IFN+RBV). Exclusion criteria were coinfections with HBV, HIV, other HCV genotypes, and/or other liver diseases. Primary outcome was pooled sustained virologic response (SVR). Heterogeneity was defined by Cochrane Q test (p value of 0.10) and I 2 statistic (≥50 %).
Results
A total of 13 studies with 641 patients were included. The pooled SVR estimate was 77 % (CI 70–83 %) (Q value = 38.4, p value <0.001, I 2 = 68.7 %) overall, 79 % (CI 73–84 %) for the 48-week group and 59 % (CI 46–70 %) for 24-week group, respectively. In studies with direct comparison of the two groups, SVR was superior in patients treated for 48 versus 24 weeks, OR 1.9 (CI 1.08–3.2, p = 0.026). In studies with direct comparison of patients with rapid virologic response (RVR), there was no difference in SVR between 48 versus 24 weeks, OR 1.74 (CI 0.65–4.64, p = 0.27).
Conclusion
Hepatitis C virus genotype 6 patients should be treated for 48 weeks, and those who achieve RVR may receive the shorter 24-week treatment duration. The high SVR (~80 %) with 48 weeks of PEG IFN+RBV therapy may be a cost-effective option for HCV-6 patients from resource-poor regions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- SVR:
-
Sustained virologic response
- RVR:
-
Rapid virologic response
- PEG IFN+RBV:
-
Pegylated interferon and ribavirin
- AASLD:
-
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases
- DDW:
-
Digestive disease week
- APASL:
-
Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver
- EASL:
-
European Association for the Study of the Liver
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- ITT:
-
Intention-to-treat
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
References
Chao DT, Abe K, Nguyen MH. Systematic review: epidemiology of hepatitis C genotype 6 and its management. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:286–296
Nguyen LH, Nguyen MH. Systematic review: Asian patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;37:921–936
Ghany M, Strader D, Thomas D, Seeff L. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 2009;49:1335–1374
Nguyen MH, Keeffe EB. Prevalence and treatment of hepatitis C virus genotypes 4, 5, and 6. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:S97–S101
Nguyen MH, Trinh HN, Garcia RT, Nguyen G, Lam KD, Keeffe EB. Higher rate of sustained virologic response in chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 treated with 48 weeks versus 24 weeks of peginterferon plus ribavirin. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:1131–1135
Fung J, Lai C, Hung I, Young J, Cheng C, Wong D, et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 6 infection: response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:808–812
Lam KDTH, Do ST, Nguyen TT, Garcia RT, Nguyen T, Phan QQ, et al. Randomized controlled trial of pegylated interferon-alfa 2a and ribavirin in treatment-naive chronic hepatitis C genotype 6. Hepatology. 2010;52:1573–1580
Thu Thuy PT, Bunchorntavakul C, Tan Dat H, Rajender Reddy K. A randomized trial of 48 versus 24 weeks of combination pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy in genotype 6 chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2012;56:1012–1018
Yuen MF, Lai CL. Response to combined interferon and ribavirin is better in patients infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 6 than genotype 1 in Hong Kong. Intervirology. 2006;49:96–98
Nguyen N, Vutien P, Trinh H, Garcia R, Wan K, Nguyen H, et al. Treatment response and tolerability to pegylated interferon (PEG Inf) and ribavirin (RBV) in treatment-naive Asian American patients with chronic hepatitis C and genotype 1,2/3 and 6. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:A791
Pham TT, Ho DT. An optimal duration of treatment for chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 patients. Hepatology. 2011;54:810A–811A
Pham TT, Ho DT. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin in chronic Hepatitis C patients with genotype 6. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:A840
Poordad F, McCone J Jr, Bacon BR, Bruno S, Manns MP, Sulkowski MS, et al. Boceprevir for untreated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1195–1206
Wantuck JM, Ahmed A, Nguyen MH. Review article: the epidemiology and therapy of chronic hepatitis C genotypes 4, 5 and 6. Alim Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:137–147
Lawitz E, Lalezari JP, Hassanein T, Kowdley KV, Poordad FF, Sheikh AM, et al. Sofosbuvir in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin for non-cirrhotic, treatment-naive patients with genotypes 1, 2, and 3 hepatitis C infection: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:401–408
Pawlotsky JM. Hepatitis C virus: standard-of-care treatment. Adv Pharmacol. 2013;67:169–215
Koff RS. Review article: the efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir, a novel, oral nucleotide NS5B polymerase inhibitor, in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Alim Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:478–487
Al Naamani K, Al Sinani S, Deschenes M. Epidemiology and treatment of hepatitis C genotypes 5 and 6. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013;27:e8–e12
Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. In Higgins JPT Green S, editors Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011
Mauss S, Berger F, Vogel M, Pfeiffer-Vornkahl H, Alshuth U, Rockstroh J, et al. Treatment results of chronic hepatitis C genotype 5 and 6 infections in Germany. Z Gastroenterol. 2012;50:441–444
Tangkijvanich P, Komolmit P, Mahachai V, Poovorawan K, Akkarathamrongsin S, Poovorawan Y. Response-guided therapy for patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 6 infection: a pilot study. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19:423–430
Tsang O, Zee J, Chan J, Li R, Kan Y, Li F, et al. Chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 responds better to pegylated interferon and ribavirin combination therapy than genotype 1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:766–771
Nguyen NH, VuTien P, Garcia RT, Trinh H, Nguyen H, Nguyen K, et al. Response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin in Asian American patients with chronic hepatitis C genotypes 1 vs 2/3 vs 6. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17:691–697
Seto W, Tsang O, Liu K, Chan J, Wong D, Fung J, et al. Role of IL28B and inosine triphosphatase polymorphisms in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 6 infection. J Viral Hepat. 2013;20:470–477
Shao X, Zhao Z, Cai Q, Zhang X, Gao Z. The dynamic analysis of the Th1/Th2 ratio during the interferon alpha/ribavirin combination therapy for HCV genotype 6 infected patients. J Hepatol 2012; 56
Qing-Xian C. The high IL-28B CC genotype contribute to the good response of chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 in China. Hepatology. 2011;54:829A–830A
Rao H, Wei L, Yang R, Chen XY, Jia S, Gao Z, et al. IL28B genotype and IFNL4 ss469415590 DG variant are both associated with response to pegylated IFN-alpha and ribavirin therapy in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2013;58:1899A
Lam K, Trinh H, Do S, Nguyen T, Garcia R, Nguyen T, et al. Randomized controlled trial of pegylated interferon-alpha 2a and ribavirin in patients with treatment-naive chronic hepatitis C genotype 6. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:S783
Pham TT, Ho DT. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patient with genotype 6. Hepatol Int. 2009;3:49
Seong MH, Kil H, Kim JY, Lee SS, Jang ES, Kim JW, et al. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of Korean patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 6. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013;19:45–50
Thanak P, Kitiyakara T, Intaraprasong P, Sobhonslidsuk A, Achalanan N, Kamalaporn P, et al. Real-world outcomes of hepatitis C treatment in thai patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:247
Weinstein T, Levine J. Early virologic response in children with hepatitis C genotype 6E. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;49:E79
Lenz O, Vijgen L, Berke J, Cummings M, Fevery B, Peeters M, et al. Virologic response and characterisation of HCV genotype 2-6 in patients receiving TMC435 monotherapy (study TMC435-C202). J Hepatol. 2013;58:445–451
Hui CK, Yuen MF, Sablon E, Chan AO, Wong BC, Lai C. Interferon and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 6: a comparison with genotype 1. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:1071–1074
Bunchorntavakul C, Siripun A, Chavalitdhamrong D. Fluvastatin monotherapy for the treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:S102–S103
Chu T, Kulkarni R, Gane EJ, Roberts SK, Stedman C, Angus P, et al. The effect of host IL28B genotype on early viral kinetics during interferon-free treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC). J Hepatol. 2011;54:S521–S522
Cheng JT, Hsien C, Sun HE, Tong M. The emerging importance of chronic hepatitis C infection in Asian Americans. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:2737–2743
Thi TTP, Ho TD. Impact of single nucleotide polymorphisms of IL28B on SVR in treatment chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 in Vietnamese. Hepatol Int. 2013;7:S366
Chen X. A prospective, randomized, open-label, multicenter study of response-guided therapy (RGT) for HCV treatment-naïve Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Int. 2013;7:S724
Han B. In vitro analyses of HCV NS5B S282T mutants in multiple HCV genotypes show low levels of reduced susceptibility to sofosbuvir (GS-7977), no cross resistance to other classes of direct-acting antivirals, and hypersensitivity to ribavirin. Hepatology 2012;56:711A
Lim JH. Changes in serum lipid profile before and after interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Int. 2012;6:170
Loh PY. Outcome of hepatitis C treatment and effect of treatment dose adjustment in treatment naïve Asian populations. Hepatol Int. 2013;7:S411
Seto WK, Tanaka Y, Liu K, Lai CL, Yuen M. The effects of IL-28B and ITPA polymorphisms on treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 6. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:1007–1008
Antaki N, Marcellin P. What is the safe duration of therapy for patients infected with HCV genotype 6? Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:78–79
Chow W, Ng H. Hepatitis C, E and G virus—three new viruses identified by molecular biology technique in the last decade. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1997;26:682–686
Lai W. Viral hepatitis C—Asia-Pacific perspectives and guidelines. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:29
Chutaputti A, et al. Managing HCV genotype 6 patients. Hepatol Int. 2011;5:47–48
McHutchison JG. The role of genetic markers in hepatitis C virus therapy: a major step for individualized care. Liver Int. 2011;31(Suppl 1):29–35
Thomas DL, Thio CL, Martin MP, Qi Y, Ge D, O’Huigin C, et al. Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nature. 2009;461:798–801
Qing-Xian C, Zhixin Z, Lin C, et al. Shortened treatment duration in treatment-naive genotype 6 chronic hepatitis C patients with rapid virological response: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2013;58:1855
Acknowledgements
This project was supported in part by grant no. 1TL1RR03197 from the NIH National center for Research Resources to Nghia H. Nguyen and Shelley A. McCormack.
Compliance with ethical requirements and Conflict of interest
All procedures were followed in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 and 2008. Nghia H. Nguyen, Shelley A. McCormack, Brittany E. Yee, Pardha Devaki, David Jencks, David T. Chao and Mindie H. Nguyen have no conflict of interest/financial disclosure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, N.H., McCormack, S.A., Yee, B.E. et al. Meta-analysis of patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 6: 48 weeks with pegylated interferon and ribavirin is superior to 24 weeks. Hepatol Int 8, 540–549 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-014-9570-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-014-9570-4