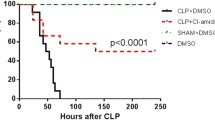
Abstract
Cirrhotic patients with dysfunctional and/or low numbers of leukocytes are often infected with bacteria, especially Gram-negative bacteria, which is characterized by producing lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is a pleiotropic cytokine that influences the production, maturation, function, and survival of various immune cells. In this paper, we reviewed not only Toll-like receptors 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway and its immunological effect, but also the specific stimulating function and autocrine performance of GM-CSF on hematopoietic cells, as well as the recent discovery of innate response activator-B cells in protection against microbial sepsis and the direct LPS–TLR4 signaling on hematopoiesis. Thus we concluded that GM-CSF might play important roles in preventing Gram-negative bacterial infections in cirrhotic patients through maintaining immune system functions and homeostasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvaniti V, D’Amico G, Fede G, Manousou P, Tsochatzis E, Pleguezuelo M, et al. Infections in patients with cirrhosis increase mortality four-fold and should be used in determining prognosis. Gastroenterology 2010;139(4):1246–1256, 56e1–56e5
Bajaj JS, O’Leary JG, Reddy KR, Wong F, Olson JC, Subramanian RM, et al. Second infections independently increase mortality in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis: the North American consortium for the study of end-stage liver disease (NACSELD) experience. Hepatology 2012;56(6):2328–2335
Kim SU, Kim DY, Lee CK, Park JY, Kim SH, Kim HM, et al. Ascitic fluid infection in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis: culture-negative neutrocytic ascites versus spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;25(1):122–128
Riordan SM, Williams R. The intestinal flora and bacterial infection in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2006;45(5):744–757
Lin Y, Yu LX, Yan HX, Yang W, Tang L, Zhang HL, et al. Gut-derived lipopolysaccharide promotes T-cell-mediated hepatitis in mice through Toll-like receptor 4. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2012;5(9):1090–1102
Benten D, Wiest R. Gut microbiome and intestinal barrier failure–the “Achilles heel” in hepatology? J Hepatol 2012;56(6):1221–1223
Schnabl B. Linking intestinal homeostasis and liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2013;29(3):264–270
Lu M, Zhang M, Takashima A, Weiss J, Apicella MA, Li XH, et al. Lipopolysaccharide deacylation by an endogenous lipase controls innate antibody responses to Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Immunol 2005;6(10):989–994
Feulner JA, Lu M, Shelton JM, Zhang M, Richardson JA, Munford RS. Identification of acyloxyacyl hydrolase, a lipopolysaccharide-detoxifying enzyme, in the murine urinary tract. Infect Immun 2004;72(6):3171–3178
Lu M, Varley AW, Ohta S, Hardwick J, Munford RS. Host inactivation of bacterial lipopolysaccharide prevents prolonged tolerance following Gram-negative bacterial infection. Cell Host Microbe 2008;4(3):293–302
Takeda K, Akira S. TLR signaling pathways. Semin Immunol 2004;16(1):3–9
Gioannini TL, Weiss JP. Regulation of interactions of Gram-negative bacterial endotoxins with mammalian cells. Immunol Res 2007;39(1–3):249–260
Bryant CE, Symmons M, Gay NJ. Toll-like receptor signalling through macromolecular protein complexes. Mol Immunol 2014
Figueroa L, Xiong Y, Song C, Piao W, Vogel SN, Medvedev AE. The Asp299Gly polymorphism alters TLR4 signaling by interfering with recruitment of MyD88 and TRIF. J Immunol 2012;188(9):4506–4515
Tsutsui H, Imamura M, Fujimoto J, Nakanishi K. The TLR4/TRIF-mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasome underlies endotoxin-induced liver injury in mice. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010;2010:641865
Knobloch J, Schild K, Jungck D, Urban K, Muller K, Schweda EK, et al. The T-helper cell type 1 immune response to Gram-negative bacterial infections is impaired in COPD. Am J Respir Crit care Med 2011;183(2):204–214
Medzhitov R, Shevach EM, Trinchieri G, Mellor AL, Munn DH, Gordon S, et al. Highlights of 10 years of immunology in Nature Reviews Immunology. Nat Rev Immunol 2011;11(10):693–702
Kopp E, Medzhitov R. Recognition of microbial infection by Toll-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol 2003;15(4):396–401
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS. Recognition of Gram-negative bacteria and endotoxin by the innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 1999;11(1):19–22
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998;282(5396):2085–2088
Gioannini TL, Teghanemt A, Zarember KA, Weiss JP. Regulation of interactions of endotoxin with host cells. J Endotoxin Res 2003;9(6):401–408
Ballinger MN, Paine R III, Serezani CH, Aronoff DM, Choi ES, Standiford TJ, et al. Role of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor during Gram-negative lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006;34(6):766–774
Pasare C, Medzhitov R. Control of B-cell responses by Toll-like receptors. Nature 2005;438(7066):364–368
Kursar M, Mittrucker HW, Koch M, Kohler A, Herma M, Kaufmann SH. Protective T cell response against intracellular pathogens in the absence of Toll-like receptor signaling via myeloid differentiation factor 88. Int Immunol 2004;16(3):415–421
Moore JW, Beattie L, Dalton JE, Owens BM, Maroof A, Coles MC, et al. B cell: T cell interactions occur within hepatic granulomas during experimental visceral leishmaniasis. PloS One 2012;7(3):e34143
Haag LM, Fischer A, Otto B, Plickert R, Kuhl AA, Gobel UB, et al. Campylobacter jejuni induces acute enterocolitis in gnotobiotic IL-10−/− mice via Toll-like-receptor-2 and -4 signaling. PloS One 2012;7(7):e40761
Reece P, Baatjes AJ, Cyr MM, Sehmi R, Denburg JA. Toll-like receptor-mediated eosinophil–basophil differentiation: autocrine signalling by granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor in cord blood haematopoietic progenitors. Immunology 2013;139(2):256–264
Ojogun N, Kuang TY, Shao B, Greaves DR, Munford RS, Varley AW. Overproduction of acyloxyacyl hydrolase by macrophages and dendritic cells prevents prolonged reactions to bacterial lipopolysaccharide in vivo. J Infect Dis 2009;200(11):1685–1693
Shao B, Munford RS, Kitchens R, Varley AW. Hepatic uptake and deacylation of the LPS in bloodborne LPS–lipoprotein complexes. Innate Immun 2012;18(6):825–833
Shao B, Kitchens RL, Munford RS, Rogers TE, Rockey DC, Varley AW. Prolonged hepatomegaly in mice that cannot inactivate bacterial endotoxin. Hepatology 2011;54(3):1051–1062
Reece P, Thanendran A, Crawford L, Tulic MK, Thabane L, Prescott SL, et al. Maternal allergy modulates cord blood hematopoietic progenitor Toll-like receptor expression and function. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;127(2):447–453
Bankoti R, Gupta K, Levchenko A, Stager S. Marginal zone B cells regulate antigen-specific T cell responses during infection. J Immunol 2012;188(8):3961–3971
Rauch PJ, Chudnovskiy A, Robbins CS, Weber GF, Etzrodt M, Hilgendorf I, et al. Innate response activator B cells protect against microbial sepsis. Science 2012;335(6068):597–601
Sander LE, Davis MJ, Boekschoten MV, Amsen D, Dascher CC, Ryffel B, et al. Detection of prokaryotic mRNA signifies microbial viability and promotes immunity. Nature 2011;474(7351):385–389
Askenase PW, Tsuji RF. B-1 B cell IgM antibody initiates T cell elicitation of contact sensitivity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2000;252:171–177
Yates JL, Racine R, McBride KM, Winslow GM. T cell-dependent IgM memory B cells generated during bacterial infection are required for IgG responses to antigen challenge. J Immunol 2013;191(3):1240–1249
Montaudouin C, Anson M, Hao Y, Duncker SV, Fernandez T, Gaudin E, et al. Quorum sensing contributes to activated IgM-secreting B cell homeostasis. J Immunol 2013;190(1):106–114
Smelt SC, Cotterell SE, Engwerda CR, Kaye PM. B cell-deficient mice are highly resistant to Leishmania donovani infection, but develop neutrophil-mediated tissue pathology. J Immunol 2000;164(7):3681–3688
Mishra BB, Rathinam VA, Martens GW, Martinot AJ, Kornfeld H, Fitzgerald KA, et al. Nitric oxide controls the immunopathology of tuberculosis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent processing of IL-1beta. Nat Immunol 2013;14(1):52–60
Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B. CD4(+)T cells: differentiation and functions. Clin Dev Immunol 2012;2012:925135
Iwasaki-Arai J, Iwasaki H, Miyamoto T, Watanabe S, Akashi K. Enforced granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor signals do not support lymphopoiesis, but instruct lymphoid to myelomonocytic lineage conversion. J Exp Med 2003;197(10):1311–1322
Gurakar A, Fagiuoli S, Gavaler JS, Hassanein T, Jabbour N, Wright HI, et al. The use of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor to enhance hematologic parameters of patients with cirrhosis and hypersplenism. J Hepatol 1994;21(4):582–586
Choi EY, Santoso S, Chavakis T. Mechanisms of neutrophil transendothelial migration. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2009;14:1596–1605
Everly JJ, Lonial S. Immunomodulatory effects of human recombinant granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rhuGM-CSF): evidence of antitumour activity. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2005;5(3):293–311
Nishijima I, Nakahata T, Watanabe S, Tsuji K, Tanaka I, Hirabayashi Y, et al. Hematopoietic and lymphopoietic responses in human granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) receptor transgenic mice injected with human GM-CSF. Blood 1997;90(3):1031–1038
Eksioglu EA, Mahmood SS, Chang M, Reddy V. GM-CSF promotes differentiation of human dendritic cells and T lymphocytes toward a predominantly type 1 proinflammatory response. Exp Hematol 2007;35(8):1163–1171
Hellman P, Eriksson H. Early activation markers of human peripheral dendritic cells. Hum Immunol 2007;68(5):324–333
Fiuza C, Salcedo M, Clemente G, Tellado JM. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor improves deficient in vitro neutrophil transendothelial migration in patients with advanced liver disease. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2002;9(2):433–439
Yong KL. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) increases neutrophil migration across vascular endothelium independent of an effect on adhesion: comparison with granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Br J Haematol 1996;94(1):40–47
Sonderegger I, Iezzi G, Maier R, Schmitz N, Kurrer M, Kopf M. GM-CSF mediates autoimmunity by enhancing IL-6-dependent Th17 cell development and survival. J Exp Med 2008;205(10):2281–2294
Piper C, Pesenacker AM, Bending D, Thirugnanabalan B, Varsani H, Wedderburn LR, et al. T cell GM-CSF expression in juvenile arthritis is contingent upon Th17 plasticity. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66(7):1955–1960
van Nieuwenhuijze A, Koenders M, Roeleveld D, Sleeman MA, van den Berg W, Wicks IP. GM-CSF as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Mol Immunol 2013;56(4):675–682
Morrissey PJ, Bressler L, Park LS, Alpert A, Gillis S. Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor augments the primary antibody response by enhancing the function of antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol 1987;139(4):1113–1119
Faith A, Fernandez MH, Caulfield J, Loke TK, Corrigan C, O’Connor B, et al. Role of cysteinyl leukotrienes in human allergen-specific Th2 responses induced by granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor. Allergy 2008;63(2):168–175
Stull DM. Colony-stimulating factors: beyond the effects on hematopoiesis. Am J Health-Syst Pharm: AJHP: Off J Am Soc Health-Syst Pharm 2002;59(7 Suppl 2):S12–S20
Dabritz J. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and the intestinal innate immune cell homeostasis in Crohn’s disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2014;306(6):G455–G465
van de Laar L, Coffer PJ, Woltman AM. Regulation of dendritic cell development by GM-CSF: molecular control and implications for immune homeostasis and therapy. Blood 2012;119(15):3383–3393
Rathinam VA, Vanaja SK, Waggoner L, Sokolovska A, Becker C, Stuart LM, et al. TRIF licenses caspase-11-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation by Gram-negative bacteria. Cell 2012;150(3):606–619
Yokoyama T, Komori A, Nakamura M, Takii Y, Kamihira T, Shimoda S, et al. Human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells function in innate immunity by producing IL-6 and IL-8 via the TLR4-NF-kappaB and -MAPK signaling pathways. Liver Int: Off J Int Assoc Study Liver 2006;26(4):467–476
Dauphinee SM, Karsan A. Lipopolysaccharide signaling in endothelial cells. Lab Investig; J Tech Methods Pathol 2006;86(1):9–22
Shao B, Lu M, Katz SC, Varley AW, Hardwick J, Rogers TE, et al. A host lipase detoxifies bacterial lipopolysaccharides in the liver and spleen. J Biol Chem 2007;282(18):13726–13735
Boaru SG, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Tihaa L, Haas U, Weiskirchen R. Expression analysis of inflammasomes in experimental models of inflammatory and fibrotic liver disease. J Inflamm (Lond) 2012;9(1):49
Fernandez J, Navasa M, Planas R, Montoliu S, Monfort D, Soriano G, et al. Primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis delays hepatorenal syndrome and improves survival in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007;133(3):818–824
Medzhitov R, Schneider DS, Soares MP. Disease tolerance as a defense strategy. Science 2012;335(6071):936–941
Schneider DS, Ayres JS. Two ways to survive infection: what resistance and tolerance can teach us about treating infectious diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2008;8(11):889–895
Peter J, Frey O, Stallmach A, Bruns T. Attenuated antigen-specific T cell responses in cirrhosis are accompanied by elevated serum interleukin-10 levels and down-regulation of HLA-DR on monocytes. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13:37
Marquez M, Fernandez-Gutierrez C, Montes-de-Oca M, Blanco MJ, Brun F, Rodriguez-Ramos C, et al. Chronic antigenic stimuli as a possible explanation for the immunodepression caused by liver cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol 2009;158(2):219–229
Garcia-Gonzalez M, Boixeda D, Herrero D, Burgaleta C. Effect of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor on leukocyte function in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1993;105(2):527–531
Seki E, Brenner DA. Toll-like receptors and adaptor molecules in liver disease: update. Hepatology 2008;48(1):322–335
Fernandez J, Gustot T. Management of bacterial infections in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2012;56(Suppl 1):S1–12
Petrasek J, Csak T, Szabo G. Toll-like receptors in liver disease. Adv Clin Chem 2013;59:155–201
Gaia S, Smedile A, Omede P, Olivero A, Sanavio F, Balzola F, et al. Feasibility and safety of G-CSF administration to induce bone marrow-derived cells mobilization in patients with end stage liver disease. J Hepatol 2006;45(1):13–19
Kubota A, Okamura S, Omori F, Shimoda K, Otsuka T, Ishibashi H, et al. High serum levels of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with liver cirrhosis and granulocytopenia. Clin Lab Haematol 1995;17(1):61–63
Eroglu A, Demirci S, Akbulut H, Sever N, Demirer S, Unal AE. Effect of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor on hepatic regeneration after 70% hepatectomy in normal and cirrhotic rats. HPB: Off J Int Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc 2002;4(2):67–73
Vassiliou I, Lolis E, Nastos C, Tympa A, Theodosopoulos T, Dafnios N, et al. The combined effect of erythropoietin and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor on liver regeneration after major hepatectomy in rats. World J Surg Oncol 2010;8:57
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81270506).
Compliance with ethical requirements and Conflict of interest
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors. Dong Xu, Manzhi Zhao, Yuhu Song, Jianxin Song, Yuancheng Huang and Junshuai Wang declare that they have no conflict of interest. There is no professional or other personal interest that could influence the position of authors presented in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Zhao, M., Song, Y. et al. Novel insights in preventing Gram-negative bacterial infection in cirrhotic patients: review on the effects of GM-CSF in maintaining homeostasis of the immune system. Hepatol Int 9, 28–34 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-014-9588-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-014-9588-7