Abstract
Objective
The aim of the this study was to analyze the status of sex-determining region Y-related high-mobility group box 4 (SOX4) expression in varied human cancers and its correlation with overall survival in patients with human cancers.
Methods
To observe initially the expression status of SOX4 in twenty kinds of human cancers at protein database (The Human Protein Atlas). We systematically and carefully searched the studies from electronic databases and seriously identified according to eligibility criteria. The correlation between SOX4 expression and overall survival in human cancers was evaluated through Review Manager.
Results
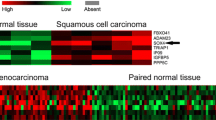
We found that SOX4 expression was significantly positive in most types of human cancer tissues, and the positive rate of SOX4 expression was about 78 % in overall cancer tissues. Furthermore, a total of 10 studies which included 1348 cancer patients were included in the final analysis. Meta-analysis showed that SOX4 overexpression was correlated with a poor overall survival and the pooled hazard ratio (HR), and corresponding 95 % confidence interval (CI) was 1.67 (95 % CI 1.01–2.78). From subgroup analyses, we present evidence that SOX4 overexpression was an unfavorable prognostic factor for colorectal cancer patients’ recurrence-free survival and gastric cancer patients’ overall survival, and the pooled HRs (95 % CI) were 1.73 (95 % CI 1.04–2.88) and 3.74 (95 % CI 1.04–13.45), respectively.
Conclusions
In summary, SOX4 is a potential prognostic biomarker in human cancers.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SOX4:
-
Sex-determining region Y-related high-mobility group box 4
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
References
Penzo-Mendez AI. Critical roles for SoxC transcription factors in development and cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(3):425–8. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.018.
Jafarnejad SM, Ardekani GS, Ghaffari M, Li G. Pleiotropic function of SRY-related HMG box transcription factor 4 in regulation of tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. 2013;70(15):2677–96. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1187-y.
Vervoort SJ, van Boxtel R, Coffer PJ. The role of SRY-related HMG box transcription factor 4 (SOX4) in tumorigenesis and metastasis: friend or foe? Oncogene. 2013;32(29):3397–409. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.506.
Schilham MW, Oosterwegel MA, Moerer P, Ya J, de Boer PA, van de Wetering M, et al. Defects in cardiac outflow tract formation and pro-B-lymphocyte expansion in mice lacking Sox-4. Nature. 1996;380(6576):711–4. doi:10.1038/380711a0.
Ya J, Schilham MW, de Boer PA, Moorman AF, Clevers H, Lamers WH. Sox4-deficiency syndrome in mice is an animal model for common trunk. Circ Res. 1998;83(10):986–94.
Cheung M, Abu-Elmagd M, Clevers H, Scotting PJ. Roles of Sox4 in central nervous system development. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000;79(1–2):180–91.
Liao YL, Sun YM, Chau GY, Chau YP, Lai TC, Wang JL, et al. Identification of SOX4 target genes using phylogenetic footprinting-based prediction from expression microarrays suggests that overexpression of SOX4 potentiates metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2008;27(42):5578–89. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.168.
Hur W, Rhim H, Jung CK, Kim JD, Bae SH, Jang JW, et al. SOX4 overexpression regulates the p53-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical implication and functional analysis in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31(7):1298–307. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq072.
Liu P, Ramachandran S, Ali Seyed M, Scharer CD, Laycock N, Dalton WB, et al. Sex-determining region Y box 4 is a transforming oncogene in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(8):4011–9. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-3055.
Moreno CS. The Sex-determining region Y-box 4 and homeobox C6 transcriptional networks in prostate cancer progression: crosstalk with the Wnt, Notch, and PI3K pathways. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(2):518–27. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090657.
Zhang J, Liang Q, Lei Y, Yao M, Li L, Gao X, et al. SOX4 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and contributes to breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2012;72(17):4597–608. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-12-1045.
Graham JD, Hunt SM, Tran N, Clarke CL. Regulation of the expression and activity by progestins of a member of the SOX gene family of transcriptional modulators. J Mol Endocrinol. 1999;22(3):295–304.
Sinner D, Kordich JJ, Spence JR, Opoka R, Rankin S, Lin SC, et al. Sox17 and Sox4 differentially regulate beta-catenin/T-cell factor activity and proliferation of colon carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(22):7802–15. doi:10.1128/mcb.02179-06.
Andersen CL, Christensen LL, Thorsen K, Schepeler T, Sorensen FB, Verspaget HW, et al. Dysregulation of the transcription factors SOX4, CBFB and SMARCC1 correlates with outcome of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(3):511–23. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604884.
Aaboe M, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Wiuf C, Sorensen FB, Thykjaer T, Sauter G, et al. SOX4 expression in bladder carcinoma: clinical aspects and in vitro functional characterization. Cancer Res. 2006;66(7):3434–42. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-3456.
Gunes S, Yegin Z, Sullu Y, Buyukalpelli R, Bagci H. SOX4 expression levels in urothelial bladder carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2011;207(7):423–7. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2011.05.005.
Barrier A, Boelle PY, Roser F, Gregg J, Tse C, Brault D, et al. Stage II colon cancer prognosis prediction by tumor gene expression profiling. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(29):4685–91. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.05.0229.
Shen R, Pan S, Qi S, Lin X, Cheng S. Epigenetic repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4 in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(4):1047–52. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.121.
Jafarnejad SM, Wani AA, Martinka M, Li G. Prognostic significance of Sox4 expression in human cutaneous melanoma and its role in cell migration and invasion. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(6):2741–52. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.100377.
Ramezani-Rad P, Geng H, Hurtz C, Chan LN, Chen Z, Jumaa H, et al. SOX4 enables oncogenic survival signals in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2013;121(1):148–55. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-05-428938.
Fang CL, Hseu YC, Lin YF, Hung ST, Tai C, Uen YH, et al. Clinical and prognostic association of transcription factor SOX4 in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52804. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052804.
Huang HY, Cheng YY, Liao WC, Tien YW, Yang CH, Hsu SM, et al. SOX4 transcriptionally regulates multiple SEMA3/plexin family members and promotes tumor growth in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e48637. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048637.
Wang C, Zhao H, Lu J, Yin J, Zang L, Song N, et al. Clinicopathological significance of SOX4 expression in primary gallbladder carcinoma. Diagn pathology. 2012;7:41. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-7-41.
Wang L, Zhang J, Yang X, Chang YW, Qi M, Zhou Z, et al. SOX4 is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013;16(4):301–7. doi:10.1038/pcan.2013.25.
de Bont JM, Kros JM, Passier MM, Reddingius RE, Sillevis Smitt PA, Luider TM, et al. Differential expression and prognostic significance of SOX genes in pediatric medulloblastoma and ependymoma identified by microarray analysis. Neuro Oncology. 2008;10(5):648–60. doi:10.1215/15228517-2008-032.
Wang L, Li Y, Yang X, Yuan H, Li X, Qi M, et al. ERG-SOX4 interaction promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 2014;74(6):647–58. doi:10.1002/pros.22783.
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17(24):2815–34.
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007;8:16. doi:10.1186/1745-6215-8-16.
Wu KP, Li Q, Lin FX, Li J, Wu LM, Li W, et al. MT1-MMP is not a good prognosticator of cancer survival: evidence from 11 studies. Tumour Bio J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2014;. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2567-8.
Pramoonjago P, Baras AS, Moskaluk CA. Knockdown of Sox4 expression by RNAi induces apoptosis in ACC3 cells. Oncogene. 2006;25(41):5626–39. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209566.
Vervoort SJ, Lourenco AR, van Boxtel R, Coffer PJ. SOX4 mediates TGF-beta-induced expression of mesenchymal markers during mammary cell epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53238. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053238.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the plan project of science and technology (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
No ethics approval was required.
Additional information
J. Chen and H. L. Ju are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Ju, H.L., Yuan, X.Y. et al. SOX4 is a potential prognostic factor in human cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol 18, 65–72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1337-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1337-4