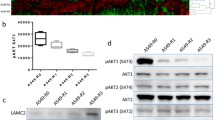
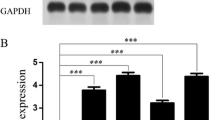
Abstract
Purpose
P21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1), a serine/threonine protein kinase which functions downstream of RAC and CDC42 GTPase, is activated by a variety of stimuli, including RAS and other growth signaling factors. The extracellular signal kinase (ERK) and protein kinase B (AKT) signal pathways have been implicated in the pathogenesis of cancers. Whether PAK1 is sensitive to KRAS mutation signals and plays a role through ERK and AKT signaling pathways in NSCLC needs to be studied.
Methods
The expression of PAK1, ERK and AKT was detected in both lung cancer cell lines and clinical samples. PAK1 RNA interference and specific inhibitor of PAK1(IPA-3) were applied to lung cancer cell lines and mouse xenograft tumors. Cell growth was measured by MTT and colony formation assays. Cell migration and invasion were detected by wound healing and transwell assays. RAS mutation was detected by Taqman probe method. Correlation between KRAS, PAK1, ERK and AKT activities was analyzed in lung cancer patients.
Results
PAK1 was highly expressed not only in RAS mutant but also in RAS wild-type lung cancer cells. Using specific inhibitor of PAK1, IPA-3 and PAK1 RNA interference, cell proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer cells were reduced significantly, accompanied by decreased activities of ERK and AKT. Dual inhibition of ERK and AKT suppressed these cellular processes to levels comparable to those achieved by reduction in PAK1 expression. In NSCLC patients, PAK1 was not correlated with KRAS mutation but was significantly positively correlated with pERK and pAKT.
Conclusion
PAK1 played roles in NSCLC proliferation and invasion via ERK and AKT signaling and suggested a therapeutic target for NSCLC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–917. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25516.
Grivaux M, Zureik M, Marsal L, Asselain B, Peureux M, Chavaillon JM, et al. Five-year survival for lung cancer patients managed in general hospitals. Rev Mal Respir. 2011;28(7):e31–e3838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmr.2008.07.001.
Guo M, Tomoshige K, Meister M, Muley T, Fukazawa T, Tsuchiya T, et al. Gene signature driving invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(4):462–81. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201606711.
Vijayalakshmi R, Krishnamurthy A. Targetable, "driver" mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2011;2(3):178–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-011-0108-0.
Liu JS, Che XM, Chang S, Qiu GL, He SC, Fan L, et al. β-elemene enhances the radiosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting Pak1 activation. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(34):9945–56. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9945.
Ong CC, Gierke S, Pitt C, Sagolla M, Cheng CK, Zhou W, et al. Small molecule inhibition of group I p21-activated kinases in breast cancer induces apoptosis and potentiates the activity of microtubule stabilizing agents. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-015-0564-5.
Ong CC, Jubb AM, Haverty PM, Zhou W, Tran V, Truong T, et al. Targeting p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) to induce apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(17):7177–82. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1103350108.
Babagana M, Johnson S, Slabodkin H, Bshara W, Morrison C, Kandel ES. P21-activated kinase 1 regulates resistance to BRAF inhibition in human cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2017;56(5):1515–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22611.
Chen MJ, Wu DW, Wang YC, Chen CY, Lee H. PAK1 confers chemoresistance and poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer via β-catenin-mediated stemness. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34933. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34933.
Hofmann C, Shepelev M, Chernoff J. The genetics of Pak. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt19):4343–54. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01392.
Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J. Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28(1–2):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1.
Higuchi M, Onishi K, Kikuchii C, Gotoh Y. Scaffolding function of PAK in the PDK1–Akt pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(11):1356–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1795.
Mao K, Kobayashi S, Jaffer ZM, Huang Y, Volden P, Chernoff J, et al. Regulation of Akt/PKB activity by P21-activated kinase in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44(2):429–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.10.016.
Shrestha Y, Schafer EJ, Boehm JS, Thomas SR, He F, Du J, et al. PAK1 is a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately activates MAPK and MET signaling. Oncogene. 2012;31(29):3397–408. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.515.
Liu F, Cheng Z, Li X, Li Y, Zhang H, Li J, et al. A novel Pak1/ATF2/miR-132 signaling axis is involved in the hematogenous metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;8:370–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.07.005.
Li LH, Wu GY, Lu YZ, Chen XH, Liu BY, Zheng MH, et al. p21-activated protein kinase 1 induces the invasion of gastric cancer cells through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(1):193–200. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5643.
Lv D, Li L, Lu Q, Li Y, Xie F, Li H, et al. PAK1-cofilin phosphorylation mediates human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration induced by apelin-13. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(5):569–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12563.
Rettig M, Trinidad K, Pezeshkpour G, Frost P, Sharma S, Moatamed F, et al. PAK1 kinase promotes cell motility and invasiveness through CRK-II serine phosphorylation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e4. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042012.
Jang I, Jeon BT, Jeong EA, Kim EJ, Kang D, Lee JS, et al. Pak1/LIMK1/cofilin pathway contributes to tumor migration and invasion in human non-small cell lung carcinomas and cell lines. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;16(3):159–65. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.3.159.
Wu DW, Wu TC, Chen CY, Lee H. PAK1 is a novel therapeutic target in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant lung adenocarcinoma activated by the PI3K/AKT signaling regardless of EGFR mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(21):5370–82. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2724.
Singhal R, Kandel ES. The response to PAK1 inhibitor IPA3 distinguishes between cancer cells with mutations in BRAF and RAS oncogenes. Oncotarget. 2012;3(7):700–8. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.587.
McDaniel AS, Allen JD, Park SJ, Jaffer ZM, Michels EG, Burgin SJ, et al. Pak1 regulates multiple c-Kit mediated RAS-MAPK gain-in-function phenotypes in Nf1+/− mast cells. Blood. 2008;112(12):4646–54. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-04-155085.
Huynh N, Liu KH, Baldwin GS, He H. P21-activated kinase 1 stimulates colon cancer cell growth and migration/invasion via ERK- and AKT-dependent pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803(9):1106–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.05.007.
Tabusa H, Brooks T, Massey AJ. Knockdown of PAK4 or PAK1 inhibits the proliferation of mutant KRAS colon cancer cells independently of RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling. Mol Cancer Res. 2013;11(2):109–21. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0466.
Gan J, Zhang Y, Ke X, Tan C, Ren H, Dong H, et al. Dysregulation of PAK1 is associated with DNA damage and is of prognostic importance in primary esophageal small cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(6):12035–50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160612035.
Mortazavi F, Lu J, Phan R, Lewis M, Trinidad K, Aljilani A, et al. Significance of KRAS/PAK1/Crk pathway in non-small cell lung cancer oncogenesis. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:381. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1360-4.
Viaud J, Peterson JR. An allosteric kinase inhibitor binds the p21-activated kinase autoregulatory domain covalently. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(9):2559–655. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0102.
Johnson GL, Lapadat R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 2002;298(5600):1911–2. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072682.
Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the raf-mek-erk mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3291–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210422.
Manning BD, Cantley LC. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 2007;129(7):1261–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase akt pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(7):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc839.
Park J, Kim JM, Park JK, Huang S, Kwak SY, Ryu KA, et al. Association of p21-activated kinase-1 activity with aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis of head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 2015;37(7):953–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.23695.
Siu MK, Wong ES, Chan HY, Kong DS, Woo NW, Tam KF, et al. Differential expression and phosphorylation of Pak1 and Pak2 in ovarian cancer: effects on prognosis and cell invasion. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(1):21–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25005.
Funding
This work was supported by the 13th five-year major new drug innovation project (2016ZX09101005), Shandong province science and technology breakthrough project (2016GSF201043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Shandong Provincial Cancer Research Institute Ethics Committee approved this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, P., Song, B., Liu, J. et al. Blockage of PAK1 alleviates the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells via inhibiting ERK and AKT signaling activity. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 892–901 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02486-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02486-5