Abstract
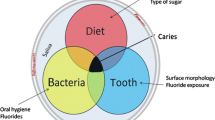
Dental caries in babies and toddlers is called Early Childhood Caries (ECC). It is an infectious and transmissible die-to-bacterial disease. Detailed knowledge regarding the acquisition and transmission of infectious agents facilitates a more comprehensive approach toward prevention. Mutans streptococci are important organisms in the initiation and progression of dental caries. Recent evidence demonstrates that these bacteria are found in the mouths of pre-dentate infants and are acquired via vertical and/or horizontal transmission from human reservoirs. This information should facilitate the focusing of clinical interventions that prevent or delay infant infection, thereby reducing the prevalence of dental caries (ECC) in babies and toddlers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of pediatric Dentistry, Originating Council: Definition of Early Childhood Caries (ECC): Pediatr Dent 2003; 25: 9.
Seow WK. Biological mechanisms of early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998; 26: 8–27.
Tinanoff N. Introduction to the early childhood caries conference: initial description and current understanding. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998; 26: 5–7.
American Academy of pediatric Dentistry, Originating Group and Review Council: Policy on ECC: Classification, Consequences, and Preventive Strategies. Pediatr Dent 2003; 25: 24–28.
Filstrup SL, Briskie D, Fonseca M, Lawrence L, Wandera A, Inglehart MR. ECC and quality of life: child and parent perspectives. Pediatr Dent 2003; 25: 431–440.
Habibian M, Beighton D, Stevenson R, Lawson M, Roberts G. Relationships between dietary behaviours, oral hygiene and mutans streptococci in dental plaque of a group of infants in southern England. Archives of Oral Biology 2002; 47: 491–498.
Poureslami HR. Study of Early Childhood Caries in children of the Kerman (Iran). Europ Archives Pediatr Dent 2006; 2: Abstract no.PD6-13.
Weerheijm KL, Uyttendaele-Speybrouck BF, Euwe HC, Groen HJ. Prolonged demand breast-feeding and nursing caries. Caries Res 1998; 32: 46–50.
Berkowitz RJ. Mutans Streptococci: Acquisition and transmission. Pediatr Dent 2006; 28: 106–109.
Van Houte J. Role of microorganisms in caries etiology. J Dent Res 1994; 73: 672–681.
Berkowitz RJ. Causes, treatment and prevention of ECC: A microbiologic perspective. J Can Dent Assoc 2003; 69: 304–307.
Li Y, Caufield PW, Dasanayake AP, Wiener HW, Vermund SH. Mode of delivery and other maternal factors influence the acquisition of streptococcus mutans in infants. J Dent Res 2005; 84: 806–811.
Law V, Seow WK. A longitudinal controlled study of factors associated with mutans streptococci infection and caries lesion initiation in children 21 to 72 months old. Pediatr Dent 2006; 28: 58–65.
Wan AL, Seow WK, Purdie DM, Bird PS, Walsh LJ, Tudehope DI. A longitudinal study of streptococcus mutans colonization in infants after tooth eruption. J Dent Res 2003; 82: 504–508.
Milgrom P, Riedy CA, Weinstein P, Tanner AC, Manibusan L, Bruss J. Dental caries and its relationship to bacterial infection, hypo-plasia, diet and oral hygiene in 6 to 36-month-old children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2000; 28: 295–306.
Ramos-Gomez FJ, Weintraup JA, Gansky SA, Hoover CI, Featherstone JD. Bacterial, behavioral and environmental factors associated with ECC. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2002; 26: 165–174.
Graves CE, Berkowitz RJ, Proskin HM, Chase I, Weinstein P, Billings R. Clinical outcomes for ECC: influence of aggressive dental surgery. J Dent Child 2004; 71: 114–117.
Ji Y, Rodis OM, Hori M, Nakai Y, Kariya N, Matsumura S, Shimono T. Risk behaviors and their association with presence of S. mutans or S. sobrinus and caries activity in 18-month-old Japanese children. Pediatr Dental J 2005; 15: 195–202.
Rodis OM, Okazaki Y, Kariya N, Ji Y, Kanao A, Hayashi M et al. Presence of S. mutans or S. sobrinus in cariostatinoculated plaque samples from Japanese mother-child pairs. Pediatr Dental J 2005; 15: 98–102.
Wan AL, Seow WK, Walsh LJ, Bird P, Tudehope DI, Purdie DM. Association of S. mutans infection and oral developmental nodules in pre-dentate infants. J Dent Res 2001; 80: 1945–1948.
Wan AL, Seow WK, Walsh LJ, Bird P, Tudehope DI, Purdie DM. Oral colonization of S. mutans in six-month-old pre-dentate infants. J Dent Res 2001; 80: 2060–2065.
Milgrom P. Response to Reisine and Douglass: psychosocial and behavioral issues in early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998; 26: 45–48.
Schroth RJ, Moffatt ME. Determinations of ECC in a rural Manitoba community: A pilot study. Pediatr Dent 2005; 27: 114–120.
Ismail AI. Prevention of Early Childhood Caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998; 26: 49–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poureslami, H.R., Van Amerongen, W.E. Early Childhood Caries (ECC): An infectious transmissible oral disease. Indian J Pediatr 76, 191–194 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0216-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0216-1