Abstract
Background
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET) is a useful staging investigation for follicular lymphoma (FL). Recent studies have shown that positive post-treatment PET is also a strong predictor of inferior overall survival.
Purpose
To evaluate the predictive value of mid- and post-treatment PET in FL patients with respect to progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Methods
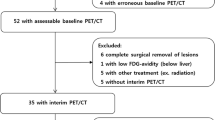
We included 57 patients with indolent FL (grade 1, 2, and 3a) who received induction chemotherapy. Mid- and post-treatment PET results were correlated with PFS and OS retrospectively and analysed using Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and Cox regression.
Results
Post-treatment PET was predictive of OS (mean OS 95.2 vs. 45.0 months for PET-negative vs. PET-positive, p < 0.001) and showed a trend towards significance for PFS (mean PFS 74.4 vs. 38.2 months for PET− vs. PET+, p = 0.083). 3-year PFS for post-treatment PET− and PET+ patients were 72 and 30 %, respectively. 3-year OS were 96 and 60 %, respectively. Mid-treatment PET was not predictive of PFS (mean PFS 78.5 vs. 51.0 months for PET− vs. PET+, p = 0.35) nor OS (mean OS 89.9 vs. 76.6 months for PET− vs. PET+, p = 0.92).
Conclusion
Post-treatment PET is predictive of OS in indolent FL. It identifies patients who might benefit from more intensive follow-up, enrolment in clinical trials or second-line therapy. Mid-treatment PET scan results did not appear to predict long-term treatment outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project. A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 1997;89:3909–18.
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. In: WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed. Lyon: WHO Press; 2008.
Wahlin BE, Yri OE, Kimby E, et al. Clinical significance of the WHO grades of follicular lymphoma in a population-based cohort of 505 patients with long follow-up times. Br J Haematol. 2012;156:225–33.
Isasi CR, Lu P, Blaufox MD. A metaanalysis of 18F-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose positron emission tomography in the staging and restaging of patients with lymphoma. Cancer. 2005;104:1066–74.
Juweid ME, Stroobants S, Hoekstra OS, et al. Use of positron emission tomography for response assessment of lymphoma: consensus of the Imaging Subcommittee of International Harmonization Project in Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:571–8.
Wohrer S, Jaeger U, Kletter K, et al. 18F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET) visualizes follicular lymphoma irrespective of grading. Ann Oncol. 2006;17:780–4.
Luminari S, Biasoli I, Arcaini L, et al. The use of FDG-PET in the initial staging of 142 patients with follicular lymphoma: a retrospective study from the FOLL05 randomized trial of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:2108–12.
Trotman J, Fournier M, Lamy T, et al. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) after induction therapy is highly predictive of patient outcome in follicular lymphoma: analysis of PET-CT in a subset of PRIMA trial participants. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3194–200.
Dupuis J, Berriolo-Riedinger A, Julian A, et al. Impact of [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography response evaluation in patients with high-tumor burden follicular lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy: a prospective study from the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte and GOELAMS. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:4317–22.
The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 1993;329:987–94.
Solal-Celigny P, Roy P, Colombat P, et al. Follicular lymphoma international prognostic index. Blood. 2004;104:1258–65.
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Haioun C. Report on the First International Workshop on Interim-PET-Scan in Lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50:1257–60.
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Haioun C, et al. Report on the Second International Workshop on interim positron emission tomography in lymphoma held in Menton, France, 8-9 April 2010. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010;51:2171–80.
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Itti E, et al. Report on the Third International Workshop on Interim Positron Emission Tomography in Lymphoma held in Menton, France, 26–27 September 2011 and Menton 2011 consensus. Leuk Lymphoma 2012.
Mikhaeel NG, Hutchings M, Fields PA, et al. FDG-PET after two to three cycles of chemotherapy predicts progression-free and overall survival in high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1514–23.
Bishu S, Quigley JM, Bishu SR, et al. Predictive value and diagnostic accuracy of F-18-fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography treated grade 1 and 2 follicular lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:1548–55.
Luminari S, Biasoli I, Versari A, et al. The prognostic role of post-induction FDG-PET in patients with follicular lymphoma: a subset analysis from the FOLL05 trial of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL). Ann Oncol. 2014;25:442–7.
Hiddemann W, Kneba M, Dreyling M, et al. Frontline therapy with rituximab added to the combination of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) significantly improves the outcome for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma compared with therapy with CHOP alone: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2005;106:3725–32.
Barrington SF, Qian W, Somer EJ, et al. Concordance between four European centres of PET reporting criteria designed for use in multicentre trials in Hodgkin lymphoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1824–33.
Tychyj-Pinel C, Ricard F, Fulham M, et al. PET/CT assessment in follicular lymphoma using standardized criteria: central review in the PRIMA study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:408–15.
Itti E, Meignan M, Berriolo-Riedinger A, et al. An international confirmatory study of the prognostic value of early PET/CT in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: comparison between Deauville criteria and DeltaSUVmax. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1312–20.
Lin C, Itti E, Haioun C, et al. Early 18F-FDG PET for prediction of prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: SUV-based assessment versus visual analysis. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:1626–32.
Le Dortz L, De Guibert S, Bayat S, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT in follicular lymphoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:2307–14.
Meignan M, Barrington S, Itti E, et al. Report on the 4th International Workshop on Positron Emission Tomography in Lymphoma held in Menton, France, 3–5 October 2012. Leuk Lymphoma 2014;55:31–7.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Ethical standard
Ethics approval was obtained from the Research and Ethics Office of the South Western Sydney Local Health District.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., Lin, M., Downe, P. et al. The prognostic value of mid- and post-treatment [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) in indolent follicular lymphoma. Ann Nucl Med 28, 805–811 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-014-0874-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-014-0874-1