Abstract
Objective
Positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) using 68Ga-labeled 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-N,N′,N″,N‴-tetraacetic acid-d-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide (DOTATOC) is usually performed about 1-h post-injection; however, because of rapid blood clearance, the waiting time for scanning could possibly be shortened without affecting diagnostic performance. The purpose of this study was to investigate the feasibility of early scanning at 30 min post-injection.
Methods
Thirty-eight patients who underwent DOTATOC-PET/CT were analyzed. After administration of 68Ga-DOTATOC, data acquisition was performed twice, at 30-min and 60-min post-injection. The number of known or suspected pathological lesions, and quantitative values of those lesions and physiological uptake were compared. SUVmax, SUVpeak, metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and total lesion uptake (TLU) were calculated as quantitative values of the pathological lesions.
Results
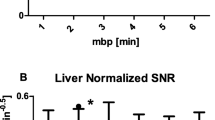
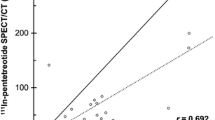
A total of 125 known or suspected pathological lesions were found at both timepoints, with no differences between the two datasets. The SUVmax, SUVpeak, MTV, and TLU were highly reproducible, with Spearman’s ρ of 0.983, 0.986, 0.918, and 0.981, respectively. The average percent differences (%DIFFave) defined as the differences of the values divided by the value at 1-h post-injection were 11.1% for SUVmax, 8.5% for SUVpeak, 15.1% for MTV, and 20.6% for TLU. Physiological uptake in the two datasets was closely comparable in the pituitary gland (Spearman’s ρ = 0.954, %DIFFave = 11.0%), liver (0.989, 3.9%), spleen (0.970, 6.3%), adrenal glands (0.879, 13.0%), and pancreatic uncus (0.946, 12.7%).
Conclusion
The diagnostic performance of visual interpretation should be comparable between DOTATOC-PET/CT images obtained at 30-min and 60-min post-injection. Some differences between quantitative values may exist; however, they appear to be minimal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Putzer D, Kroiss A, Waitz D, Gabriel M, Traub-Weidinger T, Uprimny C, et al. Somatostatin receptor PET in neuroendocrine tumours: 68 Ga-DOTA0,Tyr3-octreotide versus 68 Ga-DOTA0-lanreotide. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:364–72.
Barrio M, Czernin J, Fanti S, Ambrosini V, Binse I, Du L, et al. The impact of somatostatin receptor-directed PET/CT on the management of patients with neuroendocrine tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:756–61.
Virgolini I, Ambrosini V, Bomanji JB, Baum RP, Fanti S, Gabriel M, et al. Procedure guidelines for PET/CT tumour imaging with 68 Ga-DOTA-conjugated peptides: 68 Ga-DOTA-TOC, 68 Ga-DOTA-NOC, 68 Ga-DOTA-TATE. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:2004–10.
Bozkurt MF, Virgolini I, Balogova S, Beheshti M, Rubello D, Decristoforo C, et al. Guideline for PET/CT imaging of neuroendocrine neoplasms with (68)Ga-DOTA-conjugated somatostatin receptor targeting peptides and (18)F-DOPA. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44:1588–601.
Velikyan I, Sundin A, Sörensen J, Lubberink M, Sandström M, Garske-Román U, et al. Quantitative and qualitative intrapatient comparison of 68 Ga-DOTATOC and 68 Ga-DOTATATE: net uptake rate for accurate quantification. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:204–10.
Nakamoto Y, Ishimori T, Sano K, Temma T, Ueda M, Saji H, et al. Clinical efficacy of dual-phase scanning using (68)Ga-DOTATOC-PET/CT in the detection of neuroendocrine tumours. Clin Radiol. 2016;71:1069.e1-5.
Dirisamer A, Halpern BS, Schima W, Heinisch M, Wolf F, Beheshti M, et al. Dual-time-point FDG-PET/CT for the detection of hepatic metastases. Mol Imaging Biol. 2008;10:335–40.
Miyake KK, Nakamoto Y, Togashi K. Dual-time-point 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with colorectal cancer: clinical value of early delayed scanning. Ann Nucl Med. 2012;26:492–500.
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan (16K10346).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamoto, Y., Ishimori, T., Sano, K. et al. Clinical feasibility of early scanning after administration of 68Ga-DOTATOC. Ann Nucl Med 33, 55–60 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-018-1304-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-018-1304-6