Abstract
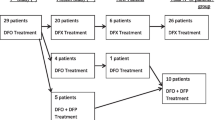
The life expectancy of thalassemic patients has increased, and now approaches that of healthy individuals, thanks to improved treatment regimens. However, pregnancy in women with β-Thalassemia Μajor remains a challenging condition. Recent advances in managing this haemoglobinopathy offer the potential for safe pregnancies with favorable outcome. However, clinical data regarding the use of chelation therapy during pregnancy are limited, and it is unclear whether these agents impose any risk to the developing fetus. Successful pregnancies following unintentional treatment with deferoxamine or deferasirox have rarely been reported. Generally, chelators are not recommended during pregnancy. Regarding the new oral chelators, data on fetotoxicity are lacking. In the present study, we describe the evolution and successful outcome of nine pregnancies in six Greek thalassemic women who received deferasirox inadvertently during early pregnancy, and review the literature regarding fetal anomalies due to chelators. Use of chelation before embarking upon a non-programmed pregnancy remains a difficult and unresolved question. In our study, chelation treatment during pregnancy did not prevent the delivery of healthy children. Nonetheless, the use of deferasirox is contraindicated in pregnant women, based on the product label. Deferasirox should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefit outweighs the potential fetal risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffbrand AV, Taher A, Cappellini MD. How I treat transfusional iron overload. Blood. 2012;120:3657–69.
Kuo KH, Mrkobrada M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deferiprone monotherapy and in combination with deferoxamine for reduction of iron overload in chronically transfused patients with β-thalassemia. Hemoglobin. 2014;38:409–21.
Aydinok Y, Kattamis A, Cappellini MD, El-Beshlawy A, Origa R, Elalfy M, et al. Effects of deferasirox-deferoxamine on myocardial and liver iron in patients with severe transfusional iron overload. Blood. 2015;125:3868–77.
Cappellini MD, Bejaoui M, Agaoglu L, Canatan D, Capra M, Cohen A, et al. Iron chelation with deferasirox in adult and pediatric patients with thalassemia major: efficacy and safety during 5 years’ follow-up. Blood. 2011;118:884–93.
Wood JC. Estimating tissue iron burden: current status and future prospects. Br J Haematol. 2015;170:15–28.
Ault P, Jones K. Understanding iron overload: screening, monitoring, and caring for patients with transfusion-dependent anemias. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2009;13:511–7.
Ho PJ, Tay L, Lindeman R, Catley L, Bowden DK. Australian guidelines for the assessment of iron overload and iron chelation in transfusion-dependent thalassaemia major, sickle cell disease and other congenital anaemias. Intern Med J. 2011;41:516–24.
Marsella M, Borgna-Pignatti C. Transfusional iron overload and iron chelation therapy in thalassemia major and sickle cell disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014;28:703–27.
Cianciulli P. Treatment of iron overload in thalassemia. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008;6(Suppl 1):208–13.
Origa R, Piga A, Quarta G, Forni GL, Longo F, Melpignano A, et al. Pregnancy and β-thalassemia: an Italian multicenter experience. Haematologica. 2010;95:376–81.
Farmaki K, Gotsis E, Tzoumari I, Berdoukas V. Rapid iron loading in a pregnant woman with transfusion-dependent thalassemia after brief cessation of iron chelation therapy. Eur J Haematol. 2008;81:157–9.
Tampakoudis P, Tsatalas C, Mamopoulos M, Tantanassis T, Christakis JI, Sinakos Z, et al. Transfusion-dependent homozygous beta-thalassaemia major: successful pregnancy in five cases. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1997;74:127–31.
Berdoukas V, Farmaki K, Carson S, Wood J, Coates T. Treating thalassemia major related iron overload: the role of deferiprone. J Blood Med. 2012;3:119–29.
Ferraioli G, Parekh P, Levitov AB, Filice C. Shear wave elastography for evaluation of liver fibrosis. J Ultrasound Med. 2014;33:197–203.
Sohawon D, Lau KK, Lau T, Bowden DK. Extra-medullary haematopoiesis: a pictorial review of its typical and atypical locations. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012;56:538–44.
Haddad A, Tyan P, Radwan A, Mallat N, Taher A. β-Thalassemia Intermedia: A Bird’s-Eye View. Turk J Haematol. 2014;31:5–16.
Vichinsky E. Non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia and thalassemia intermedia: epidemiology, complications, and management. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32:191–204.
Bosque MA, Domingo JL, Corbella J. Assessment of the developmental toxicity of deferoxamine in mice. Arch Toxicol. 1995;69:467–71.
Singer ST, Vichinsky EP. Deferoxamine treatment during pregnancy: is it harmful? Am J Hematol. 1999;60:24–6.
McElhatton PR, Roberts JC, Sullivan FM. The consequences of iron overdose and its treatment with desferrioxamine in pregnancy. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1991;10:251–9.
Al-Khabori M, Bhandari S, Al-Huneini M, Al-Farsi K, Panjwani V, Daar S. Side effects of deferasirox iron chelation in patients with beta thalassemia major or intermedia. Oman Med J. 2013;28:121–4.
Shilalukey K, Kaufman M, Bradley S, Francombe WH, Amankwah K, Goldberg E, et al. Counseling sexually active teenagers treated with potential human teratogens. J Adolesc Health. 1997;21:143–6.
Vini D, Servos P, Drosou M. Normal pregnancy in a patient with β-thalassaemia major receiving iron chelation therapy with deferasirox (Exjade®). Eur J Haematol. 2011;86:274–5.
Anastasi S, Lisi R, Abbate G, Caruso V, Giovannini M, De Sanctis V. Absence of teratogenicity of deferasirox treatment during pregnancy in a thalassaemic patient. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2011;8(Suppl 2):345–7.
Deugnier Y, Turlin B, Ropert M, Cappellini MD, Porter JB, Giannone V, et al. Improvement in liver pathology of patients with β-thalassemia treated with deferasirox for at least 3 years. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1202–11.
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted under the Declaration of Helsinki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare we have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
M. D. Diamantidis, N. Neokleous and A. Agapidou contributed equally to the study.
About this article
Cite this article
Diamantidis, M.D., Neokleous, N., Agapidou, A. et al. Iron chelation therapy of transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia during pregnancy in the era of novel drugs: is deferasirox toxic?. Int J Hematol 103, 537–544 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-1945-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-1945-y