Abstract
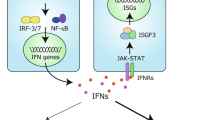
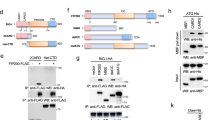
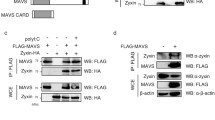
During virus infection, RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) recognize viral RNAs and recruit the adaptor protein VISA to activate downstream signaling, leading to activation of transcription factors NF-κB and IRF3, which collaborate to induce type I interferons (IFNs). IFNs further induce expression of hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) that suppress viral replication and facilitate the adaptive immune response. Dysregulated production of IFNs is implicated in various immune diseases. Here we identified Signal Recognition Particle 54 (SRP54) as a negative regulator of RLRs-induced antiviral signaling. Overexpression of SRP54 inhibited RNA virus-triggered induction of IFN-β and increased viral replication, whereas knockdown of SRP54 had opposite effects. Mechanistically, SRP54 interacted with both RIG-I and MDA5 and impaired their association with VISA. Our findings demonstrate that SRP54 acts as a negative regulator of RLRs-mediated innate immune response by disrupting the recruitment of VISA to RIG-I/MDA5.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Akopian D, Shen K, Zhang X, Shan SO (2013) Signal recognition particle: an essential protein-targeting machine. Annu Rev Biochem 82:693–721
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded rna and activation of nf-κb by toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732–738
Andrejeva J, Childs KS, Young DF, Carlos TS, Stock N, Goodbourn S, Randall RE (2004) The v proteins of paramyxoviruses bind the ifn-inducible rna helicase, mda-5, and inhibit its activation of the ifn-beta promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17264–17269
Bacher G, Lütcke H, Jungnickel B, Rapoport TA, Dobberstein B (1996) Regulation by the ribosome of the gtpase of the signal-recognition particle during protein targeting. Nature 381:248–251
Bellanné-Chantelot C, Schmaltz-Panneau B, Marty C, Fenneteau O, Callebaut I, Clauin S, Docet A, Damaj G-L, Leblanc T, Pellier I, Stoven C, Souquere S, Antony-Debré I, Beaupain B, Aladjidi N, Barlogis V, Bauduer F, Bensaid P, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Berger C, Bertrand Y, Carausu L, Fieschi C, Galambrun C, Schmidt A, Journel H, Mazingue F, Nelken B, Quah TC, Oksenhendler E, Ouachée M, Pasquet M, Saada V, Suarez F, Pierron G, Vainchenker W, Plo I, Donadieu J (2018) Mutations in the srp54 gene cause severe congenital neutropenia as well as shwachman-diamond-like syndrome. Blood 132:1318–1331
Cao X (2016) Self-regulation and cross-regulation of pattern-recognition receptor signalling in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 16:35–50
Carapito R, Konantz M, Paillard C, Miao Z, Pichot A, Leduc MS, Yang Y, Bergstrom KL, Mahoney DH, Shardy DL, Alsaleh G, Naegely L, Kolmer A, Paul N, Hanauer A, Rolli V, Muller JS, Alghisi E, Sauteur L, Macquin C, Morlon A, Sancho CS, Amati-Bonneau P, Procaccio V, Mosca-Boidron AL, Marle N, Osmani N, Lefebvre O, Goetz JG, Unal S, Akarsu NA, Radosavljevic M, Chenard MP, Rialland F, Grain A, Bene MC, Eveillard M, Vincent M, Guy J, Faivre L, Thauvin-Robinet C, Thevenon J, Myers K, Fleming MD, Shimamura A, Bottollier-Lemallaz E, Westhof E, Lengerke C, Isidor B, Bahram S (2017) Mutations in signal recognition particle srp54 cause syndromic neutropenia with shwachman-diamond-like features. J Clin Invest 127:4090–4103
Carty M, Kearney J, Shanahan KA, Hams E, Sugisawa R, Connolly D, Doran CG, Munoz-Wolf N, Gurtler C, Fitzgerald KA, Lavelle EC, Fallon PG, Bowie AG (2019) Cell survival and cytokine release after inflammasome activation is regulated by the toll-il-1r protein sarm. Immunity 50(6):1412–1424
Egea PF, Stroud RM, Walter P (2005) Targeting proteins to membranes: structure of the signal recognition particle. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:213–220
Focia PJ, Shepotinovskaya IV, Seidler JA, Freymann DM (2004) Heterodimeric gtpase core of the srp targeting complex. Science 303:373–377
Freymann DM, Keenan RJ, Stroud RM, Walter P (1997) Structure of the conserved gtpase domain of the signal recognition particle. Nature 385:361–364
Honda K, Takaoka A, Taniguchi T (2006) Type i interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 25:349–360
Hu MM, Liao CY, Yang Q, Xie XQ, Shu HB (2017) Innate immunity to rna virus is regulated by temporal and reversible sumoylation of rig-i and mda5. J Exp Med 214:973–989
Janda CY, Li J, Oubridge C, Hernández H, Robinson CV, Nagai K (2010) Recognition of a signal peptide by the signal recognition particle. Nature 465:507–510
Kowalinski E, Lunardi T, McCarthy AA, Louber J, Brunel J, Grigorov B, Gerlier D, Cusack S (2011) Structural basis for the activation of innate immune pattern-recognition receptor rig-i by viral RNA. Cell 147:423–435
Kurita K, Honda K, Suzuma S, Takamatsu H, Nakamura K, Yamane K (1996) Identification of a region of bacillus subtilis FFH, a homologue of mammalian SRP54 protein, that is essential for binding to small cytoplasmic RNA. J Biol Chem 271:13140–13146
Lei CQ, Zhang Y, Li M, Jiang LQ, Zhong B, Kim YH, Shu HB (2015) Ecsit bridges rig-i-like receptors to visa in signaling events of innate antiviral responses. J Innate Immun 7:153–164
Lian H, Zang R, Wei J, Ye W, Hu M-M, Chen Y-D, Zhang X-N, Guo Y, Lei C-Q, Yang Q, Luo W-W, Li S, Shu H-B (2018) The zinc-finger protein zcchc3 binds rna and facilitates viral rna sensing and activation of the rig-i-like receptors. Immunity 49:438–448.e435
Luirink J, Dobberstein B (1994) Mammalian and escherichia coli signal recognition particles. Mol Microbiol 11:9–13
Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, Moradpour D, Binder M, Bartenschlager R, Tschopp J (2005) Cardif is an adaptor protein in the rig-i antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis c virus. Nature 437:1167–1172
Randall RE, Goodbourn S (2008) Interferons and viruses: an interplay between induction, signalling, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J Gen Virol 89:1–47
Roers A, Hiller B, Hornung V (2016) Recognition of endogenous nucleic acids by the innate immune system. Immunity 44:739–754
Samuelsson T (1992) A mycoplasma protein homologous to mammalian SRP54 recognizes a highly conserved domain of SRP RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 20:5763–5770
Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ (2005) Identification and characterization of mavs, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates nf-kappab and irf 3. Cell 122:669–682
Watanabe Y, Uruha A, Suzuki S, Nakahara J, Hamanaka K, Takayama K, Suzuki N, Nishino I (2016) Clinical features and prognosis in anti-srp and anti-hmgcr necrotising myopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87:1038–1044
Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, Li LY, Zhai Z, Shu HB (2005) Visa is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered ifn-beta signaling. Mol Cell 19:727–740
Yang Y, Wang SY, Huang ZF, Zou HM, Yan BR, Luo WW, Wang YY (2016) The rna-binding protein mex3b is a coreceptor of toll-like receptor 3 in innate antiviral response. Cell Res 26:288–303
Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M, Taira K, Akira S, Fujita T (2004) The rna helicase rig-i has an essential function in double-stranded rna-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat Immunol 5:730–737
Zhong B, Yang Y, Li S, Wang YY, Li Y, Diao F, Lei C, He X, Zhang L, Tien P, Shu HB (2008) The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 29:538–550
Zopf D, Bernstein HD, Johnson AE, Walter P (1990) The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kd protein subunit of the signal recognition particle contains an rna binding site and can be crosslinked to a signal sequence. EMBO J 9:4511–4517
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770946, awarded to Y.Y.) and Key Research Programs of Frontier Science (awarded to Y.Y.W.) funded by Chinese Academy of Sciences. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DPW, YYW and YY designed the experiments. DPW, HYZ, BWL and TZ carried out the experiments. DPW, ZSX, YYW and YY analyzed the data. DPW wrote the paper. YY and YYW checked and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they no conflict interest.
Animal and Human Rights Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, DP., Zhang, HY., Liao, BW. et al. SRP54 Negatively Regulates IFN-Beta Production and Antiviral Response by Targeting RIG-I and MDA5. Virol. Sin. 36, 231–240 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00267-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00267-6