Abstract
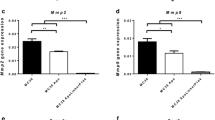
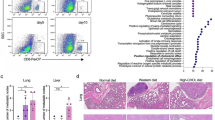
Lipoprotein(a) is a proatherogenic, prothrombotic lipoprotein that comprises apolipoprotein(a) (apo(a)) tethered to apolipoprotein B-100, which surrounds a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) moiety. Despite its molecular similarity to plasminogen, apo(a) plays distinct physiological and pathological roles both in vitro and in vivo. In this study, we examined possible target molecules and the therapeutic potential of gene therapy using a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) carrying the LK8 and LK68 (LKs) genes, which encode the cryptic kringle fragment of apo(a) (rAAV-LK), for the treatment of colon carcinoma. The results showed that AAV-produced LKs inhibited the migration of HUVECs induced by different angiogenic factors in a dose-dependent manner, and the potency was >1,000-fold than that of recombinant LK8 and LK68 proteins. A single intramuscular injection of rAAV-LKs (1 × 109 infectious particles (IP)/mouse) significantly inhibited the growth of subcutaneously transplanted LS174T tumors and reduced the number of tumor nodules in metastasized livers. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that AAVproduced LKs inhibited microvessel formation within the tumor mass, thereby inducing apoptosis in the tumor periphery, leading to the suppression of both tumor growth and metastasis. Taken together, these results suggest that AAV-produced LKs are multi-potent angiogenesis inhibitors that suppress the growth and metastasis of colon carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferretti, G., T. Bacchetti, T. P. Johnston, M. Banach, M. Pirro, and A. Sahebkar (2018) Lipoprotein(a): A missing culprit in the management of athero-thrombosis? J. Cell Physiol. 233: 2966–2981.
McLean, J. W., J. E. Tomlinson, W. J. Kuang, D. L. Eaton, E. Y. Chen, G. M. Fless, A. M. Scanu, and R. M. Lawn (1987) cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein (a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature 330: 132–137.
Hoover-Plow, J., L. A. Miles, G. M. Fless, A. M. Scanu, and E. F. Plow (1993) Comparison of the lysine binding functions of lipoprotein(a) and plasminogen. Biochemistry 49: 13681–13687.
Sha, J., B. Mccullogugh, E. Hart, F. Nassir, N. O. Davidson, and J. Hoover-Plow (2005) Apo(a) promotes thrombosis in a vascular injury model by a mechanism independent of plasminogen. J. Thromb. Haemost. 3: 2281–2289.
Chabowski, M., A. Nowak, J. Grzegrzolka, A. Piotrowska, D. Janczak, and P. Dziegiel (2018) Comparison of microvessel density using Nestin and CD34 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 38: 3889–3895.
De Palma, M., D. Biziato, and T. V. Petrova (2017) Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis Nat. Rev. Cancer 17: 457–474.
Novellasdemunt, L., P. Antas, and V. S. W. Li (2015) Targeting Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. A review in the theme: cell signaling: proteins, pathways and mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 309: C511–C521.
Ferrara, N. and A. P. Adamis (2016) Ten years of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15: 385–403.
Cao, Y., R. Cao, and N. Veitonmäki (2002) Kringle structures and antiangiogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 2: 667–681.
Grant, M. A. and R. Kalluri (2005) Structural basis for the functions of endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 70: 399–417.
Yu, H. K., J. S. Kim, H. J. Lee, J. H. Ahn, S. K. Lee, S. W. Hong, and Y. Yoon (2004) Suppression of colorectal cancer liver metastasis and extension of survival by expression of apolipoprotein (a) kringles. Cancer Res. 64: 7092–7098.
Lee, K., S. T. Yun, Y. G. Kim, Y. Yoon, and E.-C. Jo (2006) Adeno-associated virus-mediated expression of apolipoprotein (a) kringles suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth in mice. Hepatology 43: 1063–1073.
Lippi, G., M. Franchini, G. L. Salvagno, and G. C. Guidi (2007) Lipoprotein[a] and cancer: Anti-neoplastic effect besides its cardiovascular potency. Cancer Treat. Rev. 33: 427–436.
Liu, L., M. B. Boffa, and M. L. Koschinsky (2013) Apolipoprotein (a) inhibits in vitro tube formation in endothelial cells: identification of roles for Kringle V and the plasminogen activation system. PLoS One 8: e52287.
Ahn, J. H., H. K. Yu, H. J. Lee, S. W. Hong, S. J. Kim, and J. S. Kim (2014) Suppression of colorectal cancer liver metastasis by apolipoprotein(a) kringle V in a nude mouse model through the induction of apoptosis in tumor-associated endothelial cells. PLoS One 9: e93794.
Park, J. Y., B. P. Lim, K. Lee, Y. G. Kim, and E.-C. Jo (2006) Scalable production of adeno-associated virus type 2 vectors via suspension transfection. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 94: 416–430.
Naik, M. U. and U. P. Naik (2006) Junctional adhesion molecule-A-induced endothelial cell migration on vitronectin is integrin αvß3 specific. J. Cell Sci. 119: 490–499.
Oh, M., Y. J. Kim, Y. J. Son, H. S. Yoo, and J. H. Park (2017) Promotive effects of human induced pluripotent stem cell-conditioned medium on the proliferation and migration of dermal fibroblasts. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 22: 561–568.
Lee, H., D. Kim, S. M. Lim, and S. Kwon (2017) Rice callus extracts for enhancing skin wound healing. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 22: 352–358.
Pang, X., Z. Yi, X. Zhang, B. Sung, W. Qu, X. Lian, B. B. Aggarwal, and M. Liu (2009) Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 69: 5893–5900.
Kim, J. S., H. K. Yu, J. H. Ahn, H. J. Lee, S. W. Hong, K. H. Jung, S. I. Chang, Y. K. Hong, Y. A. Joe, S. M. Byun, S. K. Lee, S. I. Chung, and Y. Yoon (2004) Human apolipoprotein (a) kringle V inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo by interfering with the activation of focal adhesion kinases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 313: 534–540.
Kim, J. S., J. H. Chang, H. K. Yu, J. H. Ahn, J. S. Yum, S. K. Lee, K. H. Jung, D. H. Park, Y. Yoon, S. M. Byun, and S. I. Chung (2003) Inhibition of angiogenesis and angiogenesis-dependent tumor growth by the cryptic kringle fragments of human apolipoprotein (a). J. Biol. Chem. 278: 29000–29008.
Pàez-Ribes, M., E. Allen, J. Hudock, T. Takeda, H. Okuyama, F. Viñals, M. Inoue, G. Bergers, D. Hanahan, and O. Casanovas (2009) Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell 15: 220–231.
Ebos, J. M. L., C. R. Lee, W. Cruz-Munoz, G. A. Bjarnason, J. G. Christensen, and R. S. Kerbel (2009) Accelerated metastasis after short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 15: 232–239.
Ma, S., S. Pradeep, W. Hu, D. Zhang, R. Coleman, and A. Sood (2018) The role of tumor microenvironment in resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. F1000Resaerch 7: 326.
Roswall, P., M. Bocci, M. Bartoschek, H. Li, G. Kristiansen, S. Jansson, S. Lehn, J. Sjölund, S. Reid, C. Larsson, P. Eriksson, C. Anderberg, E. Cortez, L. H. Saal, C. Orsmark-Pietras, E. Cordero, B. K. Haller, J. Häkkinen, I. J. G. Burvenich, E. Lim, A. Orimo, M. Höglund, L. Rydén, H. Moch, A. M. Scott, U. Eriksson, and K. Pietras (2018) Microenvironmental control of breast cancer subtype elicited through paracrine platelet-derived growth factor-CC signaling. Nat. Med. 24: 463–473.
Hosaka, K., Y. Yang, M. Nakamura, P. Andersson, X. Yang, Y. Zhang, T. Seki, M. Scherzer, O. Dubey, X. Wang, and Y. Cao (2018) Dual roles of endothelial FGF-2-FGFR1-PDGF-BB and perivascular FGF-2-FGFR2-PDGFRβ signaling pathways in tumor vascular remodeling. Cell Discov. 4: 3.
Dewerchin, M. and P. Carmeliet (2014) Placental growth factor in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 18: 1339–1354.
Li, C., T. Liu, A. V. Bazhin, and Y. Yang (2017) The sabotaging role of myeloid cells in anti-angiogenic therapy: Coordination of angiogenesis and immune suppression by hypoxia. J. Cell. Physiol. 232: 2312–2322.
Liu, M. B. Boffa, and M. L. Koschinsky (2013) Apolipoprotein (a) inhibits in vitro tube formation in endotherlial cells: identification of roles for Kringle V and the plasminogen activation system. PLoS One 8(1): e52287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Yun, ST., Ahn, BY. et al. Apolipoprotein(a) Kringles for Gene Therapy of Colon Cancer. Biotechnol Bioproc E 24, 163–175 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0352-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0352-z