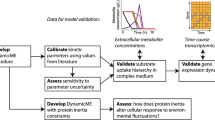
Abstract
Genome-scale models (GEMs) are predictive tools to study genotype-phenotype relationships in biological systems. Initially, genome-scale models were used for predicting the metabolic state of the organism given the nutrient condition and genetic perturbation (if any). Such metabolic (M-) models have been successfully developed for diverse organisms in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In this review, we focus our attention to genome-scale models of metabolism and macromolecular expression or ME-models. ME-models expand the scope of M-models by incorporating macromolecular biosynthesis pathways of transcription and translation. ME-models can predict the proteome investment in metabolism under any given condition. Therefore, ME-models significantly improve the quantitative prediction of gene expression. Unlike M-models that can predict biological properties in only nutrient-limited condition, ME-models can do so in both nutrient- and proteome-limited conditions. There are a few limitations of ME-models, many of which have now been largely overcome, making them more attractive to the broader research community. We finally discuss the applications of GEMs in general, and how they have been applied for biomedical, bioengineering and bioremediation purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crick, F. H. C. (1973) Project K: “The Complete Solution of E. Coli”. Perspect. Biol. Med. 17: 67–70.
Bordbar, A., J. M. Monk, Z. A. King, and B. O. Palsson (2014) Constraint-based models predict metabolic and associated cellular functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15: 107–120.
Price, N. D., J. L. Reed, and B. O. Palsson (2004) Genome-scale models of microbial cells: evaluating the consequences of constraints. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2: 886–897.
Edwards, J. S. and B. O. Palsson (1999) Systems properties of the Haemophilus influenzaeRd metabolic genotype. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 17410–17416.
Edwards, J. S. and B. O. Palsson (2000) The Escherichia coli MG1655 in silico metabolic genotype: its definition, characteristics, and capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97: 5528–5533.
Monk, J. M., C. J. Lloyd, E. Brunk, N. Mih, A. Sastry, Z. King, R. Takeuchi, W. Nomura, Z. Zhang, H. Mori, A. M. Feist, and B. O. Palsson (2017) iML1515, a knowledgebase that computes Escherichia coli traits. Nat. Biotechnol. 35: 904–908.
Gu, C., G. B. Kim, W. J. Kim, H. U. Kim, and S. Y. Lee (2019) Current status and applications of genome-scale metabolic models. Genome Biol. 20: 121.
Zhu, Y., T. Czauderna, J. Zhao, M. Klapperstueck, M. H. M. Maifiah, M. L. Han, J. Lu, B. Sommer, T. Velkov, T. Lithgow, J. Song, F. Schreiber, and J. Li (2018) Genome-scale metabolic modeling of responses to polymyxins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gigascience. 7: giy021.
Huang, X. and Y. H. Lin (2019) Reconstruction and analysis of a three-compartment genome-scale metabolic model for Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 67: 133–139.
Nogales, J., J. Mueller, S. Gudmundsson, F. J. Canalejo, E. Duque, J. Monk, A. M. Feist, J. L. Ramos, W. Niu, and B. O. Palsson (2020) High-quality genome-scale metabolic modelling of Pseudomonas putida highlights its broad metabolic capabilities. Environ. Microbiol. 22: 255–269.
Thompson, R. A., S. Dahal, S. Garcia, I. Nookaew, and C. T. Trinh (2016) Exploring complex cellular phenotypes and model-guided strain design with a novel genome-scale metabolic model of Clostridium thermocellum DSM 1313 implementing an adjustable cellulosome. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 9: 194.
Zou, W., G. Ye, J. Zhang, C. Zhao, X. Zhao, and K. Zhang (2018) Genome-scale metabolic reconstruction and analysis for Clostridium kluyveri. Genome. 61: 605–613.
Aminian-Dehkordi, J., S. M. Mousavi, A. Jafari, I. Mijakovic, and S. A. Marashi (2019) Manually curated genome-scale reconstruction of the metabolic network of Bacillus megaterium DSM319. Sci. Rep. 9: 18762.
Lu, H., F. Li, B. J. Sánchez, Z. Zhu, G. Li, I. Domenzain, S. Marcišauskas, P. M. Anton, D. Lappa, C. Lieven, M. E. Beber, N. Sonnenschein, E. J. Kerkhoven, and J. Nielsen (2019) A consensus S. cerevisiae metabolic model Yeast8 and its ecosystem for comprehensively probing cellular metabolism. Nat. Commun. 10: 3586.
Witting, M., J. Hastings, N. Rodriguez, C. J. Joshi, J. P. N. Hattwell, P. R. Ebert, M. van Weeghel, A. W. Gao, M. J. O. Wakelam, R. H. Houtkooper, A. Mains, N. Le Novère, S. Sadykoff, F. Schroeder, N. E. Lewis, H. J. Schirra, C. Kaleta, and O. Casanueva (2018) Modeling meets metabolomics-the wormjam consensus model as basis for metabolic studies in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Mol. Biosci. 5: 96.
Brunk, E., S. Sahoo, D. C. Zielinski, A. Altunkaya, A. Drager, N. Mih, F. Gatto, A. Nilsson, G. A. Preciat Gonzalez, M. K. Aurich, A. Prlic, A. Sastry, A. D. Danielsdottir, A. Heinken, A. Noronha, P. W. Rose, S. K. Burley, R. M. T. Fleming, J. Nielsen, I. Thiele, and B. O. Palsson (2018) Recon3D enables a three-dimensional view of gene variation in human metabolism. Nat. Biotechnol. 36: 272–281.
Bauer, E. and I. Thiele (2018) From network analysis to functional metabolic modeling of the human gut microbiota. mSystems. 3: e00209–17.
Magnusdottir, S. and I. Thiele (2018) Modeling metabolism of the human gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 51: 90–96.
Baldini, F., A. Heinken, L. Heirendt, S. Magnusdottir, R. M. T. Fleming, and I. Thiele (2019) The Microbiome Modeling Toolbox: from microbial interactions to personalized microbial communities. Bioinformatics. 35: 2332–2334.
Koch, S., F. Kohrs, P. Lahmann, T. Bissinger, S. Wendschuh, D. Benndorf, U. Reichl, and S. Klamt (2019) RedCom: A strategy for reduced metabolic modeling of complex microbial communities and its application for analyzing experimental datasets from anaerobic digestion. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1006759.
Machado, D., S. Andrejev, M. Tramontano, and K. R. Patil (2018) Fast automated reconstruction of genome-scale metabolic models for microbial species and communities. Nucleic Acids Res. 46: 7542–7553.
Norsigian, C. J., X. Fang, Y. Seif, J. M. Monk, and B. O. Palsson (2020) A workflow for generating multi-strain genome-scale metabolic models of prokaryotes. Nat. Protoc. 15: 1–14.
Harcombe, W. R., N. F. Delaney, N. Leiby, N. Klitgord, and C. J. Marx (2013) The ability of flux balance analysis to predict evolution of central metabolism scales with the initial distance to the optimum. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9: e1003091.
Schuetz, R., N. Zamboni, M. Zampieri, M. Heinemann, and U. Sauer (2012) Multidimensional optimality of microbial metabolism. Science. 336: 601–604.
Gianchandani, E. P., M. A. Oberhardt, A. P. Burgard, C. D. Maranas, and J. A. Papin (2008) Predicting biological system objectives de novo from internal state measurements. BMC Bioinformatics. 9: 43.
Zhao, Q., A. I. Stettner, E. Reznik, I. C. Paschalidis, and D. Segre (2016) Mapping the landscape of metabolic goals of a cell. Genome Biol. 17: 109.
Lachance, J. C., C. J. Lloyd, J. M. Monk, L. Yang, A. V. Sastry, Y. Seif, B. O. Palsson, S. Rodrigue, A. M. Feist, Z. A. King, and P. É. Jacques (2019) BOFdat: Generating biomass objective functions for genome-scale metabolic models from experimental data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1006971.
Yang, L., M. A. Saunders, J. C. Lachance, B. O. Palsson, and J. Bento (2019) Estimating cellular goals from high-dimensional biological data. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. August 4–8. Anchorage, AK, USA.
Bordbar, A., M. L. Mo, E. S. Nakayasu, A. C. Schrimpe-Rutledge, Y. M. Kim, T. O. Metz, M. B. Jones, B. C. Frank, R. D. Smith, S. N. Peterson, D. R. Hyduke, J. N. Adkins, and B. O. Palsson (2012) Model-driven multi-omic data analysis elucidates metabolic immunomodulators of macrophage activation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 8: 558.
Sorokina, O., F. Corellou, D. Dauvillee, A. Sorokin, I. Goryanin, S. Ball, F. Y. Bouget, and A. J. Millar (2011) Microarray data can predict diurnal changes of starch content in the picoalga Ostreococcus. BMC Syst. Biol. 5: 36.
Shlomi, T., M. N. Cabili, M. J. Herrgard, B. O. Palsson, and E. Ruppin (2008) Network-based prediction of human tissue-specific metabolism. Nat. Biotechnol. 26: 1003–1010.
Agren, R., S. Bordel, A. Mardinoglu, N. Pornputtapong, I. Nookaew, and J. Nielsen (2012) Reconstruction of genome-scale active metabolic networks for 69 human cell types and 16 cancer types using INIT. PLoS Comput. Biol. 8: e1002518.
Wang, Y., J. A. Eddy, and N. D. Price (2012) Reconstruction of genome-scale metabolic models for 126 human tissues using mCADRE. BMC Syst. Biol. 6: 153.
Schultz, A. and A. A. Qutub (2016) Reconstruction of tissue-specific metabolic networks using CORDA. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12: e1004808.
Vivek-Ananth, R. P. and A. Samal (2016) Advances in the integration of transcriptional regulatory information into genome-scale metabolic models. Biosystems. 147: 1–10.
Opdam, S., A. Richelle, B. Kellman, S. Li, D. C. Zielinski, and N. E. Lewis (2017) A systematic evaluation of methods for tailoring genome-scale metabolic models. Cell Syst. 4: 318–329.e6.
Sanchez, B. J., C. Zhang, A. Nilsson, P. J. Lahtvee, E. J. Kerkhoven, and J. Nielsen (2017) Improving the phenotype predictions of a yeast genome-scale metabolic model by incorporating enzymatic constraints. Mol. Syst. Biol. 13: 935.
Bekiaris, P. S. and S. Klamt (2020) Automatic construction of metabolic models with enzyme constraints. BMC Bioinformatics. 21: 19.
Thiele, I., N. Jamshidi, R. M. T. Fleming, and B. O. Palsson (2009) Genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli’s transcriptional and translational machinery: a knowledge base, its mathematical formulation, and its functional characterization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5: e1000312.
Wessely, F., M. Bartl, R. Guthke, P. Li, S. Schuster, and C. Kaleta (2011) Optimal regulatory strategies for metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli depending on protein costs. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7: 515.
Lerman, J. A., D. R. Hyduke, H. Latif, V. A. Portnoy, N. E. Lewis, J. D. Orth, A. C. Schrimpe-Rutledge, R. D. Smith, J. N. Adkins, K. Zengler, and B. O. Palsson (2012) In silico method for modelling metabolism and gene product expression at genome scale. Nat. Commun. 3: 929.
Thiele, I., R. M. T. Fleming, R. Que, A. Bordbar, D. Diep, and B. O. Palsson (2012) Multiscale modeling of metabolism and macromolecular synthesis in E. coli and its application to the evolution of codon usage. PLoS One. 7: e45635.
Yang, L., D. Ma, A. Ebrahim, C. J. Lloyd, M. A. Saunders, and B. O. Palsson (2016) solveME: fast and reliable solution of nonlinear ME models. BMC Bioinformatics. 17: 391.
O’Brien, E. J., J. A. Lerman, R. L. Chang, D. R. Hyduke, and B. O. Palsson (2013) Genome-scale models of metabolism and gene expression extend and refine growth phenotype prediction. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9: 693.
Lloyd, C. J., A. Ebrahim, L. Yang, Z. A. King, E. Catoiu, E. J. O’Brien, J. K. Liu, and B. O. Palsson (2018) COBRAme: A computational framework for genome-scale models of metabolism and gene expression. PLoS Comput. Biol. 14: e1006302.
Yang, L., N. Mih, A. Anand, J. H. Park, J. Tan, J. T. Yurkovich, J. M. Monk, C. J. Lloyd, T. E. Sandberg, S. W. Seo, D. Kim, A. V. Sastry, P. Phaneuf, Y. Gao, J. T. Broddrick, K. Chen, D. Heckmann, R. Szubin, Y. Hefner, A. M. Feist, and B. O. Palsson (2019) Cellular responses to reactive oxygen species are predicted from molecular mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 116: 14368–14373.
Anand, A., K. Chen, L. Yang, A. V. Sastry, C. A. Olson, S. Poudel, Y. Seif, Y. Hefner, P. V. Phaneuf, S. Xu, R. Szubin, A. M. Feist, and B. O. Palsson (2019) Adaptive evolution reveals a tradeoff between growth rate and oxidative stress during naphthoquinone-based aerobic respiration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 116: 25287–25292.
Barenholz, U., L. Keren, E. Segal, and R. Milo (2016) A minimalistic resource allocation model to explain ubiquitous increase in protein expression with growth rate. PLoS One. 11: e0153344.
Feist, A. M., C. S. Henry, J. L. Reed, M. Krummenacker, A. R. Joyce, P. D. Karp, L. J. Broadbelt, V. Hatzimanikatis, and B. Ø. Palsson (2007) A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction for Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 that accounts for 1260 ORFs and thermodynamic information. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 121.
Orth, J. D., T. M. Conrad, J. Na, J. A. Lerman, H. Nam, A. M. Feist, and B. O. Palsson (2011) A comprehensive genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli metabolism—2011. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7: 535.
Klumpp, S., M. Scott, S. Pedersen, and T. Hwa (2013) Molecular crowding limits translation and cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110: 16754–16759.
Liu, J. K., E. J. O’Brien, J. A. Lerman, K. Zengler, B. O. Palsson, and A. M. Feist (2014) Reconstruction and modeling protein translocation and compartmentalization in Escherichia coli at the genome-scale. BMC Syst. Biol. 8: 110.
Zhuang, K., G. N. Vemuri, and R. Mahadevan (2011) Economics of membrane occupancy and respiro-fermentation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7: 500.
Wunderling, R. (1997) SOPLEX: the sequential object-oriented simplex class library. ZIB.
Ma, D., L. Yang, R. M. T. Fleming, I. Thiele, B. O. Palsson, and M. A. Saunders (2017) Reliable and efficient solution of genome-scale models of Metabolism and macromolecular expression. Sci. Rep. 7: 40863.
Chen, K., Y. Gao, N. Mih, E. J. O’Brien, L. Yang, and B. O. Palsson (2017) Thermosensitivity of growth is determined by chaperone-mediated proteome reallocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 114: 11548–11553.
Du, B., L. Yang, C. J. Lloyd, X. Fang, and B. O. Palsson (2019) Genome-scale model of metabolism and gene expression provides a multi-scale description of acid stress responses in Escherichia coli. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1007525.
Liu, J. K., C. Lloyd, M. M. Al-Bassam, A. Ebrahim, J. N. Kim, C. Olson, A. Aksenov, P. Dorrestein, and K. Zengler (2019) Predicting proteome allocation, overflow metabolism, and metal requirements in a model acetogen. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1006848.
Yurkovich, J. T., L. Yang, and B. O. Palsson (2019) Systemslevel physiology of the human red blood cell is computed from metabolic and macromolecular mechanisms. bioRxiv. 797258.
Bryk, A. H. and J. R. Wiśniewski (2017) Quantitative analysis of human red blood cell proteome. J. Proteome Res. 16: 2752–2761.
Yang, L., A. Ebrahim, C. J. Lloyd, M. A. Saunders, and B. O. Palsson (2019) DynamicME: dynamic simulation and refinement of integrated models of metabolism and protein expression. BMC Syst. Biol. 13: 2.
Klumpp, S., Z. Zhang, and T. Hwa (2009) Growth rate-dependent global effects on gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 139: 1366–1375.
Grimbs, A., D. F. Klosik, S. Bornholdt, and M. T. Hutt (2019) A system-wide network reconstruction of gene regulation and metabolism in Escherichia coli. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1006962.
Ma, S., K. J. Minch, T. R. Rustad, S. Hobbs, S. L. Zhou, D. R. Sherman, and N. D. Price (2015) Integrated modeling of gene regulatory and metabolic networks in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11: e1004543.
Levering, J., C. L. Dupont, A. E. Allen, B. O. Palsson, and K. Zengler (2017) Integrated regulatory and metabolic networks of the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum predict the response to rising CO2 levels. mSystems. 2: e00142–16.
Covert, M. W. and B. O. Palsson (2002) Transcriptional regulation in constraints-based metabolic models of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 28058–28064.
Covert, M. W., E. M. Knight, J. L. Reed, M. J. Herrgard, and B. O. Palsson (2004) Integrating high-throughput and computational data elucidates bacterial networks. Nature. 429: 92–96.
Shlomi, T., Y. Eisenberg, R. Sharan, and E. Ruppin (2007) A genome-scale computational study of the interplay between transcriptional regulation and metabolism. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 101.
Chandrasekaran, S. and N. D. Price (2010) Probabilistic integrative modeling of genome-scale metabolic and regulatory networks in Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 107: 17845–17850.
Goelzer, A. and V. Fromion (2017) Resource allocation in living organisms. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 45: 945–952.
Bonneau, R., M. T. Facciotti, D. J. Reiss, A. K. Schmid, M. Pan, A. Kaur, V. Thorsson, P. Shannon, M. H. Johnson, J. C. Bare, W. Longabaugh, M. Vuthoori, K. Whitehead, A. Madar, L. Suzuki, T. Mori, D. E. Chang, J. Diruggiero, C. H. Johnson, L. Hood, and N. S. Baliga (2007) A predictive model for transcriptional control of physiology in a free living cell. Cell. 131: 1354–1365.
Wang, Z., S. A. Danziger, B. D. Heavner, S. Ma, J. J. Smith, S. Li, T. Herricks, E. Simeonidis, N. S. Baliga, J. D. Aitchison, and N. D. Price (2017) Combining inferred regulatory and reconstructed metabolic networks enhances phenotype prediction in yeast. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13: e1005489.
Sastry, A. V., Y. Gao, R. Szubin, Y. Hefner, S. Xu, D. Kim, K. S. Choudhary, L. Yang, Z. A. King, and B. O. Palsson (2019) The Escherichia coli transcriptome mostly consists of independently regulated modules. Nat. Commun. 10: 5536.
O’Brien, E. J. and B. O. Palsson (2015) Computing the functional proteome: recent progress and future prospects for genome-scale models. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 34: 125–134.
Heckmann, D., C. J. Lloyd, N. Mih, Y. Ha, D. C. Zielinski, Z. B. Haiman, A. A. Desouki, M. J. Lercher, and B. O. Palsson (2018) Machine learning applied to enzyme turnover numbers reveals protein structural correlates and improves metabolic models. Nat. Commun. 9: 5252.
Nilsson, A., J. Nielsen, and B. O. Palsson (2017) Metabolic models of protein allocation call for the kinetome. Cell Syst. 5: 538–541.
Heckmann, D., A. Campeau, C. J. Lloyd, P. V. Phaneuf, Y. Hefner, M. Carrillo-Terrazas, A. M. Feist, D. J. Gonzalez, and B. O. Palsson (2020) Kinetic profiling of metabolic specialists demonstrates stability and consistency of in vivo enzyme turnover numbers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 117: 23182–23190.
Salvy, P. and V. Hatzimanikatis (2020) The ETFL formulation allows multi-omics integration in thermodynamics-compliant metabolism and expression models. Nat. Commun. 11: 30.
Ataman, M., D. F. Hernandez Gardiol, G. Fengos, and V. Hatzimanikatis (2017) redGEM: Systematic reduction and analysis of genome-scale metabolic reconstructions for development of consistent core metabolic models. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13: e1005444.
Erdrich, P., R. Steuer, and S. Klamt (2015) An algorithm for the reduction of genome-scale metabolic network models to meaningful core models. BMC Syst. Biol. 9: 48.
Rohl, A. and A. Bockmayr (2017) A mixed-integer linear programming approach to the reduction of genome-scale metabolic networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 18: 2.
Hyduke, D. R., N. E. Lewis, and B. O. Palsson (2013) Analysis of omics data with genome-scale models of metabolism. Mol. Biosyst. 9: 167–174.
Ben Guebila, M. and I. Thiele (2019) Predicting gastrointestinal drug effects using contextualized metabolic models. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1007100.
Pusa, T., M. G. Ferrarini, R. Andrade, A. Mary, A. Marchetti-Spaccamela, L. Stougie, and M. F. Sagot (2020) MOOMIN — Mathematical explOration of ‘Omics data on a MetabolIc Network. Bioinformatics. 36: 514–523.
Ebrahim, A., E. Brunk, J. Tan, E. J. O’Brien, D. Kim, R. Szubin, J. A. Lerman, A. Lechner, A. Sastry, A. Bordbar, A. M. Feist, and B. O. Palsson (2016) Multi-omic data integration enables discovery of hidden biological regularities. Nat. Commun. 7: 13091.
Dos Santos, F. B., B. G. Olivier, J. Boele, V. Smessaert, P. De Rop, P. Krumpochova, G. W. Klau, M. Giera, P. Dehottay, B. Teusink, and P. Goffin (2017) Probing the genome-scale metabolic landscape of Bordetella pertussis, the causative agent of whooping cough. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 83: e01528–17.
Brynildsen, M. P., J. A. Winkler, C. S. Spina, I. C. MacDonald, and J. J. Collins (2013) Potentiating antibacterial activity by predictably enhancing endogenous microbial ROS production. Nat. Biotechnol. 31: 160–165.
Greenhalgh, K., J. Ramiro-Garcia, A. Heinken, P. Ullmann, T. Bintener, M. P. Pacheco, J. Baginska, P. Shah, A. Frachet, R. Halder, J. V. Fritz, T. Sauter, I. Thiele, S. Haan, E. Letellier, and P. Wilmes (2019) Integrated in vitro and in silico modeling delineates the molecular effects of a synbiotic regimen on colorectal-cancer-derived cells. Cell Rep. 27: 1621–1632.e9.
Cesur, M. F., B. Siraj, R. Uddin, S. Durmuş, and T. Çakır (2020) Network-based metabolism-centered screening of potential drug targets in Klebsiella pneumoniae at genome scale. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 9: 447.
Wu, H. Q., M. L. Cheng, J. M. Lai, H. H. Wu, M. C. Chen, W. H. Liu, W. H. Wu, P. M. H. Chang, C. Y. F. Huang, A. P. Tsou, M. S. Shiao, and F. S. Wang (2017) Flux balance analysis predicts Warburg-like effects of mouse hepatocyte deficient in miR-122a. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13: e1005618.
King, Z. A., E. J. O’Brien, A. M. Feist, and B. O. Palsson (2017) Literature mining supports a next-generation modeling approach to predict cellular byproduct secretion. Metab. Eng. 39: 220–227.
Niu, W., L. Kramer, J. Mueller, K. Liu, and J. Guo (2019) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the de novo stereospecific biosynthesis of 1,2-propanediol through lactic acid. Metab. Eng. Commun. 8: e00082.
Zheng, Y., Q. Yuan, X. Yang, and H. Ma (2017) Engineering Escherichia coli for poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate) production guided by genome-scale metabolic network analysis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 106: 60–66.
Mohite, O. S., T. Weber, H. U. Kim, and S. Y. Lee (2019) Genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of actinomycetes for antibiotics production. Biotechnol. J. 14: e1800377.
Dahal, S., S. Poudel, and R. A. Thompson (2016) Genome-scale modeling of thermophilic microorganisms. pp. 103–119. In: I. Nookaew (ed.). Network Biology. Springer, Cham, Switzerland.
Zhuang, K., M. Izallalen, P. Mouser, H. Richter, C. Risso, R. Mahadevan, and D. R. Lovley (2011) Genome-scale dynamic modeling of the competition between Rhodoferax and Geobacter in anoxic subsurface environments. ISME J. 5: 305–316.
Zhuang, K., E. Ma, D. R. Lovley, and R. Mahadevan (2012) The design of long-term effective uranium bioremediation strategy using a community metabolic model. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109: 2475–2483.
Scheibe, T. D., R. Mahadevan, Y. Fang, S. Garg, P. E. Long, and D. R. Lovley (2009) Coupling a genome-scale metabolic model with a reactive transport model to describe in situ uranium bioremediation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2: 274–286.
Tobalina, L., R. Bargiela, J. Pey, F. A. Herbst, I. Lores, D. Rojo, C. Barbas, A. I. Peláez, J. Sánchez, M. von Bergen, J. Seifert, M. Ferrer, and F. J. Planes (2015) Context-specific metabolic network reconstruction of a naphthalene-degrading bacterial community guided by metaproteomic data. Bioinformatics. 31: 1771–1779.
Lloyd, C. J., Z. A. King, T. E. Sandberg, Y. Hefner, C. A. Olson, P. V. Phaneuf, E. J. O’Brien, J. G. Sanders, R. A. Salido, K. Sanders, C. Brennan, G. Humphrey, R. Knight, and A. M. Feist (2019) The genetic basis for adaptation of model-designed syntrophic co-cultures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15: e1006213.
Hanemaaijer, M., B. G. Olivier, W. F. M. Roling, F. J. Bruggeman, and B. Teusink (2017) Model-based quantification of metabolic interactions from dynamic microbial-community data. PLoS One. 12: e0173183.
Pacheco, A. R., M. Moel, and D. Segre (2019) Costless metabolic secretions as drivers of interspecies interactions in microbial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 10: 103.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Queen’s University and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) [RGPIN-2020-06325].
The authors declare no conflict of interest. No ethical approval was required. No informed consent was required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahal, S., Zhao, J. & Yang, L. Genome-scale Modeling of Metabolism and Macromolecular Expression and Their Applications. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 931–943 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0061-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0061-2