Abstract
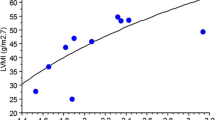
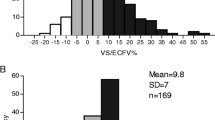
Volume management is an essential component of anti-hypertensive therapy. Different volume phenotypes have been proposed. We sought to study the total blood volume (TBV), plasma volume (PV), and red blood cell volume (RBV) in hypertensive patients. We included patients followed in an outpatient cardiology clinic from 1998 to 2003. Blood volume (BV) parameters were measured using radioisotope iodine-131-labeled albumin dilution technique. Values were expressed as percentage (%) deviation from ideal volumes. A total of 95 patients were included. The intravascular volume distribution as percent deviation from normal volume ranged from − 23 to + 28% for TBV, − 22 to + 36% for PV and − 29 to + 37% for RBV. There was no significant correlation between systolic BP and any of the BV parameters (TBV and SBP, r = − 0.03; PV and SBP, r = − 0.12; RBV and SBP, r = − 0.08). Patients with hypertension have a wide variation in BV parameters. BV does not correlate with SBP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weidmann, P., Hirsch, D., Beretta-Piccoli, C., Reubi, F. C., & Ziegler, W. H. (1977). Interrelations among blood pressure, blood volume, plasma renin activity and urinary catecholamines in benign essential hypertension. The American Journal of Medicine, 62, 209–218.
Feldschuh, J., & Katz, S. (2007). The importance of correct norms in blood volume measurement. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 334, 41–46.
Mayet, J., & Hughes, A. (2003). Cardiac and vascular pathophysiology in hypertension. Heart, 89, 1104–1109.
Laragh, J. H., Sealey, J. E., Niarchos, A. P., & Pickering, T. G. (1982). The vasoconstriction-volume spectrum in normotension and in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Federation Proceedings, 41, 2415–2423.
Feldschuh, J., & Enson, Y. (1977). Prediction of the normal blood volume. Relation of blood volume to body habitus. Circulation, 56, 605–612.
Chrysant, S. G., Danisa, K., Kem, D. C., Dillard, B. L., Smith, W. J., & Frohlich, E. D. (1979). Racial differences in pressure, volume and renin interrelationships in essential hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex : 1979), 1, 136–141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Human and Animal Studies
No human or animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Conflict of Interest
Marat Fudim is supported by an American Heart Association grant 17MCPRP33460225 and NIH T32 grant 5T32HL007101; he consults for Coridea, AxonTherapies, and Galvani. Renato D. Lopes research grants: Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic PLC, Sanofi-Aventis; consulting/advisory board fees: Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim. Michael Feldschuh is an employee of Daxor. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Clinical Relevance
Hypertension is one of the major health risk factors, and uncontrolled hypertension is highly prevalent. The physiology of hypertension is complex and knowledge of volume phenotypes might be relevant to clinical management.
Additional information
Associate Editor Ana Barac oversaw the review of this article
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fudim, M., Blumer, V.L., Lopes, R.D. et al. Correlation of Quantitated Intravascular Volume with Blood Pressure in Patients with Systemic Hypertension. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 13, 528–530 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-019-09910-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-019-09910-4