Abstract
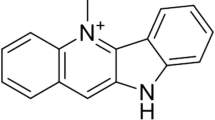
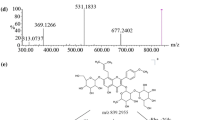
Rutaecarpine, an alkaloid originally isolated from Evodia rutaecarpa, has been used for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders in Asia. In the present study, the phase I and phase II metabolites of rutaecarpine were investigated in freshly isolated hepatocytes from male Sprague–Dawley rats. The individual metabolites were characterized via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The incubation of rutaecarpine with freshly isolated hepatocytes for 2 h yielded five major phase I metabolites. In addition, three glucuronide conjugates and four sulfate conjugates were observed. Because the majority of metabolites observed in vivo were identified, freshly isolated hepatocytes might be useful for the identification of certain metabolites formed from drug candidates from a reduced number of experimental animals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dickins M, Peterson RE (1980) Effects of a hormone-supplemented medium on cytochrome P-450 content and mono-oxygenase activities of rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Biochem Pharmacol 29:1231–1238
Kane RE, Tector J, Brems JJ, Li AP, Kaminski DL (1997) Sulfation and glucuronidation of acetaminophen by cultured hepatocytes replicating in vivo metabolism. ASAIO Trans 36(3):M607–M610
Lee SH, Kim SI, Park JG, Lee ES, Jahng Y (2001) A simple synthesis of rutaecarpine. Heterocylces 55(8):1555–1559
Lee SK, Lee J, Lee ES, Jahng Y, Kim DH, Jeong TC (2004) Characterization of in vitro metabolites of rutaecarpine in rat liver microsomes using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:1073–1080
Lee SK, Lee DW, Jeon TW, Jin CH, Kim GH, Jun IH, Lee DJ, Kim SI, Kim DH, Jahng Y, Jeong TC (2005) Characterization of the phase 2 metabolites of rutaecarpine in the rat by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Xenobiotica 35(12):1135–1145
Lee SK, Lee JH, Yoo HH, Kim DH, Jahng Y, Jeong TC (2006) Characterization of human liver cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the metabolism of rutaecarpine. J Pharm Biomed Anal 41(1):304–309
Moon TC, Murakami M, Kudo I, Son KH, Kang SS, Chang HW (1999) A new class of COX-2 inhibitor, rutaecarpine from Evodia rutaecarpa. Inflamm Res 48:621–625
O’Brien PJ, Chan K, Silber PM (2004) Human and animal hepatocytes in vitro with extrapolation in vivo. Chem Biol Interact 150:97–114
Parkinson A, Ogilvie BW, Buckley DB, Kazmi F, Czerwinski M, Parkinson O (2013) Chapter 6: Biotransformation of xenobiotics. In: Klaassen CD (ed) Casarett & Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons, 8th edn. McGraw Hill Education, New York, pp 185–366
Sheu JR, Hung WC, Lee YM, Yen MH (1996) Mechanism of inhibition of platelet aggregation by rutaecarpine, an alkaloid isolated from Evodia rutaecarpa. Eur J Pharmacol 318:469–475
Sheu JR, Hung WC, Wu CH, Lee YM, Yen MH (2000) Antithrombotic effect of rutaecarpine, an alkaloid isolated from Evodia rutaecarpa, on platelet plug formation in in vivo experiments. Br J Haematol 110:110–115
Ueng YF, Yu HJ, Lee CH, Peng C, Jan WC, Ho LK, Chen CF, Don MJ (2005) Identification of the microsomal oxidation metabolites of rutaecarpine, a main active alkaloid of the medicinal herb Evodia rutaecarpa. J Chromatogr A 1076:103–109
Woo HG, Lee CH, Noh MS, Lee JJ, Jung YS, Baik EJ, Moon CH, Lee SH (2001) Rutacarpine, a quinazolinocarboline alkaloid, inhibits prostaglandin production in RAW264.7 macrophages. Planta Med 67:505–509
Yang KH, Kim BS, Munson AE, Holsapple MP (1986) Immunosuppression induced by chemicals requiring metabolic activation in mixed cultures of rat hepatocytes and murine splenocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 83:420–429
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2013R1A2A2A07067609) and from Yeungnam University (214-A-345-027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Dong Wook Lee and Youra Kang have contributed equally for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.W., Kang, Y., Kang, M.J. et al. Phase I and phase II metabolite identification of rutaecarpine in freshly isolated hepatocytes from male Sprague–Dawley rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 40, 972–979 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0937-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0937-7