Abstract
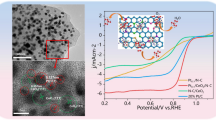
Cost-effective electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) play a key role in the field of renewable energy. Although tremendous efforts have been devoted to the search of alternative materials, Pt/C is still the most efficient electrocatalyst for the HER. Nevertheless, decreasing the loading of Pt in the designed eletrocatalysts is of significance. However, with low Pt loading, it is challenging to maintain excellent catalytic performance. Herein, a new catalyst (Pt/NPC) was prepared by dispersing Pt nanoparticles (PtNPs) with an average diameter of 1.8 nm over a three-dimensional (3D) carbon network co-doped with N and P. Because of the high electronegativity of the N and P dopants, PtNPs were uniformly dispersed on the carbon network via high electronic affinity between Pt and carbon, affording a Pt/NPC catalyst; Pt/NPC exhibited superior HER activity, attributed to the down-shift of the Pt d-band caused by the donation of charge from N and P to Pt. The results show that Pt/NPC with an ultralow Pt loading of 1.82 wt.% exhibits excellent HER performance, which corresponds to a HER mass activity 20.6-fold greater than that observed for commercial 20% Pt/C at an overpotential of 20 mV vs. RHE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dresselhaus, M. S.; Thomas, I. L. Alternative energy technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 332–337.
Qi, J.; Lai, X. Y.; Wang, J. Y.; Tang, H. J.; Ren, H.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, L. J.; Yu, R. B.; Ma, G. H. et al. Multi-shelled hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6749–6773.
Gong, M.; Wang, D. Y.; Chen, C. C.; Hwang, B. J.; Dai, H. J. A mini review on nickel-based electrocatalysts for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 28–46.
Zhang, Y. J.; Gong, Q. F.; Li, L.; Yang, H. C.; Li, Y. G.; Wang, Q. B. MoSe2 porous microspheres comprising monolayer flakes with high electrocatalytic activity. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1108–1115.
Yang, H. C.; Zhang, Y. J.; Hu, F.; Wang, Q. B. Urchin-like CoP nanocrystals as hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen reduction reaction dual-electrocatalyst with superior stability. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7616–7620.
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Advancing the electrochemistry of the hydrogen-evolution reaction through combining experiment and theory. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 52–65.
Chen, C.; Kang, Y. J.; Huo, Z. Y.; Zhu, Z. W.; Huang, W. Y.; Xin, H. L.; Snyder, J. D.; Li, D. G.; Herron, J. A.; Mavrikakis, M. et al. Highly crystalline multimetallic nanoframes with three-dimensional electrocatalytic surfaces. Science 2014, 343, 1339–1343.
Bai, S.; Wang, C. M.; Deng, M. S.; Gong, M.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y. J. Surface polarization matters: Enhancing the hydrogen-evolution reaction by shrinking Pt shells in Pt-Pdgraphene stack structures. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12120–12124.
Li, M.; Ma, Q.; Zi, W.; Liu, X. J.; Zhu, X. J.; Liu, S. Z. Pt monolayer coating on complex network substrate with high catalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400268.
Cheng, H. Y.; Zhu, Y. A.; Chen, D.; Å strand, P. O.; Li, P.; Qi, Z. W.; Zhou, X. G. Evolution of carbon nanofibersupported Pt nanoparticles of different particle sizes: A molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 23711–23722.
Cargnello, M.; Doan-Nguyen, V. V. T.; Gordon, T. R.; Diaz, R. E.; Stach, E. A.; Gorte, R. J.; Fornasiero, P.; Murray, C. B. Control of metal nanocrystal size reveals metal-support interface role for ceria catalysts. Science 2013, 341, 771–773.
Prabhuram, J.; Wang, X.; Hui, C. L.; Hsing, I.-M. Synthesis and characterization of surfactant-stabilized Pt/C nanocatalysts for fuel cell applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 11057–11064.
Liu, J. Y. Advanced electron microscopy of metal-support interactions in supported metal catalysts. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 934–948.
Lee, I.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, J. P.; Yin, Y. D.; Zaera, F. Encapsulation of supported Pt Nanoparticles with mesoporous silica for increased catalyst stability. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 115–123.
Lai, X. Y.; Halpert, J. E.; Wang, D. Recent advances in micro-/nano-structured hollow spheres for energy applications: From simple to complex systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5604–5618.
Tang, H. J.; Hessel, C. M.; Wang, J. Y.; Yang, N. L.; Yu, R. B.; Zhao, H. J.; Wang, D. Two-dimensional carbon leading to new photoconversion processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4281–4299.
Holme, T.; Zhou, Y. K.; Pasquarelli, R.; O’ Hayre, R. First principles study of doped carbon supports for enhanced platinum catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 9461–9468.
Pylypenko, S.; Borisevich, A.; More, K. L.; Corpuz, A. R.; Holme, T.; Dameron, A. A.; Olson, T. S.; Dinh, H. N.; Gennette, T.; O’Hayre, R. Nitrogen: Unraveling the secret to stable carbon-supported Pt-alloy electrocatalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2957–2964.
Zhou, Y. K.; Neyerlin, K.; Olson, T. S.; Pylypenko, S.; Bult, J.; Dinh, H. N.; Gennett, T.; Shao, Z. P.; O’ Hayre, R. Enhancement of Pt and Pt-alloy fuel cell catalyst activity and durability via nitrogen-modified carbon supports. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1437–1446.
Yu, D. S.; Xue, Y. H.; Dai, L. M. Vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays co-doped with phosphorus and nitrogen as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2863–2870.
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Li, L. H.; Xing, T.; Chen, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Toward design of synergistically active carbon-based catalysts for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5290–5296.
Zhang, J. T.; Qu, L. T.; Shi, G. Q.; Liu, J. Y.; Chen, J. F.; Dai, L. M. N,P-codoped carbon networks as efficient metalfree bifunctional catalysts for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2230–2234.
Li, R.; Wei, Z. D.; Gou, X. L.; Xu, W. Phosphorus-doped graphene nanosheets as efficient metal-free oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9978–9984.
Yang, D. S.; Bhattacharjya, D.; Inamdar, S.; Park, J.; Yu, J. S. Phosphorus-doped ordered mesoporous carbons with different lengths as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16127–16130.
Pan, L. J.; Yu, G. H.; Zha, D. Y.; Lee, H. R.; Zhao, W. T.; Liu, N.; Wang, H. L.; Tee, B. C.-K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y. et al. Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9287–9292.
Zhang, J. T.; Zhao, Z. H.; Xia, Z. H.; Dai, L. M. A metalfree bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 444–452.
Ren, H.; Shao, H.; Zhang, L. J.; Guo, D.; Jin, Q.; Yu, R. B.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. J. et al. A new graphdiyne nanosheet/Pt nanoparticle-based counter electrode material with enhanced catalytic activity for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500296.
Han, C. L.; Wang, S. P.; Wang, J.; Li, M. M.; Deng, J.; Li, H. R.; Wang Y. Controlled synthesis of sustainable N-doped hollow core–mesoporous shell carbonaceous nanospheres from biomass. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1809–1819.
Ding, W.; Wei, Z. D.; Chen, S. G.; Qi, X. Q.; Yang, T.; Hu, J. S.; Wang, D.; Wan, L. J.; Alvi, S. F.; Li, L. Spaceconfinement-induced synthesis of pyridinic- and pyrrolicnitrogen- doped graphene for the catalysis of oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11755–11759.
Shi, Q.; Wang, Y. D.; Wang, Z. M.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, B.; Wu, N.; Han, C.; Xie, S.; Gou, Y. Z. Three-dimensional (3D) interconnected networks fabricated via in-situ growth of N-doped graphene/carbon nanotubes on Co-containing carbon nanofibers for enhanced oxygen reduction. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 317–328.
Wu, J.; Zheng, X. J.; Jin, C.; Tian, J. H.; Yang, R. Z. Ternary doping of phosphorus, nitrogen, and sulfur into porous carbon for enhancing electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Carbon 2015, 92, 327–338.
Ji, Y. J.; Wu, Y. E.; Zhao, G. F.; Wang, D. S.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Li, Y. D. Porous bimetallic Pt-Fe nanocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogenation of acetone. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2706–2713.
Han, X. P.; Cheng, F. Y.; Zhang, T. R.; Yang, J. G.; Hu, Y. X.; Chen, J. Hydrogenated uniform Pt clusters supported on porous CaMnO3 as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction and evolution. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2047–2051.
Zeng, M.; Li, Y. G. Recent advances in heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14942–14962.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21425103) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. SBK201341397).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2016_1281_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
1.82 wt.% Pt/N, P co-doped carbon overwhelms 20 wt.% Pt/C as a high-efficiency electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Hu, F., Yang, H. et al. 1.82 wt.% Pt/N, P co-doped carbon overwhelms 20 wt.% Pt/C as a high-efficiency electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 10, 238–246 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1281-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1281-9