Abstract
Background
Previous reports have shown that patients with bilateral primary breast cancer (BPBC) had comparable or moderately poor survival compared with patients experiencing unilateral primary breast cancer (UPBC). However, studies are conflicting in their analyses of correlations between survival and clinicopathological and prognostic characteristics in BPBC patients. The aim of our study was to compare the clinicopathological features and prognoses of BPBC and UPBC patients in Heilongjiang Province, northeast China.
Methods
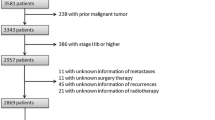
We retrospectively reviewed the records of 2,695 patients who underwent modified radical mastectomy or lumpectomy from 2005 to 2008 in the Tumor Hospital of Harbin Medical University. Eighty-one patients (3.0 %) had BPBC and 2,614 patients had UPBC. Multivariate analysis was performed using Cox’s proportional hazards model.
Results
There were significant differences between patients with BPBC and UPBC in the age of onset (referring to the age when the first tumor in BPBC was diagnosed), T stage, menopause status (referring to the age when the second tumor in BPBC was diagnosed), and breast cancer family history. The overall 5-year survival of patients with BPBC was 70.1 % compared with 87.1 % for patients with UPBC (p = 0.004). Furthermore, multivariate analysis showed that HER-2 status, menopause status, and mammary disease history were significant factors affecting survival among the patients with BPBC.
Conclusions
Our results confirmed previous findings that BPBC patients had moderately poor survival. However, when T stages were matched, BPBC patients had a survival rate similar to UPBC patients. Premenopause status, HER-2 positivity and family history of breast cancer were major risk factors for BPBC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bener A, Ayub H, Kakil R, Ibrahim W. Patterns of cancer incidence among the population of Qatar: a worldwide comparative study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2008;9:19–24.
Bener A, El Ayoubi HR, Basha B, Joseph S, Chouchane L. Breast cancer screening barriers: knowledge, attitudes and practices of women toward breast cancer. Breast J. 2011;17:115–6.
Love RR, Desta Z, Flockhart D, Skaar T, Ogburn ET, Ramamoorthy A, et al. CYP2D6 genotypes, endoxifen levels, and disease recurrence in 224 Filipino and Vietnamese women receiving adjuvant tamoxifen for operable breast cancer. Springerplus. 2013;2:52.
Ziegler RG, Anderson WF, Gail MH. Increasing breast cancer incidence in China: the numbers add up. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1339–41.
Linos E, Spanos D, Rosner BA, Linos K, Hesketh T, Qu JD, et al. Effects of reproductive and demographic changes on breast cancer incidence in China: a modeling analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1352–60.
Verkooijen HM, Chatelain V, Fioretta G, Vlastos G, Rapiti E, Sappino AP, et al. Survival after bilateral breast cancer: results from a population-based study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;105:347–57.
Heron DE, Komarnicky LT, Hyslop T, Schwartz GF, Mansfield CM. Bilateral breast carcinoma: risk factors and outcomes for patients with synchronous and metachronous disease. Cancer. 2000;88:2739–50.
Carmichael AR, Bendall S, Lockerbie L, Prescott R, Bates T. The long-term outcome of synchronous bilateral breast cancer is worse than metachronous or unilateral tumours. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28:388–91.
Shahedi K, Emanuelsson M, Wiklund F, Gronberg H. High risk of contralateral breast carcinoma in women with hereditary/familial non-BRCA1/BRCA2 breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2006;106:1237–42.
Imyanitov EN, Hanson KP. Molecular pathogenesis of bilateral breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2003;191:1–7.
Gollamudi SV, Gelman RS, Peiro G, Schneider LJ, Schnitt SJ, Recht A, et al. Breast-conserving therapy for stage I–II synchronous bilateral breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1997;79:1362–9.
Kollias J, Ellis IO, Elston CW, Blamey RW. Prognostic significance of synchronous and metachronous bilateral breast cancer. World J Surg. 2001;25:1117–24.
Newman LA, Sahin AA, Cunningham JE, Bondy ML, Mirza NQ, Vlastos GS, et al. A case–control study of unilateral and bilateral breast carcinoma patients. Cancer. 2001;91:1845–53.
Jobsen JJ, van der Palen J, Ong F, Meerwaldt JH. Synchronous, bilateral breast cancer: prognostic value and incidence. Breast. 2003;12:83–8.
Polednak AP. Bilateral synchronous breast cancer: a population-based study of characteristics, method of detection, and survival. Surgery. 2003;133:383–9.
Aminuddin A, Zakaria Z, Fuad AF, Kamsiah J, Othman F, Das S, et al. High C reactive protein associated with increased pulse wave velocity among urban men with metabolic syndrome in Malaysia. Saudi Med J. 2013;34:266–75.
Beckmann KR, Buckingham J, Craft P, Dahlstrom JE, Zhang Y, Roder D, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of bilateral breast cancer in an Australian cohort. Breast. 2011;20:158–64.
Kuo WH, Yen AM, Lee PH, Chen KM, Wang J, Chang KJ, et al. Cumulative survival in early-onset unilateral and bilateral breast cancer: an analysis of 1907 Taiwanese women. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:563–70.
Fisher ER, Sass R, Fisher B. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Project for Breast Cancers (protocol no. 4). X. Discriminants for tenth year treatment failure. Cancer. 1984;53:712–23.
Amodeo C, Caglia P, Gandolfo L, Veroux M, Donati M, Cavallaro G, et al. Bilateral breast cancer. Tumori. 2003;89:175–6.
Kuo WH, Yen AM, Lee PH, Hou MF, Chen SC, Chen KM, et al. Incidence and risk factors associated with bilateral breast cancer in area with early age diagnosis but low incidence of primary breast cancer: analysis of 10-year longitudinal cohort in Taiwan. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;99:221–8.
Chaudary MA, Millis RR, Hoskins EO, Halder M, Bulbrook RD, Cuzick J, et al. Bilateral primary breast cancer: a prospective study of disease incidence. Br J Surg. 1984;71:711–4.
Dawson LA, Chow E, Goss PE. Evolving perspectives in contralateral breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1998;34:2000–9.
Singletary SE, Connolly JL. Breast cancer staging: working with the sixth edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:37–47.
Kheirelseid EA, Jumustafa H, Miller N, Curran C, Sweeney K, Malone C, et al. Bilateral breast cancer: analysis of incidence, outcome, survival and disease characteristics. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;126:131–40.
Lan NH, Laohasiriwong W, Stewart JF. Survival probability and prognostic factors for breast cancer patients in Vietnam. Glob Health Action. 2013;6:1–9.
Vuoto HD, Garcia AM, Candas GB, Zimmermann AG, Uriburu JL, Isetta JA, et al. Bilateral breast carcinoma: clinical characteristics and its impact on survival. Breast J. 2010;16:625–32.
Takahashi H, Watanabe K, Takahashi M, Taguchi K, Sasaki F, Todo S. The impact of bilateral breast cancer on the prognosis of breast cancer: a comparative study with unilateral breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12:196–202.
Robbins GF, Berg JW. Bilateral primary breast cancer; a prospective clinicopathological study. Cancer. 1964;17:1501–27.
Nicoletto MO, Donach M, De Nicolo A, Artioli G, Banna G, Monfardini S. BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 mutations as prognostic factors in clinical practice and genetic counselling. Cancer Treat Rev. 2001;27:295–304.
Diaz R, Munarriz B, Santaballa A, Palomar L, Montalar J. Synchronous and metachronous bilateral breast cancer: a long-term single-institution experience. Med Oncol. 2012;29:16–24.
Steinmann D, Bremer M, Rades D, Skawran B, Siebrands C, Karstens JH, et al. Mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in patients with bilateral breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:850–8.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Mrs. He and Mrs. Rong for helping us to gather the patients’ documents. This work was supported by the Bureau of Technology and Science of Harbin (Grant Number: 2009RFXXS017 to C.L.) and by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant Number: LC2012C08 to M.Q.).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Xing and Q. Meng contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Y., Meng, Q., Sun, L. et al. Survival analysis of patients with unilateral and bilateral primary breast cancer in Northeast China. Breast Cancer 22, 536–543 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-014-0517-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-014-0517-3