Abstract
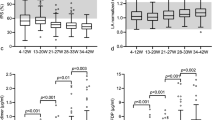
This work was designated to monitor the coagulation abnormalities associated with the gradual progression of liver diseases. The study included fifty patients; forty were diagnosed with liver cirrhosis with different stages categorized according to the Childs-Pugh classification and another ten patients were diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Haemostatic variables including fibrinogen (FI), calcium (FIV), transglutaminase (FXIII), prothrombin time (PT) and platelet count were estimated in patients and compared with the baseline levels of healthy subjects (n = 10). The results demonstrated that the fibrinogen level was progressively decreased, whereas PT was progressively prolonged in Child A, Child B and Child C groups. The maximum deterioration was observed in HCC patients. Calcium significantly increased in mild (Child A) and moderate (Child B) but not in Child C cirrhosis and HCC patients. FXIII level did not show any significant changes in cirrhotic patients compared to healthy group. Some of the haemostatic variables we investigated were correlated with serum albumin and bilirubin but not with aminotransferases (ALT and AST). The results indicated that the haemostatic abnormalities in fibrinogen, calcium and PT (but not FXIII) were deteriorated in parallel with the gradual regression of the constitutional function of liver.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muciño-Bermejo J, Carrillo-Esper R, Uribe M, Méndez-Sánchez N. Coagulation abnormalities in the cirrhotic patient. Ann Hepatol. 2013;12(5):713–24.
Páramo JA, Rocha E. Hemostasis in advanced liver disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1993;19(3):184–90.
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the esophagus for bleeding esophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–9.
Solomon L. Hematologic complications of liver disease and alcoholism. In: Hoffman R, Benz E, editors. Basic principles and practice of hematology. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1994.
Amitrano L, Guardascione MA, Brancaccio V, Balzano A. Coagulation disorders in liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2002;22(1):83–96.
Mammen EF. Coagulation abnormalities in liver disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1992;6(6):1247–57.
Tripodi A. Hemostasis in chronic liver disease. Thromb Haemost J. 2006;4(9):2064–5.
Wang FJ, Cao J, Ma LP, Jin ZX. Study on cellular and serum concentration of calcium and magnesium in peripheral blood cells of cirrhosis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2004;12(3):144–7.
Lisman T, Leebeek FW, Mosnier LO, Bouma BN, Meijers JC, Janssen HL, et al. Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor deficiency in cirrhosis is not associated with increased plasma fibrinolysis. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:131–9.
Tacke F, Fiedler K, Von Depka M, Luedde T, Hecker H, Manns MP, et al. Clinical and prognostic role of plasma coagulation factor XIII activity for bleeding disorders and 6-year survival in patients with chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2006;26(2):173–81.
Clauss A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haemat. 1957;17:237–46.
Flckensher K, Aab A, Stüber W. A photometric assay for blood coagulation factor XIII Thromb. Haemostasis. 1991;65:353–540.
Faulkner WR, Meites S. Selected methods of clinical chemistry, vol. 9. Washington DC: American Association for Clinical Chemistry; 1982.
Guo J, Friedman SL. Hepatic fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27(4):413–26.
Poynard T, Ratziu V, Benhamou Y, Opolon P, Cacoub P, Bedossa P. Natural history of HCV infection. Bailliere’s Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;14(2):211–28.
Poynard T, Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Goodman Z, McHutchison J, Albrecht J. Rates and risk factor of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2001;34:730–9.
Miller FD, Abu-Raddad LJ. Evidence of intense ongoing endemic transmission of hepatitis C virus in Egypt. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:14757–62.
Shi L, Zhhang SL, Li K, Hong Y, Wang Q, Li Y, et al. NS5ATP9, a gene up regulated by HCV NS5A protein. Cancer Lett. 2008;259(2):192–7.
Turcotte J, Child C. The liver and portal hypertension. In: Child CI, editor. Surgery and portal hypertension. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1964. p. 50–8.
Ordinas A, Escolar G, Cirera I, Viñas M, Cobo F, Bosch J, et al. Existence of a platelet–adhesion defect in patients with cirrhosis independent of hematocrit: studies under flow conditions. Hepatology. 1996;24(5):1137–42.
Repke D, Gemmell CH, Guha A, Turitto VT, Broze GJJ, Nemerson Y. Hemophilia as a defect of the tissue factor pathway of blood coagulation: effect of factors VIII and IX on factor X activation in a continuous-flow reactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:7623–7.
Blombäck B, Blombäck M. The molecular structure of fibrinogen. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1972;202:77–97.
Arif S, Khan AS, Khan AR. Changes in fibrinogen level in liver cirrhosis. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2002;14(2):19–21.
Violi F, Ferro D, Basili S, Quintarelli C, Saliola M, Alessandri C, et al. Hyperfibrinolysis increases the risk of gastrointestinal hemorrhage in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1992;15(4):672–6.
Hu KQ, Yu AS, Tiyyagura L, Redeker AG, Reynolds TB. Hyperfibrinolytic activity in hospitalized cirrhotic patients in a referral liver unit. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(5):1581–6.
Miatto O, Casaril M, Gabrielli GB, Nicoli N, Bellisola G, Corrocher R. Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum copper and plasma fibrinogen in hepatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1985;55(4):774–8.
Martinz J, Palascak J, Kawasniak D. Abnormal sialic acid content of the dysfibrinogenemia associated with liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1978;61(2):535–8.
Ratnoff OD, Forman WB. Criteria for the differentiation of dysfibrinogenemia states. Semin Hematol. 1976;13:141–57.
Davi EW, Fujikawa K, Kisiel W. The coagulation cascade: initiation, maintenance and regulation. Biochemistry. 1991;30(43):10363–70.
Butt AK, Khan AA, Alam A, Shah SW, Shafqat F, Naqvi AB. Predicting hospital mortality in cirrhotic patients: comparison of child and acute physiology, age and chronic health evaluation (APACHE 111) scoring systems. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:2469–75.
Grimaudo S, Craxi A, Gentile S, Di Paolantonio T, Vaccaro A, Venezia G, et al. Prolonged prothrombin time, Factor VII and activated FVII levels in chronic liver disease are partly dependent on Factor VII gene polymorphisms. Dig Liver Dis. 2005;37:446–50.
Weisel JW. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Adv Protein Chem. 2005;70:247–99.
El Borai MS, Ibrahim WM, Hessien M, El-keey M. Effect of alpha-tocopherol on tissue transglutaminase and reversibility of thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Turkish J of Biochem. 2005;31(1):13–20.
Klingemann HG, Brunswig D, Liehr H. Fibrinogen and fibrin structure in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Z Gastroenterol. 1978;16(9):564–73.
Knittel T, Fellmer P, Ramadori G. Gene expression and regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type I in hepatic stellate cells of rat liver. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:745–54.
Abdel-Aziz G, Lebeau G, Rescan PY. Reversibility of hepatic fibrosis in experimentally induced cholestasis in rat. Am J Pathol. 1990;137:1333–42.
Mirza A, Liu SL, Frizell E, Zhu J, Maddukuri S, Martinez J, Schwarting R, Norton P, Zern MA, et al. A role for tissue transglutaminase in hepatic injury and fibrogenesis, and its regulation by NF-kappaB. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(2):281–8.
Ikura Y, Ohsawa M, Okada M, Iwai Y, Wakasa K. The significance of platelet consumption in the development of thrombocytopenia in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Med Sci. 2013;346(3):199–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hessien, M., Ayad, M., Ibrahim, W.M. et al. Monitoring Coagulation Proteins During Progression of Liver Disease. Ind J Clin Biochem 30, 210–216 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-014-0429-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-014-0429-1