Abstract
Background
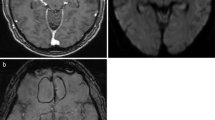
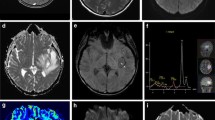
Diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) is helpful for detection of brain abscess and pelvic abscess in adults. In the present study, we evaluated the diagnostic performance of DWI in children and young adults with abdominal and soft tissue abscess formations.
Methods
Seventeen patients (11 females, aged 13 ± 6 years) with suspected abdominal or soft-tissue abscess underwent routine MRI including free-breathing DWI and contrast-enhanced T1w imaging. Seventeen random age-matched patients with non-purulent abdominal fluid collections served as controls. Mean apparent diffusion coefficent (ADC) was measured for abscess, muscle, liver, spleen and kidney tissue as well as for cerebrospinal fluid, urine and free abdominal fluid.
Results
All fluid collections were identified on diffusion-weighted images. Thirteen of 14 confirmed abscess formations showed an ADC < 1.0 × 10−3 mm2/s with a mean value of 0.80 ± 0.38 mm2/s. One tuberculous softtissue abscess had a higher ADC of 1.85 × 10−3 mm2/s. Ring enhancement on T1w imaging was seen in three nonpurulent fluid collections. There were no false-positive findings in the control group.
Conclusions
Diffusion-weighted MRI is highly sensitive for abscess and may add specificity to contrast-enhanced T1w imaging of ring-enhancing fluid collections. DWI with free-breathing rapid image acquisition and without the need of intravenous contrast application constitutes a particularly useful choice in pediatric imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000;217:331–345.
Guzman R, Barth A, Lövblad KO, El-Koussy M, Weis J, Schroth G, et al. Use of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating purulent brain processes from cystic brain tumors. J Neurosurg 2002;97:1101–1107.
Koh DM, Collins DJ. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;188:1622–1635.
Sun YS, Zhang XP, Tang L, Ji JF, Gu J, Cai Y, et al. Locally advanced rectal carcinoma treated with preoperative chemotherapy and radiation therapy: preliminary analysis of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for early detection of tumor histopathologic downstaging. Radiology 2010;254:170–178.
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Luijten PR, Nievelstein RAJ. ADC measurements of lymph nodes: inter- and intra-observer reproducibility study and an overview of the literature. Eur J Radiol 2010;75:215–220.
Kiryu S, Dodanuki K, Takao H, Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Takazoe M, et al. Free-breathing diffusion-weighted imaging for the assessment of inflammatory activity in Crohn’s disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 2009;29:880–886.
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Vermoolen MA, Bierings MB, Mali WP, Nievelstein RA. Whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging for staging malignant lymphoma in children. Pediatr Radiol 2010;40:1592–1602.
MacKenzie JD, Gonzalez L, Hernandez A, Ruppert K, Jaramillo D. Diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging for pediatric musculoskeletal disorders. Pediatr Radiol 2007;37:781–788.
Oto A, Schmid-Tannwald C, Agrawal G, Kayhan A, Lakadamyali H, Orrin S, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of abdominopelvic abscesses. Emerg Radiol 2011;18:515–524.
Unal O, Koparan HI, Avcu S, Kalender AM, Kisli E. The diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in soft tissue abscesses. Eur J Radiol 2009;77:490–494.
Harish S, Chiavaras MM, Kotnis N, Rebello R. MR imaging of skeletal soft tissue infection: utility of diffusion-weighted imaging in detecting abscess formation. Skeletal Radiol 2011;40:285–294.
Sepahdari AR, Aakalu VK, Kapur R, Michals EA, Saran N, French A, et al. MRI of orbital cellulitis and orbital abscess: the role of diffusion-weighted imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;193:W244–250.
Singh P, Yadav MK, Singh SK, Lal A, Khandelwal N. Case series: diffusion weighted MRI appearance in prostatic abscess. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2011;21:46–48.
Mishra AM, Gupta RK, Saksena S, Prasad KN, Pandey CM, Rathore D, et al. Biological correlates of diffusivity in brain abscess. Magn Reson Med 2005;54:878–885.
Tomar V, Yadav A, Rathore RK, Verma S, Awasthi R, Bharadwaj V, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient with higher b-value correlates better with viable cell count quantified from the cavity of brain abscess. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:2120–2125.
Abdel Razek AA, Gaballa G, Elhawarey G, Megahed AS, Hafez M, Nada N. Characterization of pediatric head and neck masses with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 2009;19:201–208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neubauer, H., Platzer, I., Mueller, V.R. et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI of abscess formations in children and young adults. World J Pediatr 8, 229–234 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-012-0362-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-012-0362-4