Abstract
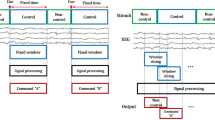
Asynchronous brain–computer interface (BCI) systems are more practicable than synchronous ones in real-world applications. A key challenge in asynchronous BCI design is to discriminate intentional control (IC) and non-intentional control (NC) states. In this paper, we present a two-stage asynchronous protocol for a steady-state visual-evoked potential-based BCI. First, we estimate a threshold using canonical correlation analysis coefficients in synchronous mode; then, we combine it with a sliding window strategy to continuously detect the mental state of the user. If the current state is judged as an IC state, then the system will output command. Our results show that the average positive predictive value of the system is 77.06 % and that its average false-positive rate in the NC state and IC state are 2.37 and 12.05 %, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolpaw JR, Birbaumer N, McFarland DJ, Pfurtscheller G, Vaughan TM. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002;113(6):767–91.
Pfurtscheller G, Neuper C, Muller GR, Obermaier B, Krausz G, Schlogl A, Scherer R, Graimann B, Keinrath C, Skliris D, et al. Graz-bci: state of the art and clinical applications. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2003;11(2):1–4.
Farwell LA, Donchin E. Talking off the top of your head: toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1988;70(6):510–23.
Birbaumer N. Breaking the silence: brain–computer interfaces (bci) for communication and motor control. Psychophysiology 2006;43(6):517–32.
Ortner R, Allison B, Korisek G, Gaggl H, Pfurtscheller G. An SSVEP BCI to control a hand orthosis for persons with tetraplegia. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2011;19(1):1–5.
Middendorf M, McMillan G, Calhoun G, Jones KS. Brain-computer interfaces based on the steady-state visual-evoked response. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng. 2000;8(2):211–4.
Lin Z, Zhang C, Wu W, Gao X. Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for ssvep-based bcis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2006;53(12):2610–4.
Muller-Putz GR, Pfurtscheller G. Control of an electrical prosthesis with an ssvep-based bci. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008;55(1):361–4.
Mason SG, Birch GE. A brain-controlled switch for asynchronous control applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2000;47.10: 1297–307.
Provost, F. Machine learning from imbalanced data sets 101. In: Proceedings of the AAAI’ 2000 workshop on imbalanced data sets, 2000.
He H, Garcia EA. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2009;21.9: 1263–84.
Ren R, Bin G, Gao X. Idle state detection in ssvep-based brain-computer interfaces. In: Bioinformatics and biomedical engineering, 2008. ICBBE 2008. The 2nd international conference on, p. 2012–5. IEEE, 2008.
Wang N, Qian T, Zhuo Q, Gao X. Discrimination between idle and work states in bci based on ssvep. In: Advanced computer control (ICACC), 2010 2nd international conference on, volume 4, p. 355–8. IEEE, 2010.
Zhang ZM, Deng ZD. A kernel canonical correlation analysis based idle-state detection method for SSVEP-based brain-computer interfaces. Adv Mater Res. 2012;341: 634–40.
Cecotti H. A self-paced and calibration-less ssvep-based brain–computer interface speller. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2010;18(2):127–33.
Horki P, Neuper C, Pfurtscheller G, Müller-Putz G. Asynchronous steady-state visual evoked potential based bci control of a 2-dof artificial upper limb. Biomedizinische Technik/Biomed Eng. 2010;55(6):367–74.
Faller J, Mller-Putz G, Schmalstieg D, Pfurtscheller G. An application framework for controlling an avatar in a desktop-based virtual environment via a software ssvep brain-computer interface. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2010;19(1): 25–34.
Hjorth B. An on-line transformation of eeg scalp potentials into orthogonal source derivations. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1975;39(5):526–30.
Friman O, Volosyak I, Graser A. Multiple channel detection of steady-state visual evoked potentials for brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2007;54(4):742–50.
Townsend G, Graimann B, Pfurtscheller G. Continuous eeg classification during motor imagery-simulation of an asynchronous bci. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 2004;12(2):258–65.
Parini S, Maggi L, Turconi AC, Andreoni G. A robust and self-paced BCI system based on a four class SSVEP paradigm: algorithms and protocols for a high-transfer-rate direct brain communication. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2009.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (Grand No. 11YZ141,12ZZ150) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60905065,61105122), the Ministry of Transport of the Peoples Republic of China (Grant No. 2012319810190),the Shanghai Phosphor Science Foundation ,china (Grand No.11QA1402900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, B., Li, X., Xie, H. et al. Asynchronous Brain–Computer Interface Based on Steady-State Visual-Evoked Potential. Cogn Comput 5, 243–251 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-013-9202-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-013-9202-7