Abstract
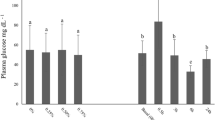
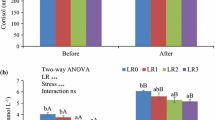
To test the effects of probiotic bacteria against crowding stress, juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus were fed commercial feed supplemented with 1 × 1010 cfu/g pellets of Lactobacillus rhamnosus for 3 weeks. The fish were confined and subjected to crowding for 7 and 14 days after which their physiological condition was investigated. The administration of probiotic prophylaxis improved growth performance even in the stressed fish. After 7 days of stress exposure, fish receiving probiotic-supplemented feed showed proactive behavior and coping responses to the stressor, as evidenced by elevated plasma glucose levels and osmolality, stabilized plasma electrolytes, and a higher RNA:DNA ratio. Fish stressed for 7 days and fed normal commercial diet showed impairment of plasma electrolytes; after 14 days, the plasma osmolality, electrolytes, glucose, and RNA:DNA ratio decreased, indicating physiological maladaptation to the stressor. The growth rate was also found to be reduced, suggesting that energy demand exceeded the energy available from metabolism and dietary uptake. This latter effect was not observed in fish fed the probiotic-supplemented diet. The results suggest that probiotic bacteria prophylaxis may increase energy availability for metabolic support of the crowding stress response and improve the stress coping capacity of fish.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwama GK, Afonso LOB, Vijayan MM (2006) Stress in fish. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB (eds) The physiology of fishes. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 319–342
Bonga SEW (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Barton BA (2000) Stress. In: Stickney RR (ed) Encyclopedia of aquaculture. Wiley, New York, pp 892–898
Bondad-Reantaso MG, Subasinghe RP, Arthur JR, Ogawa K, Chinabut S, Adlard R, Tan Z, Shariff M (2005) Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Vet Parasitol 132:249–272
Balcázar JL, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Cunningham D, Vendrell D, Múzquiz JL (2006) The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet Microbiol 114:173–186
Wang Y, Li J, Lin J (2008) Probiotics in aquaculture: challenges and outlook. Aquaculture 281:1–4
Suchanit N, Futami K, Endo M, Maita M, Katagiri T (2010) Immunological effects of glucan and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, a probiotic bacterium, on Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus intestine with oral Aeromonas challenges. Fish Sci 76:833–840
Pirarat N, Kobayashi T, Katagiri T, Maita M, Endo M (2006) Protective effects and mechanisms of a probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus rhamnosus against experimental Edwardsiella tarda infection in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Vet Immunol Immunop 113:339–347
Rollo A, Sulpizio R, Nardi M, Silvi S, Orpianesi C, Caggiano M, Cresci A, Carnevali O (2006) Live microbial feed supplement in aquaculture for improvement of stress tolerance. Fish Physiol Biochem 32:167–177
Taoka Y, Maeda H, Jo J, Jeon M, Bai SC, Lee W, Yuge K, Koshio S (2006) Growth, stress tolerance and non-specific immune response of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus to probiotics in a closed recirculating system. Fish Sci 72:310–321
Hernandez LHH, Barrera TC, Mejia JC, Mejia GC, Del Carmen M, Dosta M, De Lara Andrade R, Sotres JAM (2010) Effects of the commercial probiotic Lactobacillus casei on the growth, protein content of skin mucus and stress resistance of juveniles of the Porthole livebearer Poecilopsis gracilis (Poecilidae). Aquacult Nutr 16:407–411
Auperin B, Baroiller JF, Ricordel MJ, Fostier A, Prunet P (1997) Effect of confinement stress on circulating levels of growth hormone and two prolactins in freshwater-adapted tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gen Comp Endocr 4:35–44
Caldarone EM, Wagner M, St. Onge-Burns J, Buckley LJ (2001) Protocol and guide for estimating nucleic acids in larval fish using a fluorescence microplate reader. Northeast Fisheries Science Center Reference Document 01-11. National Marine Fisheries Service, Woods Hole
Fonseca VF, Vinagre C, Cabral HN (2006) Growth variability of juvenile soles Solea solea and Solea senegalensis, and comparison with RNA:DNA ratios in the Tagus estuary, Portugal. J Fish Biol 68:1551–1562
Davis KB (2006) Management of physiological stress in finfish aquaculture. N Am J Aquacult 68:116–121
Hrubec TC, Cardinale JL, Smith SA (2000) Hematology and plasma chemistry reference intervals for cultured tilapia (Oreochromis Hybrid). Vet Clin Pat 29:7–12
Chen C, Wooster GA, Getchell RG, Bowser PR, Timmons MB (2003) Blood chemistry of healthy, nephrocalcinosis-affected and ozone-treated tilapia in a recirculation system, with application of discriminant analysis. Aquaculture 218:89–102
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Van Weerd JH, Komen J (1998) The effects of chronic stress on growth in fish: a critical appraisal. Comp Biochem Phys A 120:107–112
Cech JJ Jr (2000) Osmoregulation in bony fishes. In: Stickney RR (ed) Encyclopedia of aquaculture. Wiley, New York, pp 614–622
Manzon LA (2002) The role of prolactin in fish osmoregulation: a review. Gen Comp Endocr 125:291–310
Lall SP (2002) The minerals. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish nutrition. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 260–309
Cataldi E, Mandich A, Ozzimo A, Cataudella S (2005) The interrelations between stress and osmoregulation in a euryhaline fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. J Appl Ichthyol 21:229–231
Tseng Y, Hwang P (2008) Some insights into energy metabolism for osmoregulation in fish. Comp Biochem Phys C 148:419–429
Ellis T, North B, Scott AP, Bromage NR, Porter M, Gadd D (2002) The relationship between density and welfare in farmed rainbow trout. J Fish Biol 61:493–531
Boujard T, Labbe L, Auperin B (2002) Feeding behaviour, energy expenditure and growth of rainbow trout in relation to stocking density and food accessibility. Aquac Res 33:1233–1242
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Bradley G, Baker RTM, Davies SJ (2010) Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) I. Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria. Aquacult Nutr 16:504–510
El-Haroun ER, Goda AMA-S, Kabir Chowdhury MA (2006) Effect of dietary probiotic Biogen® supplementation as a growth promoter on growth performance and feed utilization of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquac Res 37:1473–1480
Portz DE, Woodley CM, Cech JJ Jr (2006) Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 16:125–170
Scholz-Ahrens KE, Ade P, Marten B, Weber P, Timm W, Asil Y, Glüer C, Schrezenmeir J (2007) Prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics affect mineral absorption, bone mineral content, and bone structure. J Nutr 137:838S–846S
Sigiura SH, Hardy RW (2000) Environmentally friendly feeds. In: Stickney RR (ed) Encyclopedia of aquaculture. Wiley, New York, pp 299–310
Vijayan MM, Pereira C, Grau EG, Iwama GK (1997) Metabolic responses associated with confinement stress in tilapia: the role of cortisol. Comp Biochem Physiol C 116:89–95
Weber LP, Higgins PS, Carlson RI, Janz DM (2003) Development and validation of methods for measuring multiple biochemical indices of condition in juvenile fishes. J Fish Biol 63:637–658
Buckley LJ, Caldarone E, Ong TL (1999) RNA–DNA ratio and other nucleic acid-based indicators for growth and condition of marine fishes. Hydrobiologia 401:265–277
Chícharo MA, Chícharo L (2008) RNA:DNA ratio and other nucleic acid derived indices in marine ecology. Int J Mol Sci 9:1453–1471
Gwak W, Tsusaki T, Tanaka M (2003) Nutritional condition, as evaluated by RNA/DNA ratios, of hatchery-reared Japanese flounder from hatch to release. Aquaculture 219:503–514
Davis MW (2010) Fish stress and mortality can be predicted using reflex impairment. Fish Fish 11:1–11
Dawkins MS (2004) Using behaviour to assess animal welfare. Anim Welfare 13:S3–S7
Koolhaas JM, Korte SM, De Boer SF, Van der Vegt BJ, Van Reenen CG, Hopster H, De Jong IC, Ruis MAW, Blokhuis HJ (1999) Coping styles in animals: current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neurosci Biobehav R 23:925–935
Øverli Ø, Winberg S, Pottinger TG (2005) Behavioral and neuroendocrine correlates of selection for stress responsiveness in rainbow trout—a review. Integr Comp Biol 45:463–474
Chandroo KP, Duncan IJH, Moccia D (2004) Can fish suffer? Perspectives on sentience, pain, fear and stress. Appl Anim Behav Sci 86:225–250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, A.T., Maita, M., Futami, K. et al. Effects of a probiotic bacterial Lactobacillus rhamnosus dietary supplement on the crowding stress response of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus . Fish Sci 77, 633–642 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-011-0367-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-011-0367-2