Abstract
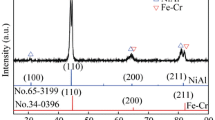
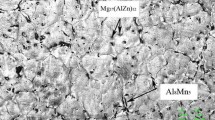
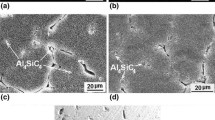
Dry sliding wear tests were performed for 7075 Al alloy under a load of 25–250 N at 25–200 °C. The wear behaviors and mechanisms under various testing conditions were explored. A mild-to-severe wear transition is noticed to occur with an increase in the load at 25–200 °C. With the temperature increasing, the wear loss decreases constantly under the low load of less than 50 N. It can be suggested that the 7075 Al alloy presents a high wear resistance under a high ambient temperature and low load. Its high wear resistance is found to be attributed to the existence of mechanically mixing layer (MML). The predominant wear mechanism is adhesive and abrasive wear at room temperature. With the ambient temperature and load increasing, oxidative wear and plastic extrusive wear successively prevail due to thermal oxidation and softening of matrix.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Millier WS, Zhuang L, Bottema J, Wittebrood AJ, Smet PD, Haszler A, Vieregge A. Recent development in aluminium alloys for the automotive industry. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct. 2000;280(1):37.
Zhang ZH, Xiong BQ, Liu SF, Zhu BH, Zuo YT. Changes of microstructure of different quench sensitivity 7000 aluminum alloy after end quenching. Rare Met. 2014;33(3):270.
Yang WW, Guo ZM, Cao HQ, Luo J, Ye AP. Fabrication and mechanical properties of high-performance aluminum alloy. Rare Met. 2014;33(4):400.
Li XM, Stranik MJ. Effect of compositional variations on characteristics of coarse intermetallic particles in overaged 7000 aluminum alloys. Mater Sci Tech-Lond. 2001;17(11):1324.
Yan LM, Shen J, Li JP, Mao BP. Static softening behavior of 7055 alloy during the interval time of multi-pass hot compression. Rare Met. 2013;32(3):241.
Singh J, Alpas AT. Elevated temperature wear of Al 6061 and Al 6061-20% Al203. Scr Mater. 1995;32(7):1099.
Wilson S, Alpas AT. Effect of temperature on the sliding wear performance of Al alloys and Al matrix composites. Wear. 1996;196(1):270.
Zhang J, Alpas AT. Transition between mild and severe wear in aluminum alloys. Acta Mater. 1997;45(2):513.
Venkataramana B, Sundararajan G. Correlation between the characteristics of the mechanically mixed layer and wear behavior of aluminum, Al-7075 alloy and Al-MMCs. Wear. 2000;245(1–2):22.
Elmadagli M, Alpas AT. Sliding wear of an Al-18.5 wt% Si alloy tested in an argon atmosphere and against DLC coated counterfaces. Wear. 2006;261(7–8):823.
Elleuch R, Elleuch K, Mnif R, Fridrici V, Kapasa P, Khelifati G. Comparative study on wear behavior of magnesium and aluminum alloys. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol. 2006;220(6):479.
Straffelini G, Molinari A. Mild sliding wear of Fe–0.2% C, Ti–6% Al–4% V and Al-7072 a comparative study. Tribol Lett. 2011;41(1):237.
Pauschitz A, Roy M, Franek F. Mechanisms of sliding wear of metals and alloys at elevated temperatures. Tribol Int. 2008;41(7):584.
Wang SQ, Wei MX, Wang F, Cui XH, Dong C. Transition of mild wear to severe wear in oxidative wear of H21 steel. Tribol Lett. 2008;32(2):67.
Wei MX, Chen KM, Wang SQ, Cui XH. Analysis for wear behaviors of oxidative wear. Tribol Lett. 2011;42(1):1.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51071078), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK2012250), the Research Fund Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of High-End Structural Materials (No. hsm1303) and the Opening Foundation of Jiangsu Province Material Tribology Key Laboratory (No. Kjsmcx201302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, ZR., Sun, Y., Li, XX. et al. Dry sliding wear performance of 7075 Al alloy under different temperatures and load conditions. Rare Met. 41, 1057–1062 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0504-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0504-7