Abstract
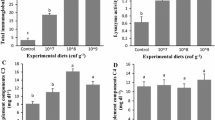
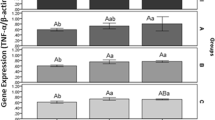
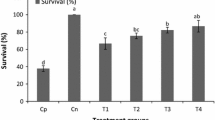
A feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effects of different levels of dietary Lactobacillus plantarum on hemato-immunological parameters and resistance against Streptococcus iniae infection in juvenile Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baerii. Fish (14.6 ± 2.3 g) were fed three experimental diets prepared by supplementing a basal diet with L. plantarum at different concentrations [1 × 107, 1 × 108 and 1 × 109 colony-forming units (cfu) g−1] and a control (non-supplemented basal) diet for 8 weeks. Innate immune responses (immunoglobulin (Ig), alternative complement activity (ACH50) and lysozyme activity) were significantly higher in fish fed the 1 × 108 and 1 × 109 cfu g−1 L. plantarum diet compared to the other groups (P < 0.05). Furthermore, fish fed on various levels of L. plantarum significantly showed higher red blood cell (RBC), hemoglobin (Hb), white blood cell (WBC) and monocyte compared to those of the control group (P < 0.05). At the end of the feeding experiment, some fish were challenged with S. iniae to quantify the level of disease resistance. The mortality after S. iniae challenge was decreased in fish fed a probiotic. These results indicated that dietary supplementation of L. plantarum improved immune response and disease resistance of Siberian sturgeon juvenile.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nomoto K (2005) Prevention of infections by probiotics. J Biosci Bioeng 100:583–592
Geraylou Z, Souffreau C, Rurangwa E, De Meester L, Courtin CM, Delcour JA et al (2013) Effects of dietary arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides (AXOS) and endogenous probiotics on the growth performance, non-specific immunity and gut microbiota of juvenile Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:766–775
Verschuere L, Rombaut G, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W (2000) Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:655–671
Gatesoupe FJ (1999) The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 180:147–165
Irianto A, Austin B (2002) Probiotics in aquaculture. J Fish Dis 25:633–642
Talpur AD, Ikhwanuddin M, Abdullah MDD, Bolong AA (2013) Indigenous Lactobacillus plantarum as probiotic for larviculture of blue swimming crab, Portunus pelagicus (Linnaeus, 1758): effects on survival, digestive enzyme activities and water quality. Aquaculture 416–417:173–178
Kongnum K, Hongpattarakere T (2012) Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from digestive tract of wild shrimp on growth and survival of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:170–177
Giri SS, Sukumaran V, Oviya M (2013) Potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum VSG3 improves the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34(2):660–666
Vieira FN, Buglione CC, Mourino JPL, Jatoba A, Martins ML, Schleder DD et al (2010) Effect of probiotic supplemented diet on marine shrimp survival after challenge with Vibrio harveyi. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 62(3):631–638
Carnevali O, Zamponi MC, Sulpizio R, Rollo A, Nardi M, Orpianesi C et al (2004) Administration of probiotic strain to improve sea bream wellness during development. Aquac Int 12(4–5):377–386
Chiu CH, Guu YK, Liu CH, Pan TM, Cheng W (2007) Immune responses and gene expression in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, induced by Lactobacillus plantarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23:364–377
Iman MKA, Wafaa TA, Elham SA, Mohammad MNA, Kawther E, Osama MS et al (2013) Evaluation of Lactobacillus plantarum as a probiotic in aquaculture: emphasis on growth performance and innate immunity. J Appl Sci Res 9(1):572–582
Son VM, Chang CC, Wu MC, Guu YK, Chiu CH, Cheng W (2009) Dietary administration of the probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum, enhanced the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:691–698
Iwashita MKP, Nakandakare IB, Terhune JS, Wood T, Ranzani-Paiva MJT (2015) Dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus oryzae enhance immunity and disease resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus iniae infection in juvenile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 43:60–66
Kim D, Beck BR, Saet Byeol Heo, Kim J, Kim HD, Lee SM et al (2013) Lactococcus lactis BFE920 activates the innate immune system of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), resulting in protection against Streptococcus iniae infection and enhancing feed efficiency and weight gain in large-scale field studies. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1585–1590
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015) Interaction effects of dietary supplementation of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and β-glucan on growth performance, digestibility and immune response of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(1):33–42
Geraylou Z, Vanhove MPM, Souffreau C, Rurangwa E, Buyse J, Ollevier F (2014) In vitro selection and characterization of putative probiotics isolated from the gut of Acipenser baerii (Brandt, 1869). Aquac Res 45:341–352
Pourghanbar Moghadam N, Issazadeh K, Mirpour M (2014) In vitro antagonistic effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus PTCC 1643 (DSM 20079) and Lactobacillus plantarum PTCC, 1058 (ATCC 8014) against isolated bacteria from urinary tract infections. Int J Mol Clin Microbiol 1:377–382
Martins ML, Tavares-Dias M, Fujimoto RY, Onaka EM (2004) Nomura DT Haematological alterations of Leporinus macrocephalus (Osteichtyes: Anostomidae) naturally infected by Goezia leporini (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in fishponds. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 56:640–646
Collier HB (1994) The standardization of blood hemoglobin determinations. Can Med Assoc J 50:550–552
Ghiasi F, Mirzargar SS, Badakhshan H, Shamsi S (2010) Effects of low concentration of cadmium on the level of lysozyme in serum, leukocyte count and phagocytic index in Cyprinus carpio under the wintering conditions. J Fish Aquat Sci 5:113–119
Seiverd CE (1964) Hematology for medical technologists. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, p 946
Siwicki AK, Anderson DP (1993) Nonspecific defense mechanisms assay in fish: II. Potential killing activity of neutrophils and macrophages, lysozyme activity in serum and organs and total immunoglobulin level in serum. Fish Dis Diagn Prev Methods 105–112. Olsztyn, Poland
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ellis TA (1990) Lysozyme assays. In: Stolen JS, Fletcher TC, Anderson DP, Roberson BS, Van Muiswinkel WB (eds) Techniques in fish immunology. SOS Publications, Fair Haven, pp 101–103
Sunyer J, Tort L (1995) Natural hemolytic and bactericidal activities of sea bream Sparus aurata serum are affected by the alternative complement pathway. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 45(3):333–345
Brunt J, Newaj-Fyzul A, Austin B (2007) The development of probiotics for the control of multiple bacterial diseases of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 30:573–579
Tewary A (2011) Patra B Oral administration of baker’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) acts as a growth promoter and immunomodulator in Labeo rohita (Ham.). J Aquac Res Dev 2:1–7
Faramazi M, Kiaalvandi S, Lashkarbolooki M, Iranshahi F (2011) The investigations of Lactobacillus acidophilis as probiotics on grown performance and disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Am Eurasian J Sci Res 6(1):32–38
Dias DC, Leonardo AFG, Tachibana L, Correa CF, Bordon CAC, Romagosa E, Ranzani-Paiva MJT (2012) Effect of incorporating probiotics into the diet of matrinxa (Brycon amazonicus) breeders. J Appl Ichthyol 28:40–45
Dahiya T, Sihag RC, Gahlawat SK (2012) Effect of probiotics on the haematological parameters of Indian Magur (Clarius batrachus L.). J Fish Aqua Sci 7:279–290
Ayoola SO, Ajani EK, Fashae OF (2013) Effect of probiotics (Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) on growth performance and hematological profile of Clarias gariepinus juveniles. World J Fish Mar Sci 5:01–08
Naseri S, Khara H, Shakoori M (2015) Evaluation of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis as probiotic and Fe ion effects on haematological parameters of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss frys. Comp Clin Pathol 24(6):1521–1526
Azarin H, Aramli MS, Imanpour MR, Rajabpour M (2015) Effect of a probiotic containing Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis and ferroin solution on growth performance, body composition and haematological parameters in Kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum) Fry. Probiots Antimicro. Prot 7:31–37
Staykov Y, Spring P, Denev S, Sweetman J (2007) Effect of a mannan oligosaccharide on the growth performance and immune status of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac Int 15:153–161
Kim DH, Austin B (2006) Innate immune responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) induced by probiotics. Fish Shellfish Immunol 21:513–524
Panigrahi A, Kiron V, Kobayashi T, Puangkaew J, Satoh S, Sugita H (2004) Immune responses in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss induced by a potential probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus JCM 1136. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 102:379–388
Balcazar JL, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Vendrell D, Calvo AC, Marquez I et al (2007) Changes in intestinal microbiota and humoral immune response following probiotic administration in brown trout (Salmo trutta). Br J Nutr 97:522–527
Nayak SK (2010) Probiotics and immunity: a fish perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:2–14
Akrami R, Iri Y, Rostami HK, Mansour MR (2013) Effect of dietary supplementation of fructooligosacharide (FOS) on growth performance, survival, Lactobacillus bacterial population and hemato-immunological parameters of stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus) juvenile. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1235–1239
Sakai M (1999) Current research status of fish immostimulants. Aquaculture 172:63–92
Aly SM, Ahmed YA, Aziz AAG, Mohamed MF (2008) Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:128–136
Perez-Sanchez T, Balcázar JL, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Gioacchini G, Blas I et al (2011) Expression of immune-related genes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) induced by probiotic bacteria during Lactococcus garvieae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:196–211
Ellis AE (1999) Immunity to bacteria in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:291–308
Cerezuela R, Guardiola FA, González P, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2012) Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis, Tetraselmis chuii, and Phaeodactylum tricornutum, singularly or in combination, on the immune response and disease resistance of sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:342–349
Salton MRJ, Ghuysen JM (1959) The structure of di- and tetra-saccharides released from cell walls by lysozyme and Streptomyces F1 enzyme and the β(1-4) Nacetylhexosaminidase activity of these enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 36:552–554
Glynn AA (1969) The complement lysozyme sequence in immune bacteriolysis. Immunology 16:463–471
Hjelmeland K, Christie M, Raa J (1983) Skin mucus protease from rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, and its biological significance. J Fish Biol 23:13–22
Klockar M, Roberts P (1976) Stimulation of phagocytosis by human lysozyme. Acta Haematol 55:289–295
Jolle SP, Jolle SJ (1984) What’s new in lysozyme research? always a model system, today as yesterday. Mol Cell Biochem 63:165–189
Liu CH, Chiu CH, Wang SW, Cheng W (2012) Dietary administration of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20, enhaces the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:699–706
Aly SM, Mohamed MF, John G (2008) Effect of probiotics on the survival, growth and challenge infection in Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac Res 39:647–656
Chiu CH, Cheng CH, Gua WR, Guu YK, Cheng W (2010) Dietary administration of the probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae P13 enhanced the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:1053–1059
Merrifield D, Balcázar J, Daniels C, Zhou Z, Carnevali O, Sun Y et al (2014) In: Ringø E, Merrifield DL (eds) Aquaculture nutrition: gut health, probiotics and prebiotics. Wiley-Blackwell Scientific Publication, London
Sharifuzzaman SM, Austin B (2009) Influence of probiotic feeding duration on disease resistance and immune parameters in rainbow trout. Fish Shellfish Immunol 27:440–445
Hoa NT, Baccigalupi L, Huxham A (2000) Characterization of Bacillus species used for oral bacteriotherapy and bacterioprophylaxis of gastrointestinal disorders. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5241–5247
Dash G, Prakash Raman R, Pani Prasad K, Makesh M, Pradeep MA, Sen S (2015) Evaluation of paraprobiotic applicability of Lactobacillus plantarumin improving the immune response and disease protection in giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man, 1879). Fish Shellfish Immunol 43:167–174
Pandiyan P, Balaraman D, Thirunavukkarasu R, George EGJ, Subaramaniyan K, Manikkam S et al (2013) Probiotics in aquaculture. Drug Invention Today 5(1):55–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Moheb Ali Pourgholam, Hossein Khara, Reza Safari, Mohammad Ali Yazdani Sadati and Mohammad Sadegh Aramli declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All fish manipulations were conducted in accordance with the guidelines on the care and use of animals for scientific purposes (National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourgholam, M.A., Khara, H., Safari, R. et al. Hemato-Immunological Responses and Disease Resistance in Siberian Sturgeon Acipenser baerii Fed on a Supplemented Diet of Lactobacillus plantarum . Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 9, 32–40 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-016-9229-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-016-9229-7