Abstract
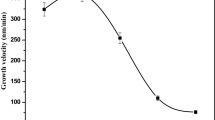
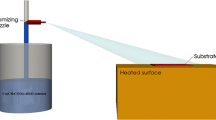
Cobalt oxide thin films are prepared by the nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique using cobalt chloride as the precursor material. The structural, optical, morphological and electrical properties are investigated as a function of substrate temperature (300–450 °C). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis reveals that all the films are polycrystalline in nature, having cubic structure with preferential orientation along the (111) plane. The optical spectra show that the films are transparent (68 %) in the IR region. The optical band gap values are calculated for different substrate temperature. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra of the films indicate the presence of indigo, blue and green emission peaks with an ultraviolet emission peak centered around 368nm. SEM images reveals small sphere-like structures for the prepared Co3O4 films. The maximum conductivity obtained is 1.48 x 10−3 S/cm at 350 °C. The activation energy varies between 0.039 and 0.138 eV for the substrate temperature variation from 300-450 Q°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kandalkar SG, Dhawale DS, Kim C-K, Lokhande CD (2010) Synth Met 160:1299–1302
YalanWanga H, Wang X (2013) Electrochimic Acta 92:298–303
Kandalkar SG, Gunjakar JL, Lokhande CD (2008) Appl Surf Sci 254:5540–5544
Shinde VR, Mahadik SB, Gujar TP, Lokhande CD (2006) Appl Surf Sci 252:7487–7492
Wollenstein J, Burgmair M, Plescher G, Sulima T, Hildenbrand J, Böttner H, Eisele I (2003) Sensors Actuators B 93:442–448
Avila GA, Barrera CE, Huerta AL, Muhl S (2004) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 82:269–278
Guyon C, Barkallah A, Rousseau F, Giffard K, Morvan D, Tatoulian M (2011) Surf Coat Technol 206:1673–1679
Do J-S, Weng C-H (2005) J Power Sources 146:482–486
Louardi A, Rmili A, Ouachtari F, Bouaoud A, Elidrissi B, Erguig H (2011) J Alloys Compd 509:9183–9189
Klepper KB, Nilsen O, Fjellvag H (2007) Thin Solid Films 515:7772–7781
Tototzintle-Huitle H, Prokhorov E, Mendoza-Galvan A, Urbina JE, GonzalezHernandez J (2003) J PhysChem Solids 64:975–980
Cheng C-S, Serizawa M, Sakata H, Hirayama T (1998) Mater Chem Phys 53:225–230
Dupin JC, Gonbeau D, Benqlilou-Moudden H, Vinatier Ph, Levasseur A (2001) Thin Solid Films 384:23–32
Kung C-W, Lin C-Y, Li T-J, Vittal R, Ho K-C (2011) Procedia Engineering 25:847–850
Shelke PN, Khollam YB, Hawaldar RR, Gunjal SD, Udawant RR, Sarode MT, Takwaleb MG, Mohite KC (2013) Fuel 112:542–549
Mariappan R, Ponnuswamy V, Suresh P, Suresh R, Ragavendar M, Sankar C (2013) Mater Sci Semicond Process 16:825–832
Suresh R, Ponnuswamy V, Mariappan R, Senthil Kumar N (2014) Ceram Int 40:437–445
Mariappan R, Ponnuswamy V, Ragavendar M (2013) Met Mater Int 19:1–8
Sethupathi N, Thirunavukkarasu P, Vidhya VS, Thangamuthu R, Kiruthika GVM, Perumal K, Bajaj Hari C, Jayachandran M (2012) J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23:1087–1093
Scherrer P (1918) Göttinger Nachrichten Gesell 2:98
Mariappan R, Ponnuswamy V, Chandra Bose A, Chithambararaj A, Suresh R, Ragavendar M (2014) Superlattice Microst 65:184–194
Kadam LD, Patil PS (2001) Mater Chem Phys 68:225–232
Pal J, Chauhan P (2010) Mater Charact 61:575–579
Cao B, Sunand F, Cai W, Electrochem S (2005) Solid-State Lett 8:G237–G240
Li Y, Meng GW, Zhang LD (2000) Appl Phys Lett 76:15–20 doi:10.1063/1.126238
Patil PS, Kadam LD, Lokhande CD (1996) Thin Solid Films 272:29–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manickam, M., Ponnuswamy, V., Sankar, C. et al. Influence of Substrate Temperature on the Properties of Cobalt Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Nebulizer Spray Pyrolysis (NSP) Technique. Silicon 8, 351–360 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-015-9316-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-015-9316-5